
In political science, voter turnout is the percentage of eligible voters who participated in an election. Eligibility varies by country, and the voting-eligible population should not be confused with the total adult population.

Liberal Alliance of Montenegro was a Montenegrin separatist, liberal and anti-war political party, active between 1990 and 2005. The Liberal Alliance was a full member of the Liberal International from 1994 until its dissolution in 2005.
Regular elections in Croatia are mandated by the Constitution and legislation enacted by Parliament. The presidency, Parliament, county prefects and assemblies, city and town mayors, and city and municipal councils are all elective offices. Since 1990, seven presidential elections have been held. During the same period, ten parliamentary elections were also held. In addition, there were nine nationwide local elections. Croatia has also held three elections to elect members of the European Parliament following its accession to the EU on 1 July 2013.
Elections in Greece gives information on elections and election results in Greece.
Elections in Slovakia gives information on election and election results in Slovakia.

All elections in the Czech Republic are based on the principle of universal suffrage. Any adult citizen who is at least 18 years old can vote, except those who have been stripped of their legal capacities by a court, usually on the basis of mental illness. Elected representatives are elected directly by the citizens without any intermediaries. Election laws are not part of the constitution, but – unlike regular laws – they cannot be changed without the consensus of both houses of the Parliament. The Czech Republic uses a two-round plurality voting system for the Presidential and Senate elections and an open party-list proportional representation system for all other elections. The proportional representation system uses the D'Hondt method for allocating seats.
Elections in Hungary are held at two levels: general elections to elect the members of the National Assembly and local elections to elect local authorities. European Parliament elections are also held every 5 years.

Elections in Lithuania are held to select members of the parliament, the president, members of the municipal councils and mayors, as well as delegates to the European Parliament. Lithuanian citizens can also vote in mandatory or consultative referendums.
Legislative elections were held on 23 September 2001.

In voting, a ballot is considered spoilt, spoiled, void, null, informal, invalid or stray if a law declares or an election authority determines that it is invalid and thus not included in the vote count. This may occur accidentally or deliberately. The total number of spoilt votes in a United States election has been called the residual vote. In Australia, such votes are generally referred to as informal votes, and in Canada they are referred to as rejected votes.
A referendum on a proposed draft of the new Serbian constitution was held on October 28 and 29 October 2006 and resulted in the draft constitution being approved by the Serbian electorate. The constitution is Serbia's first as an independent state since the Kingdom of Serbia's 1903 constitution. Over 6.6 million people were entitled to vote in the national referendum.

The Romanian presidential impeachment referendum of 2007 was conducted in order to determine whether the president of Romania Traian Băsescu should be forced to step down.

The 2012 Italian local elections were held on 6–7 May, with a second round on 20–21 May. In Italy, direct elections were held in 948 municipalities: in each municipality (comune) were chosen mayor and members of the City Council. Of the 948 municipalities, 28 were provincial capitals and only 176 had a population higher than 15,000 inhabitants.

A referendum on impeaching President Traian Băsescu was held in Romania on 29 July 2012. The referendum was required after Parliament voted in favour of impeaching Băsescu on 6 July, and had to take place within a month. It was the second referendum on impeaching Băsescu, the first having been held in May 2007, in which 74% of voters chose to keep him in office. Băsescu was later narrowly re-elected in 2009.

Snap elections to the Verkhovna Rada took place on 26 October 2014.

Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 27 October 1872. The Radical Left remained the largest group in the National Council.

Municipal elections were held in Bosnia and Herzegovina on 2 October 2016.
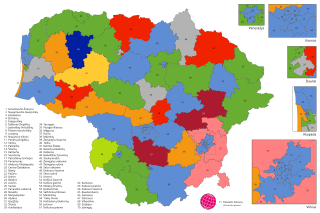
Parliamentary elections were held in Lithuania on 11 and 25 October 2020 to elect the 141 members of the Seimas. 71 were elected in single-member constituencies using the two-round system, and the remaining 70 in a single nationwide constituency using proportional representation. The first round was held on 11 October and the second round on 25 October.
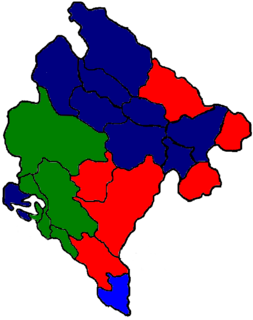
Montenegrin municipal elections were held in all 21 municipalities, between June 2000 and October 2002.

Montenegrin municipal elections were held in all 21 municipalities, between April 2004 and October 2006. It resulted in the decisive victory of the ruling Coalition for European Montenegro in 18 out of 21 municipalities, where he has secured a majority, on its own or in a coalition with national minority parties.














