Related Research Articles
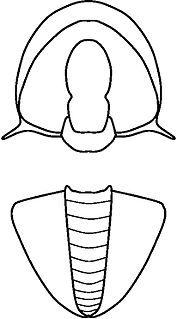
Acidiscus Rasetti, 1966, is a genus of Eodiscinid trilobite belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864). It lived during the Botomian stage = late Lower Cambrian Stage 4 ; the upper Botomian boundary corresponds to base of the Middle Cambrian, Miaolingian Series and Wuliuan stage.

Acimetopus Rasetti, 1966, is a genus of Eodiscinid trilobite belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864). It lived during the Botomian stage. = late Lower Cambrian Stage 4 ; the upper Botomian boundary corresponds to base of the Middle Cambrian, Miaolingian Series and Wuliuan stage.
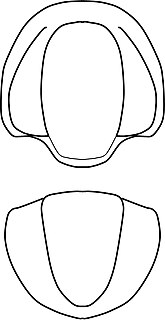
Bathydiscus is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the Botomian stage.
Parapagetia is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 524 to 518.5 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period.
Laudonia is an extinct genus of trilobites that lived during the early part of the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 524 to 518.5 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period. There are currently two named species assigned to it.
Korobovia Korovnikov, 2007, is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the later part of the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 524 to 518.5 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period.

Yunnanocephalus is a genus of ptychopariid trilobite. It lived during the late Atdabanian and Botomian stages, in what are currently Antarctica, Australia and China. It was a "moderately common" member of the Chengjiang Fauna. Yunnanocephalus is the only genus currently assigned to the Yunnanocephalidae family.

Tsunyidiscus is a trilobite belonging to the Suborder Eodiscina. Tsunyidiscus appeared near the end of the Lower Cambrian, during the late Atdabanian stage of geologic time and some collections suggest it may have survived into the Botomian. The genus is very small, oculate and isopypous with a narrow dome-shaped glabella and a narrow bullet-shaped pygidial axis. Thorax consists of three segments. Tsunyidiscus is the only genus currently attributed to the family Tsunyidiscidae.
Lemdadella is an extinct genus of redlichiid trilobites that lived during the late Atdabanian stage, which lasted from 530 to 524 million years ago during the early part of the Cambrian Period.
Fallotaspidella is an extinct genus of redlichiid trilobites. It lived during the late Atdabanian stage, which lasted from 530 to 524 million years ago during the early part of the Cambrian Period.
Acrocephalella is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived from 501 to 497 million years ago during the Guzhangian of the late Cambrian Period.
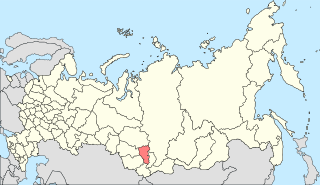
South Central Siberia is a geographical region north of the point where Russia, China, Kazakhstan and Mongolia come together.

Lonchodomas is a genus of trilobites, that lived during the Ordovician. It was eyeless, like all raphiophorids, and had a long straight sword-like frontal spine, that gradually transforms into the relatively long glabella. Both the glabellar spine and the backward directed genal spines are subquadrate in section. Lonchodomas has five thorax segments and the pleural area of the pygidium has two narrow furrows. Lonchodomas occurred in what are today Argentina, Canada (Newfoundland), Estonia, Latvia, Norway, Sweden, the Russian Federation and the United States.

Phalagnostus is a genus of small trilobites, in the order Agnostida. It lived during the Middle Cambrian, in what are now Canada, China, the Czech Republic, Denmark, England, France, the Russian Federation, Wales, Sweden, and possibly the United States (Vermont). The headshield is almost entirely effaced and wider than the tailshield. The pygidium is also very effaced, but the ovate pygidial axis is well defined and a border furrow is also present.
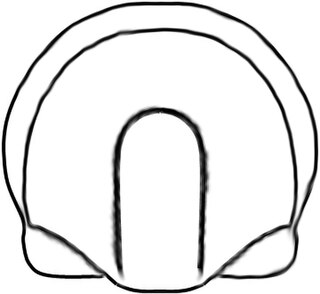
Mallagnostus Howell, 1935, is a trilobite genus belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864) according to Whittington et al. 1997. It lived during the late Lower Cambrian, with remains found in USA, Canada (Newfoundland), Spain, England, Russia, Mongolia, and the early Middle Cambrian as reported from China and Russia (Yakutia).

Itagnostus is a genus of trilobite restricted to the Middle Cambrian. Its remains have been found in Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America.

Delgadella is a diminutive trilobite that lived during the late Lower Cambrian and has been found in Russia, Mongolia, Spain, Italy (Sardinia), Portugal, Morocco and Canada (Newfoundland). It can be recognized by its strongly effaced headshield and tailshield, with narrow but distinct furrows and borders along its margins, and three thorax segments.
Tannudiscus Pokrovskaya (1959) is a genus of Eodiscinid trilobites belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida. It lived during the late Lower Cambrian, with remains found in Canada (Newfoundland), China (Gansu), The United Kingdom (England), and the Russian Federation.

Kuznetsk Alatau Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik' on the Kuznetsk Alatau, a mountain ridge in the Altai-Sayan mountain region in southwestern Siberia. The Kuznetsk Alatau consists of several ranges of medium height, between which there are river valleys. The reserve is in the watershed of the Tom River and the Chuly River. It is spread over three districts of Kemerovo Oblast: Tisulsky District, Mezhdurechensky District, and Novokuznetsky District. The reserve was established in 1989 and covers an area of 412,900 ha (1,594 sq mi).

The Sayan montane conifer forests ecoregion covers the mid-elevation levels of the Sayan Mountains, the high mountain range between the taiga of Siberia, Russia to the north, and the steppes of Mongolia to the south. The slopes of the mountains at the mid-altitudes are covered by Temperate coniferous forest. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic realm, with a cold semi-arid climate. It covers 35,741,835 km2 (13,800,000 sq mi).
References
- 1 2 Sepkoski, Jack (2002). "A compendium of fossil marine animal genera (Trilobita entry)". Bulletins of American Paleontology. 364: 560. Archived from the original on 5 September 2006. Retrieved 12 January 2006.
- ↑ Poletaeva, O.K. (1973). "New Early Cambrian trilobites from the Sanashtykgol Horizon of the Altay-Sayan Region". Paleontological Journal. 7 (1): 51–56.cited inPaleobiology Database. "Abakania" . Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ↑ Repina, L.N.; Romanenko, E.V.; Fedjanina, E.S.; Pegel, T.V. (1999). "Trilobites from the Lower and Lowermost middle Cambrian of the Kiya river reference section (Kuznetsk, Alatau)". Annales de Paléontologie. 85 (1): 3–56. doi:10.1016/s0753-3969(99)80007-x.cited inPaleobiology Database. "Abakania" . Retrieved 17 December 2021.