A pyroclastic flow is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter that flows along the ground away from a volcano at average speeds of 100 km/h but is capable of reaching speeds up to 700 km/h. The gases and tephra can reach temperatures of about 1,000 °C (1,800 °F).

Pico Island is an island in the Central Group of the Portuguese Azores. The landscape features an eponymous volcano, Ponta do Pico, which is the highest mountain in Portugal, the Azores, and the highest elevation of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. In the tradition of the Portuguese poet, Raul Brandão, Pico is referred to as the Ilha Preta, for its black volcanic soils, which nourish its UNESCO-designated vineyards that once allowed the development of the island's economy. Pico is the second largest and, geologically speaking, the most recently formed island of the Azores, being around 300,000 years old.
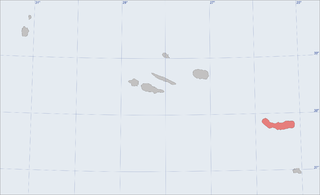
São Miguel Island, nicknamed "The Green Island", is the largest and most populous island in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. The island covers 760 km2 (290 sq mi) and has around 140,000 inhabitants, with 45,000 people residing in Ponta Delgada, the archipelago's largest city.

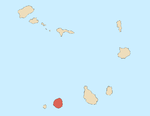
Fogo is an island in the Sotavento group of Cape Verde in the central Atlantic Ocean. Its population is 35,837 (2015), with an area of 476 km2. It reaches the highest altitude of all the islands in Cape Verde, rising to 2,829 metres above sea level at the summit of its active volcano, Pico do Fogo.

Faial Island, also known as Fayal Island, is a Portuguese island of the Central Group or Grupo Central of the Azores, in the Atlantic Ocean.

The Capelinhos is a monogenetic volcano located on the western coast of Faial Island in the Azores. It is part of the larger volcanic complex of Capelo, which includes 20 scoria cones and lava fields that are aligned west-northwest to east-southeast from the Caldeira Volcano caldera. Although the name "Capelinhos" is associated with the volcano, it technically refers to the western cape of the parish of Capelo. It can be considered the westernmost point of Europe; there are more westerly islands in the Azores archipelago but they lie on the North American Plate.

Praia do Norte is a civil parish of the municipality of Horta, located along the northern coast between Cedros and Capelo, on the Portuguese island of Faial, in the archipelago of the Azores. The population in 2011 was 250, in an area of 13.85 square kilometres (5.35 sq mi). It is the least populous parish on the island, reached along the Estrada Regional E.R.1-1ª regional roadway from the urban centre of Horta. It contains the localities Cerca, Fajã and Praia do Norte.

Chã das Caldeiras is a small community of approximately 700 inhabitants in the crater of the volcano Pico do Fogo on the island of Fogo, Cape Verde. The village consists of two main neighborhoods: Portela and Bangaeira, founded in 1920 and 1917, respectively. At an elevation of about 1,700 meters, it is the highest village in Cape Verde. It is part of the municipality of Santa Catarina do Fogo. The main organizing body in the village is the Associação dos Agricultores de Chã, an agricultural cooperative that holds considerable sway over the local economy. Chã is the only area in Cape Verde that grows significant quantities of grapes and produces export-quality wines.

Água de Pau Massif is a stratovolcanic complex, located in the central part of the island of São Miguel, in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. More recognizable for the Lagoa do Fogo at its centre, the volcanic complex includes centuries of geomorphological structures that include lava domes, cones and encrusted lava flows that have marked its history from, the last, 45,000 years BC.

Pico do Fogo is an active stratovolcano located on the island of Fogo, Cape Verde, rising to 2,829 metres (9,281 ft) above sea level. The main cone last erupted in 1680, causing mass emigration from the island. A subsidiary vent erupted in 1995. The only deadly eruption was in 1847 when earthquakes killed several people.
The following is a list of notable natural disasters that have affected the Azores:
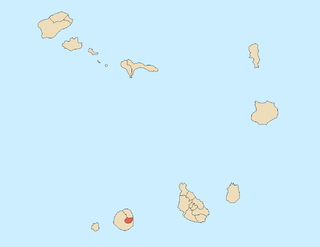
Santa Catarina do Fogo is a concelho (municipality) of Cape Verde. Situated in the southeastern part of the island of Fogo, it covers 32% of the island area (152.95 km2), and is home to 14% of its population. Its seat is the city Cova Figueira. The Municipality of Santa Catarina do Fogo was created in 2005; before 2005, it was a parish of the Municipality of São Filipe.

Mount Pico is a currently dormant stratovolcano located on Pico Island, in the mid-Atlantic archipelago of the Azores. It is the highest mountain in Portugal, at 2,351 metres (7,713 ft) above sea level, and is one of the highest Atlantic mountains; it is more than twice the elevation of any other peak in the Azores. It has been a designated nature reserve since 1972.

Cabeça Fundão is a settlement in the southern part of the island of Fogo, Cape Verde and sits on the foot of the mountain rim of Bordeira. It is situated 16 km east of the island capital São Filipe. In 2010 its population was 177. The village is located on the road from Achada Furna to Chã das Caldeiras (EN3-FG05). Its elevation is about 1,570 meters. Cabeça Fundão lies directly south of the Fogo Natural Park.
The Picos Volcanic Fissural System is a system of scoria cones that build up the central region of the island of São Miguel. This volcano is very young with most of it only 5000 years old. The only recorded eruption was in 1652, but seven other eruptions have taken place in the cinder cone group in the last 10,000 years.

The Azores Geopark is a network of 121 geographically-dispersed sites of geographic heritage and marine areas that covers the nine volcanic islands of the archipelago of the Azores. This network is managed by the Azores Geopark Association, a non-profit association, with its headquarters in Horta on the island of Faial, established 19 May 2010. It is part of the European Geoparks Network and the UNESCO Global Geoparks Network. The Association's mission is to ensure the geological conservation, environmental education and sustainable development, while promoting the well-being of the population and a respect for the environment.

The Architecture of Cape Verde has different architectural styles. Unlike the African mainland, Cape Verde was uninhabited until 1461 when the Portuguese arrived, whereas most of the other islands were first inhabited after the end of the 15th century. Its architecture was introduced in the 1460s and has its first origins from Portuguese settlers from the Madeira Islands. The Manueline was its first architectural style, and was followed by Renaissance, Baroque, Pombaline, Early Modern and Modern.

Funco is a traditional Capeverdean house that originated in Africa.

Bordeira is a semicircular mountain in the middle of the island Fogo. It is a crater rim, up to 1 km high, formed by a prehistoric collapse of the volcano Pico do Fogo. At a maximum elevation of 2,692 metres (8,832 ft), it is the second highest point in the nation behind Pico do Fogo. The name literally means the "border". It forms part of Fogo Natural Park. Opening to the east, it effectively protects the northern, western and southern part of the island against lava flows from the volcano. The settlement Chã das Caldeiras lies at the foot of Bordeira, in the caldera. The east side of the Bordeira cliff is much steeper than the west side.