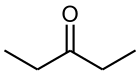
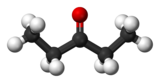
In chemistry, a hydration reaction is a chemical reaction in which a substance combines with water. In organic chemistry, water is added to an unsaturated substrate, which is usually an alkene or an alkyne. This type of reaction is employed industrially to produce ethanol, isopropanol, and butan-2-ol.

Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, butanone.

Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the formula C2H4O. It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of a silver catalyst.
In organic chemistry, hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the net addition of a formyl group and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention: production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resultant aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in speciality chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and pharmaceuticals. The development of hydroformylation is one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.

Methylamine is an organic compound with a formula of CH3NH2. This colorless gas is a derivative of ammonia, but with one hydrogen atom being replaced by a methyl group. It is the simplest primary amine.
In chemistry, homogeneous catalysis is catalysis where the catalyst is in same phase as reactants, principally by a soluble catalyst a in solution. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysis describes processes where the catalysts and substrate are in distinct phases, typically solid-gas, respectively. The term is used almost exclusively to describe solutions and implies catalysis by organometallic compounds. Homogeneous catalysis is an established technology that continues to evolve. An illustrative major application is the production of acetic acid. Enzymes are examples of homogeneous catalysts.

Dimethoxyethane, also known as glyme, monoglyme, dimethyl glycol, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, dimethyl cellosolve, and DME, is a colorless, aprotic, and liquid ether that is used as a solvent, especially in batteries. Dimethoxyethane is miscible with water.

Butan-2-ol, or sec-butanol, is an organic compound with formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3. Its structural isomers are 1-butanol, isobutanol, and tert-butanol. 2-Butanol is chiral and thus can be obtained as either of two stereoisomers designated as (R)-(−)-butan-2-ol and (S)-(+)-butan-2-ol. It is normally encountered as a 1:1 mixture of the two stereoisomers — a racemic mixture.
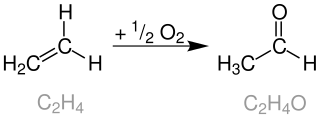
The Wacker process or the Hoechst-Wacker process refers to the oxidation of ethylene to acetaldehyde in the presence of palladium(II) chloride and copper(II) chloride as the catalyst. This chemical reaction was one of the first homogeneous catalysis with organopalladium chemistry applied on an industrial scale.

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of n, the material is either a dense brown solid or a soluble reddish salt. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis, notably for the industrial production of acetic acid and hydroformylation.
The chemical compound 1,2-dichloroethane, commonly known as ethylene dichloride (EDC), is a chlorinated hydrocarbon. It is a colourless liquid with a chloroform-like odour. The most common use of 1,2-dichloroethane is in the production of vinyl chloride, which is used to make polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, furniture and automobile upholstery, wall coverings, housewares, and automobile parts. 1,2-Dichloroethane is also used generally as an intermediate for other organic chemical compounds, and as a solvent. It forms azeotropes with many other solvents, including water and other chlorocarbons.

Methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK, 4-methylpentan-2-one) is an organic compound with the condensed chemical formula (CH3)2CHCH2C(O)CH3. This ketone is a colourless liquid that is used as a solvent for gums, resins, paints, varnishes, lacquers, and nitrocellulose.

Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%. An estimated 270,000 tons were produced in 2005.

Ethylenediamine (abbreviated as en when a ligand) is the organic compound with the formula C2H4(NH2)2. This colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor is a basic amine. It is a widely used building block in chemical synthesis, with approximately 500,000 tonnes produced in 1998. Ethylenediamine is the first member of the so-called polyethylene amines.

1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde. This six-membered ring compound is the oxidized derivative of 1,4-hydroquinone. The molecule is multifunctional: it exhibits properties of a ketone, being able to form oximes; an oxidant, forming the dihydroxy derivative; and an alkene, undergoing addition reactions, especially those typical for α,β-unsaturated ketones. 1,4-Benzoquinone is sensitive toward both strong mineral acids and alkali, which cause condensation and decomposition of the compound.
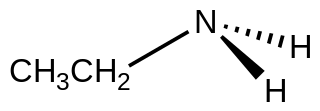
Ethylamine, also known as ethanamine, is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2NH2. This colourless gas has a strong ammonia-like odor. It condenses just below room temperature to a liquid miscible with virtually all solvents. It is a nucleophilic base, as is typical for amines. Ethylamine is widely used in chemical industry and organic synthesis.

Methyl vinyl ketone (MVK, IUPAC name: butenone) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH=CH2. It is a reactive compound classified as an enone, in fact the simplest example thereof. It is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic liquid with a pungent odor. It is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is a useful intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds.

Crotonaldehyde is a chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=CHCHO. The compound is usually sold as a mixture of the E- and Z-isomers, which differ with respect to the relative position of the methyl and formyl groups. The E-isomer is more common (data given in Table is for the E-isomer). This lachrymatory liquid is moderately soluble in water and miscible in organic solvents. As an unsaturated aldehyde, crotonaldehyde is a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis. It occurs in a variety of foodstuffs, e.g. soybean oils.

Isopropylamine is an organic compound, an amine. It is a hygroscopic colorless liquid with ammonia-like odor. It is miscible with water and flammable. It is a valuable intermediate in chemical industry.
Isopropyl alcohol is a colorless, flammable organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor.