
Vanillin is an organic compound with the molecular formula C8H8O3. It is a phenolic aldehyde. Its functional groups include aldehyde, hydroxyl, and ether. It is the primary component of the extract of the vanilla bean. Synthetic vanillin is now used more often than natural vanilla extract as a flavoring in foods, beverages, and pharmaceuticals.

Daucus carota, whose common names include wild carrot, European wild carrot, bird's nest, bishop's lace, and Queen Anne's lace, is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae. It is native to temperate regions of the Old World and was naturalized in the New World.

4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as p-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA), is a monohydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water and chloroform but more soluble in polar organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is primarily known as the basis for the preparation of its esters, known as parabens, which are used as preservatives in cosmetics and some ophthalmic solutions. It is isomeric with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, known as salicylic acid, a precursor to aspirin, and with 3-hydroxybenzoic acid.
Salicylic aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4OH(CHO). Along with 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, it is one of the three isomers of hydroxybenzaldehyde. This colorless oily liquid has a bitter almond odor at higher concentration. Salicylaldehyde is a precursor to coumarin and a variety of chelating agents.

Phenanthrenoids are chemical compounds formed with a phenanthrene backbone. These compounds occur naturally in plants, although they can also be synthesized.

Pinosylvin is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH=CHC6H3(OH)2. A white solid, it is related to trans-stilbene, but with two hydroxy groups on one of the phenyl substituents. It is very soluble in many organic solvents, such as acetone.

Carrot seed oil is the essential oil extract of the seed from the carrot plant Daucus carota. The oil has a woody, earthy sweet smell and is yellow or amber-coloured to pale orange-brown in appearance. The pharmacologically active constituents of carrot seed extract are three flavones: luteolin, luteolin 3'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, and luteolin 4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside. Rather than the extract the distilled (ethereal) oil is used in perfumery and food aromatization. The main constituent of this oil is carotol.

Gastrodia elata is a saprophytic perennial herb in the family Orchidaceae. It is found in Nepal, Bhutan, India, Japan, Korea, Siberia, Taiwan, and China.
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.64) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Protocatechuic acid (PCA) is a dihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid. It is a major metabolite of antioxidant polyphenols found in green tea. It has mixed effects on normal and cancer cells in in vitro and in vivo studies.

3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CHO. It is a colorless solid although most samples appear tan. Two other isomers of hydroxybenzaldehyde exist.

In biochemistry, naturally occurring phenols are natural products containing at least one phenol functional group. Phenolic compounds are produced by plants and microorganisms. Organisms sometimes synthesize phenolic compounds in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research. Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants.

Gastrodin is a chemical compound which is the glucoside of gastrodigenin. It has been isolated from the orchid Gastrodia elata and from the rhizome of Galeola faberi. It can also be produced by biotransformation of 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde by Datura tatula cell cultures.
2,4-Bis(4-hydroxybenzyl)phenol is a phenolic compound produced by the saprophytic orchid Gastrodia elata and by the myco-heterotroph orchid Galeola faberi.
Galeola faberi is an orchid species in the genus Galeola found in central and southern China, as well as in Nepal, the eastern Himalayas, Vietnam and Sumatra.
Gastrol is a phenolic compound produced by the saprophytic orchid Gastrodia elata.
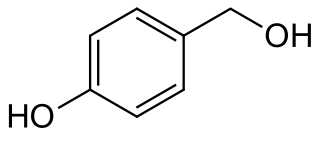
Gastrodigenin is a phenolic compound found in the rhizome of Gastrodia elata.
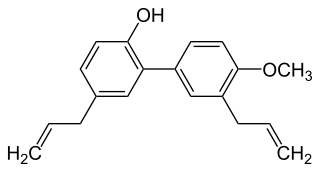
4-O-Methylhonokiol is a neolignan, a type of phenolic compound. It is found in the bark of Magnolia grandiflora and in M. virginiana flowers.
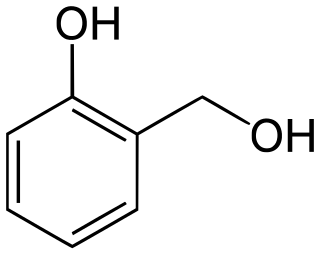
Salicyl alcohol (saligenin) is an organic compound with the formula C6HOH(CH2OH. It is a white solid that is used as a precursor in organic synthesis.
4-Chlorophenol is an organic compound with the formula C6H4ClOH. It is one of three monochlorophenol isomers. It is a colorless or white solid that melts easily and exhibits significant solubility in water. Its pKa is 9.14.















