
One of the most extensive bushfire seasons in Australia's history. Victoria experienced the longest continuously burning bushfire complex in Australia's history, with fires in the Victorian Alps and Gippsland burning over 1 million hectares of land over the course of 69 days. See Bushfires in Australia for an explanation of regional seasons.
In Australia, during winter and spring 2001, low rainfall across combined with a hot, dry December created ideal conditions for bushfires. On the day of Christmas Eve, firefighters from the Grose Vale Rural Fire Service (RFS) brigade attended a blaze in rugged terrain at the end of Cabbage Tree Rd, Grose Vale, believed to have been caused by power lines in the Grose Valley.

The Eyre Peninsula bushfire of 2005, an event also known locally as Black Tuesday and by South Australian Government agencies as the Wangary bushfire, was a bushfire that occurred during January 2005 on the lower part of the Eyre Peninsula, a significant part of South Australia's wheat belt, where most of the land is either cropped or grazed. The fire resulted in 780 square kilometres (301 sq mi) of land being burnt, the loss of nine lives, injury to another 115 people, and huge property damage. It was South Australia's worst bushfire since the Ash Wednesday fires of 1983. Heat from the fire reached 1,000 °C (1,830 °F), with speeds up to 100 kilometres per hour (62 mph).

The Australian bushfire season ran from late December 2008 to April/May 2009. Above average rainfalls in December, particularly in Victoria, delayed the start of the season, but by January 2009, conditions throughout South eastern Australia worsened with the onset of one of the region's worst heat waves. On 7 February, extreme bushfire conditions precipitated major bushfires throughout Victoria, involving several large fire complexes, which continued to burn across the state for around one month. 173 people lost their lives in these fires and 414 were injured. 3,500+ buildings were destroyed, including 2,029 houses, and 7,562 people displaced.

A moderately extensive bushfire season, particularly in western Victoria where fires were most prominent, occurred in mid-late January 2006 as conditions persisted across the state.
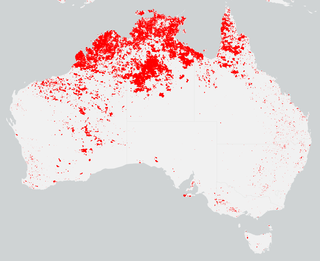
The Australian bushfire season over the summer of 2007–2008, experienced fire occurrence below average for the season as some regions experienced increased rainfall and reduced fuel as a result of extensive fires during the previous 2006–07 season, particularly in Victoria where the fires in the 2006–07 season burnt over 1.1 million hectares of land. Fires in Victoria during the 2007–08 season burnt less than a fifth of the land area usually burnt during an average bushfire season.

The Black Saturday bushfires were a series of bushfires that either ignited or were already burning across the Australian state of Victoria on and around Saturday, 7 February 2009, and were one of Australia's all-time worst bushfire disasters. The fires occurred during extreme bushfire weather conditions and resulted in Australia's highest-ever loss of human life from a bushfire, with 173 fatalities. Many people were left homeless and family-less as a result.

A bushfire season occurred predominantly from June 2009 to May 2010. Increased attention has been given to this season as authorities and government attempt to preempt any future loss of life after the Black Saturday bushfires during the previous season, 2008–09. Long range weather observations predict very hot, dry and windy weather conditions during the summer months, leading to a high risk of bushfire occurrence.

During the summer of 2010–11, a relative lack of bushfires occurred along Eastern Australia due to a very strong La Niña effect, which instead contributed to severe flooding, in particular the 2010–11 Queensland floods and the 2011 Victorian floods. As a result of these weather patterns, most major fire events took place in Western Australia and South Australia. Some later significant fire activity occurred in Gippsland in eastern Victoria, an area which largely missed the rainfall that lead to the flooding in other parts of the state.

The summer of 2012–13 had above average fire potential for most of the southern half of the continent from the east coast to the west. This is despite having extensive fire in parts of the country over the last 12 months. The reason for this prediction is the abundant grass growth spurred by two La Niña events over the last two years.
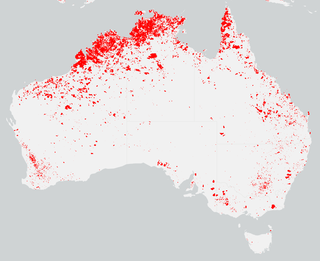
The summer of 2013–14 was at the time, the most destructive bushfire season in terms of property loss since the 2008–09 Australian bushfire season, with the loss of 371 houses and several hundred non-residential buildings as a result of wild fires between 1 June 2015 and 31 May 2016. The season also suffered 4 fatalities; 2 died in New South Wales, 1 in Western Australia and 1 in Victoria. One death was as a direct result of fire, 2 died due to unrelated health complications while fighting fires on their property, and a pilot contracted by the NSW Rural Fire Service died during an accident.
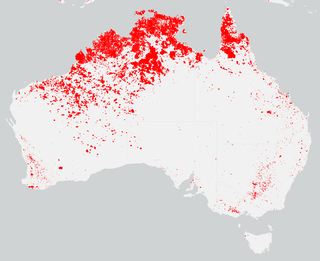
The bushfire season in the summer of 2014–15, was expected to have the potential for many fires in eastern Australia after lower than expected rainfall was received in many areas. Authorities released warnings in the early spring that the season could be particularly bad.

The most destructive bushfire season in terms of property loss since the 2008–09 Australian bushfire season, occurred in the summer of 2015–16, with the loss of 408 houses and at least 500 non-residential buildings as a result of wild fires between 1 June 2015 and 31 May 2016. The season also suffered the most human fatalities since the 2008–09 Australian bushfire season; 6 died in Western Australia, 2 in South Australia and 1 in New South Wales. 8 deaths were as a direct result of fire, and a volunteer firefighter died due to unrelated health complications while on duty.

The 2015 Pinery bushfire was a bushfire that burned from 25 November to 2 December 2015, and primarily affected the Lower Mid North and west Barossa Valley regions immediately north of Gawler in the Australian state of South Australia. At least 86,000 hectares of scrub and farmland in the council areas of Light, Wakefield, Clare and Gilbert Valleys, and Mallala were burned during its duration.
The 2018 Tathra bushfire was a bushfire that burned between 18 and 19 March 2018 and primarily affected parts of the South Coast region in the Australian state of New South Wales. The fire, understood to have been caused by a failure in electrical infrastructure, began in the locality of Reedy Swamp, near Tarraganda, which spread east towards Tathra in the municipality of the Bega Valley Shire.
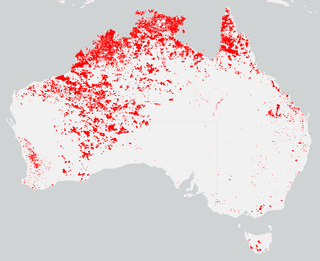
The bushfires were predicted to be "fairly bleak" in parts of Australia, particularly in the east, by the Bushfire and Natural Hazards Cooperative Research Centre (CRC) chief executive, Richard Thornton, in September 2018. Large bushfires had already burned through southern New South Wales during winter. The outlook for spring was of a higher likelihood of fires with a twice the normal chance of an El Nino for summer. Many parts of eastern Australia including Queensland, New South Wales and Gippsland, in Victoria, were already in drought. Above normal fire was also predicted for large parts of Southern Australia and Eastern Australia by the Bushfire and Natural Hazards CRC. The forecast noted that Queensland had recorded the ninth driest and fourth hottest period on record from April to November. New South Wales recorded the fourth hottest period and eighth driest on record, while Victoria experiences the 13th driest and seventh hottest period on record. Authorities in New South Wales brought forward the start of the bushfire season for much of the state from October 2018 to the beginning of August 2018.
The 2018 Central Queensland bushfires were a series of 1,250 bushfires which ignited and moved across areas of the Central Queensland region of Australia in November and December 2018, during the 2018-19 Australian bushfire season.
The 2020–21 Australian bushfire season was the season of summer bushfires in Australia. Following the devastating 2019–20 bushfires in Australia, authorities were urged to prepare early for the 2020–21 Australian bushfire season. The bushfire outlook for July to September 2020 was predicting a normal fire potential in Queensland with a good grass growth in many areas giving an increased risk of grass fires, an above normal season in the Kimberley region of Western Australia as a result of good rains from tropical cyclones, a normal but earlier season in the Northern Territory, an above normal season on the south coast of New South Wales and normal seasons elsewhere.














