
Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase is a mitochondrial homodimer apoenzyme that focuses on the catalysis of methylmalonyl CoA to succinyl CoA. The enzyme is bound to adenosylcobalamin, a hormonal derivative of vitamin B12 in order to function. Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase deficiency is caused by genetic defect in the MUT gene responsible for encoding the enzyme. Deficiency in this enzyme accounts for 60% of the cases of methylmalonic acidemia.

Amino acid synthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids).

The acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme is a protein found in plants and micro-organisms. ALS catalyzes the first step in the synthesis of the branched-chain amino acids.
In enzymology, a ketol-acid reductoisomerase (EC 1.1.1.86) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-hydroxy-2-methylbutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.178) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase (acylating) (EC 1.2.1.25) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a leucine dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a valine dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.4.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a leucine 2,3-aminomutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a precorrin-8X methylmutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Threonine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.19, systematic name L-threonine ammonia-lyase (2-oxobutanoate-forming), also commonly referred to as threonine deaminase or threonine dehydratase, is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of L-threonine into α-ketobutyrate and ammonia:
In enzymology, a 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate hydroxymethyltransferase (EC 2.1.2.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme acetolactate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.5) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme dihydroxy-acid dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.9) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-isopropylmalate synthase (EC 2.3.3.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a leucine transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a valine-3-methyl-2-oxovalerate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a valine-pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
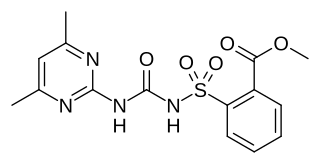
Sulfometuron methyl is an organic compound used as a herbicide. It is classed as a sulfonylurea. It functions via the inhibitition of acetolactate synthase enzyme, which catalyses the first step in biosynthesis of the branched-chain amino acids valine, leucine and isoleucine.








