| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1992 List of years in Georgia (country) | ||||
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1992 List of years in Georgia (country) | ||||

Zviad Konstantines dze Gamsakhurdia was a Georgian politician, human rights activist, dissident, professor of English language studies and American literature at Tbilisi State University, and writer who became the first democratically elected President of Georgia in May 1991.

Mingrelia is a historic province in the western part of Georgia, formerly known as Odishi. It is primarily inhabited by the Mingrelians, a subgroup of Georgians.
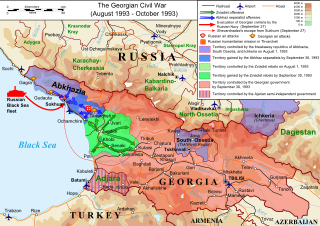
The Georgian Civil War lasted from 1991 to 1993 in the South Caucasian country of Georgia. It consisted of inter-ethnic and international conflicts in the regions of South Ossetia and Abkhazia, as well as the violent military coup d'état against the first democratically-elected President of Georgia, Zviad Gamsakhurdia, and his subsequent uprising in an attempt to regain power.

The Abkhazia conflict is a territorial dispute over Abkhazia, a region on the eastern coast of the Black Sea in the South Caucasus, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. The conflict involves Georgia, Russian Federation and Russian-backed self-proclaimed Republic of Abkhazia, internationally recognised only by Russia, Venezuela, Nicaragua, Nauru, and Syria; Georgia and all other United Nations members consider Abkhazia a sovereign territory of Georgia. However, as of 2023, Georgia lacks de facto control over the territory.

Tengiz Kitovani was a Georgian politician and military commander with high-profile involvement in the Georgian Civil War early in the 1990s when he commanded the National Guard of Georgia.

The ethnic cleansing of Georgians in Abkhazia, also known in Georgia as the genocide of Georgians in Abkhazia, refers to the ethnic cleansing, massacres, and forced mass expulsion of thousands of ethnic Georgians living in Abkhazia during the Georgian-Abkhaz conflict of 1992–1993 and 1998 at the hands of Abkhaz separatists and their allies. Armenians, Greeks, Russians, and opposing Abkhazians were also killed.
Russia and Georgia have had relations for centuries. The contacts between the two date back to the 15th and 16th centuries, and the most important stage started in the 1580s, when the Georgian kingdom of Kakheti and the Russian Empire signed a treaty of alliance in 1587. Since then, Georgia–Russia relations have been developing vibrantly and culminated in the Treaty of Georgievsk, which established eastern Georgia as a protectorate of Russia. At that time, Georgia saw Russia as a powerful Christian and modernizing neighbor, capable of protecting Georgia from invading Muslim empires and North Caucasian raiders.

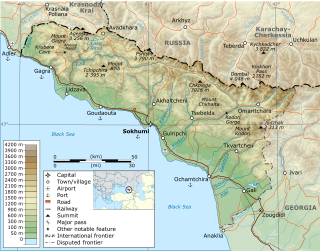
The history of Abkhazia, a region in the South Caucasus, spans more than 5,000 years from its settlement by the lower-paleolithic hunter-gatherers to its present status as a partially recognized state.
The War in Abkhazia was fought between Georgian government forces for the most part and Abkhaz separatist forces, Russian government armed forces and North Caucasian militants between 1992 and 1993. Ethnic Georgians who lived in Abkhazia fought largely on the side of Georgian government forces. Ethnic Armenians and Russians within Abkhazia's population largely supported the Abkhazians and many fought on their side. The separatists received support from thousands of North Caucasus and Cossack militants and from the Russian Federation forces stationed in and near Abkhazia.
The Sukhumi riot was a riot in Sukhumi, Abkhaz Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Union, in July 1989, triggered by an increasing inter-ethnic tensions between the Abkhaz and Georgian communities and followed by several days of street fighting and civil unrest in Sukhumi and throughout Abkhazia.
In June and July 2008 a series of bombings took place in Georgia's breakaway republic of Abkhazia, killing 4 and injuring 18 people.

Abkhazia, officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It covers 8,665 square kilometres (3,346 sq mi) and has a population of around 245,000. Its capital and largest city is Sukhumi.
Giorgi (Gia) Karkarashvili is a Georgian politician and retired major general who served as Georgia's Minister of Defense from May 1993 to March 1994. A former Soviet army captain, he was a high-profile military commander during the civil war and wars against the secessionists in Abkhazia and South Ossetia in the 1990s. A gunshot wound received in the 1995 attack in Moscow left him severely disabled. He was a member of the Parliament of Georgia from 1999 to 2004. He is currently a member of the Our Georgia – Free Democrats party led by Irakli Alasania.
Vakhtang "Loti" Kobalia is a retired Georgian colonel involved in the civil war of the early 1990s in which he commanded forces loyal to the ousted President Zviad Gamsakhurdia.
The War in Abkhazia from 1992 to 1993 was waged chiefly between Georgian government forces on one side, Russian military forces on other side supporting separatist forces demanding independence of Abkhazia from Georgia. http://www.historyorb.com/russia/georgia.php Ethnic Georgians, who lived in Abkhazia fought largely on the side of Georgian government forces. Ethnic Armenians and Russians within Abkhazia's population, largely supported Abkhazians and many fought on their side. The separatists were supported by thousands of the North Caucasus and Cossack militants and by the Russian Federation forces stationed in and near Abkhazia.

The Battle of Sukhumi took place in 1992 between Abkhazian separatists and terrorists and the Georgian National Guard. The battle marked the start of 1992–1993 War in Abkhazia.

The 1991–1992 Georgian coup d'état, also known as the Tbilisi War, or the Putsch of 1991–1992, was an internal military conflict that took place in the newly independent Republic of Georgia following the fall of the Soviet Union, from 22 December 1991 to 6 January 1992. The coup, which triggered the Georgian Civil War, pitted factions of the National Guard loyal to President Zviad Gamsakhurdia against several paramilitary organizations unified at the end of 1991 under the leadership of warlords Tengiz Kitovani, Jaba Ioseliani and Tengiz Sigua.
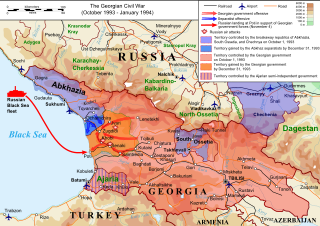
The Battle of Poti was a series of engagements around Poti, Georgia during the Georgian Civil War, between rebels supporting the ousted Georgian president Zviad Gamsakhurdia, the so-called 'Zviadists', and Russian forces supporting the Georgian Head of State Eduard Shevardnadze. A group of Russian Marines of the Black Sea Fleet landed in the Georgian port city in late October 1993 to protect an important railway between Poti and the Georgian capital Tbilisi. In November clashes between the Russians and the Zviadists erupted, with the Russian Major General Boris Djukov, claiming no Russian casualties. The fighting ended when the Georgian Armed Forces broke through the rebels' defenses and entered their capital Zugdidi on the 6th of November.
Relations between Georgia and the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria began in 1991, when both countries declared independence from the Soviet Union. They continued to pursue relations until Chechnya was re-annexed by Russia in 2000.