
Maltase is one type of alpha-glucosidase enzymes located in the brush border of the small intestine. This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of disaccharide maltose into two simple sugars of glucose. Maltase is found in plants, bacteria, yeast, humans, and other vertebrates. It is thought to be synthesized by cells of the mucous membrane lining the intestinal wall.
Hydrolase is a class of enzymes that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases.
In enzymology, an ADP-sugar diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.21) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alpha-factor-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.48) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a lipopolysaccharide-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.39) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phospholipid-translocating ATPase (EC 3.6.3.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an UDP-sugar diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.45) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme acyloxyacyl hydrolase (EC 3.1.1.77, AOAH) was discovered because it catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a 2-(acetamidomethylene)succinate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(acetamidomethylene)succinate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.66) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an amidase (EC 3.5.1.4, acylamidase, acylase (misleading), amidohydrolase (ambiguous), deaminase (ambiguous), fatty acylamidase, N-acetylaminohydrolase (ambiguous)) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of an amide. In this way, the two substrates of this enzyme are an amide and H2O, whereas its two products are monocarboxylate and NH3.
In enzymology, a choloylglycine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.24) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyldiaminopimelate deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.47) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, Nα-benzyloxycarbonylleucine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.64) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a proclavaminate amidinohydrolase (EC 3.5.3.22) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a succinyl-diaminopimelate desuccinylase (EC 3.5.1.18) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-deoxy-8-phosphooctulonate synthase (EC 2.5.1.55) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
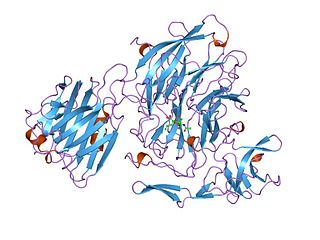
In molecular biology, glycoside hydrolase family 33 is a family of glycoside hydrolases.
Lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase is an enzyme with systematic name CMP-3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate:lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate transferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase (hydrolysing) (EC 3.2.1.183, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase, GNE (gene), siaA (gene), neuC (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine hydrolase (2-epimerising). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction




