
An election is a formal group decision-making process whereby a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.

Referendums in the United Kingdom are occasionally held at a national, regional or local level. Historically, national referendums are rare due to the long-standing principle of parliamentary sovereignty. Legally there is no constitutional requirement to hold a national referendum for any purpose or on any issue. However, the UK Parliament is free to legislate through an Act of Parliament for a referendum to be held on any question at any time.

Proposition 60 was an amendment of the Constitution of California, enacted in 2004, guaranteeing the right of a party participating in a primary election to also participate in the general election that follows. It was proposed by the California Legislature and approved by the voters in referendum held as part of the November 2004 election, by a majority of 67%.

Proposition 62 was a California ballot proposition on the November 2, 2004 ballot. It failed to pass with 5,119,155 (46.1%) votes in favor and 5,968,770 (53.9%) against.
Romania elects on a national level a head of state – the president – and a legislature. The president is elected for a five-year term by the people. The Romanian Parliament has two chambers. The Chamber of Deputies has currently 330 members, elected for a four-year term by party-list proportional representation on closed lists. The Senate has currently 136 members, elected for a four-year term by party-list proportional representation on closed lists.

A consultative referendum on the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe was held in the Netherlands on 1 June 2005 to decide whether the government should ratify the proposed Constitution of the European Union. The result was a "No" vote.
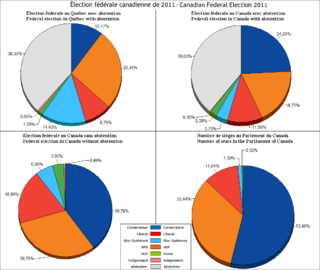
Abstention is a term in election procedure for when a participant in a vote either does not go to vote or, in parliamentary procedure, is present during the vote but does not cast a ballot. Abstention must be contrasted with "blank vote", in which a voter casts a ballot willfully made invalid by marking it wrongly or by not marking anything at all. A "blank voter" has voted, although their vote may be considered a spoilt vote, depending on each legislation, while an abstaining voter has not voted. Both forms may or may not, depending on the circumstances, be considered to be a protest vote. Abstention is related to political apathy and low voter turnout.
A three-question referendum was held in Poland on 30 June 1946. Known as the people's referendum or three times yes referendum it was held as a result of a State National Council order of 27 April 1946. The referendum presented an opportunity for the forces vying for political control of Poland following World War II to test their popularity among the general population. However, the results were forged and the referendum failed to meet democratic standards.
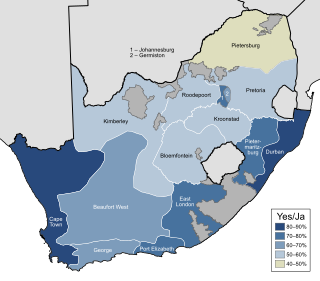
A referendum on ending apartheid was held in South Africa on 17 March 1992. The referendum was limited to white South African voters, who were asked whether or not they supported the negotiated reforms begun by State President F. W. de Klerk two years earlier, in which he proposed to end the apartheid system that had been implemented since 1948. The result of the election was a large victory for the "yes" side, which ultimately resulted in apartheid being lifted. Universal suffrage was introduced two years later for the country's first non-racial elections.
General elections were held in Italy on 26 March 1934. At the time, the country was a single-party state with the National Fascist Party (PNF) as the only legally permitted party.
General elections were held in Italy on 24 March 1929 to elect the members of the Chamber of Deputies. By this time, the country was a single-party state with the National Fascist Party (PNF) as the only legally permitted party.

The United Kingdom Alternative Vote referendum, also known as the UK-wide referendum on the Parliamentary voting system was held on Thursday 5 May 2011 in the United Kingdom to choose the method of electing MPs at subsequent general elections. It occurred as a provision of the Conservative–Liberal Democrat coalition agreement drawn up in 2010 and also indirectly in the aftermath of the 2009 expenses scandal. It operated under the provisions of the Parliamentary Voting System and Constituencies Act 2011 and was the first national referendum to be held under provisions laid out in the Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000. Many local elections were also held on this day.

General elections were held in Zambia on 5 December 1973. They were the first elections held since the country was formally declared a one-party state in August, with the United National Independence Party (UNIP) as the only legally permitted party. UNIP leader Kenneth Kaunda was automatically elected to a third five-year term as President, and was confirmed in office via a referendum in which 88.8% of voters approved his candidacy. UNIP also won all 125 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was 39% of the 1,746,107 registered voters for the presidential election, and 33% for the National Assembly election.

General elections were held in Zambia on 12 December 1978. At the time, the country was a one-party state with the United National Independence Party (UNIP) as the sole legal party. UNIP leader Kenneth Kaunda was automatically elected to a fourth five-year term as President, with 80.7% of voters voting to confirm him in office. UNIP also won all 125 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was around 65% in the parliamentary election, but 66.7% in the presidential election.

General elections were held in Zambia on 27 October 1983. At the time, the country was a one-party state, with the United National Independence Party (UNIP) as the only legally permitted party. Its leader, Kenneth Kaunda was automatically re-elected for a fifth term as President, and was confirmed in office with over 95% of the vote. UNIP also won all 125 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was around 63% in the parliamentary election, but 65.5% in the presidential election.

General elections were held in Zambia on 26 October 1988. At the time, the country was a one-party state with the United National Independence Party (UNIP) as the sole legal party. UNIP leader Kenneth Kaunda was automatically re-elected for a sixth five-year term as President with 95.5% of the vote, whilst UNIP also won all 125 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was around 60% in the parliamentary elections, but 58.8% in the presidential elections.

Presidential elections were held in the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 1 November 1970. The only candidate was Joseph Mobutu, who had taken power in a military coup five years earlier. The elections took the format of a "yes" or "no" vote for Mobutu's candidacy. According to official figures, Mobutu was confirmed in office with near-unanimous support, with only 157 "no" votes out of over 10.1 million total votes cast. Mobutu also received around 30,000 more "yes" votes than the number of registered voters, even though voting was not compulsory.

Presidential elections were held in Zaire on 3 December 1977. They were the first held after a new constitution was promulgated in 1974.
A referendum on creating administrative regions was held in Portugal on 8 November 1998. Two proposals were put to voters, the first on implementing the regions, and the second specifically asking whether voters approved of the new region for their area. The proposals were rejected by wide margins by voters.

The 2020 California Proposition 18 would allow 17-year-olds to vote in primary and special elections if they will turn 18 by the subsequent general election.














