
Acacia adenogonia is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to north western Australia.

Acacia auratiflora, commonly known as the orange-flowered wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves. It is listed as an endangered species.

Acacia consanguinea is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemism to south western Australia.

Acacia consobrina is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to south western Australia.
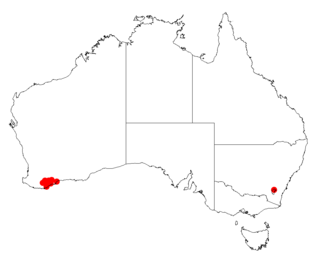
Acacia declinata is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area along the south coast in south western Australia.

Acacia dissona is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia donaldsonii is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemism in an area of south western Australia.

Acacia hadrophylla is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia lanuginophylla, or woolly wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to south western Australia. It is currently listed as a vulnerable species according to the Environment Protection Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.
Acacia manipularis is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to north western Australia.

Acacia obesa is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is native to a small area of south western Australia.

Acacia ophiolithica is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves where it is endemic to a small area along the south west coast of Australia.

Acacia pharangites, commonly known as Wongan gully wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area of south western Australia and is listed as endangered according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.

Acacia recurvata, commonly known as the recurved wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area of western Australia.
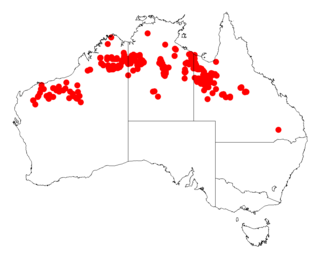
Acacia retivenea, commonly known as the net-veined wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic across northern Australia.

Acacia undosa is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia vittata, commonly known as Lake Logue wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in western Australia.

Acacia wilsonii, also known as Wilson's wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area of western Australia. It was listed as an endangered species in 2018 according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 by Australian authorities and according to Biodiversity Conservation Act 2016 by Western Australian authorities.
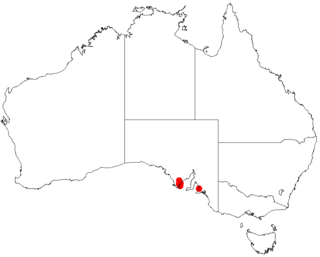
Acacia whibleyana is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia, section Plurinerves. It is native to South Australia.

Acacia dolichophylla, also known as Chewings Range wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to arid parts of central Australia.



















