
Acacia bakeri, known as the marblewood, white marblewood, Baker's wattle or scrub wattle, is one of the largest of all acacias, growing to 40 m (130 ft) tall. It is a long-lived climax rainforest tree from eastern Australia. Unlike most acacias, fire is not required for seed germination. This tree is considered vulnerable to extinction. Its former habitat is lowland subtropical rainforest, which has been mostly cleared in the 19th and 20th centuries.

Acacia effusifolia is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to an area in the Mid West and the Wheatbelt regions of Western Australia.

Acacia gonoclada, also known as ganambureng, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to northern Australia.

Acacia hamersleyensis, also known as Karijini wattle or Hamersley Range wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is endemic to a small area in central Western Australia.

Acacia hopperiana is a small tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia multispicata, commonly known as spiked wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia oncinocarpa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to northern Australia.

Acacia orthocarpa, also commonly known as Pilbara weeping wattle, needle-leaf wattle or straight-podded wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to tropical parts of northern Australia. The indigenous Nyangumarta peoples know it as yartupu.

Acacia sibina is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae the is endemic to parts of western Australia.
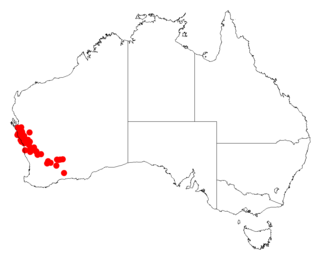
Acacia signata is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia eremaea is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area in western Australia.

Acacia pharangites, commonly known as Wongan gully wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to the Wongan Hills of south western Australia and is listed as endangered according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.

Acacia subtilinervis, also known as the net-veined wattle, is a rare wattle in the Juliflorae subgenus found in eastern Australia.

Acacia juncifolia, commonly known as rush-leaf wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to north eastern Australia.

Acacia pilligaensis, commonly known as Pillaga wattle or pinbush wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.
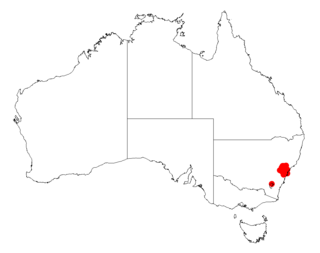
Acacia saliciformis is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.
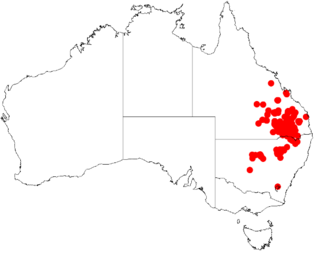
Acacia burrowii, commonly known as Burrow's wattle, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to eastern Australia.

Acacia cretata is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.
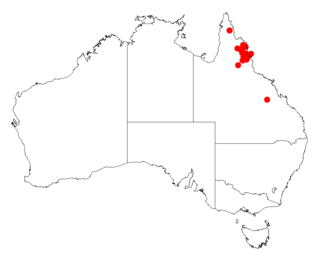
Acacia guymeri is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia. It was listed as vulnerable according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 but was delisted in 2013. It is still listed as Vulnerable according to the Nature Conservation Act 1992 in Queensland.

Acacia rhodoxylon, also known as rosewood, ringy rosewood or spear wattle, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.




















