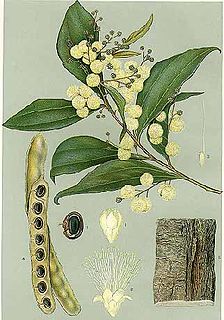
Acacia binervata, commonly known as two-veined hickory, is a shrub or tree that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia oncinocarpa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to northern Australia.

Acacia thomsonii, commonly known as Thomson's wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that native to parts of northern Australia.

Acacia dorsenna is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to Western Australia.

Acacia ryaniana is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to an area along the west coast of Australia.

Acacia scirpifolia is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to western Australia
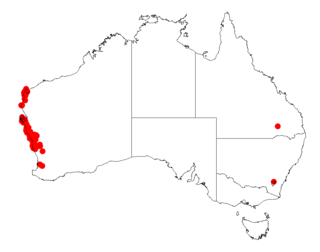
Acacia spathulifolia commonly known as Gold carpet or the Gold carpet wattle is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to coastal parts of western Australia.

Acacia eremaea is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area in western Australia.

Acacia hemignosta commonly known as the clubleaf wattle, is a tree or shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to northern parts of Australia.

Acacia vittata, commonly known as Lake Logue wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in western Australia.

Acacia cretacea, also known as chalky wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to South Australia.
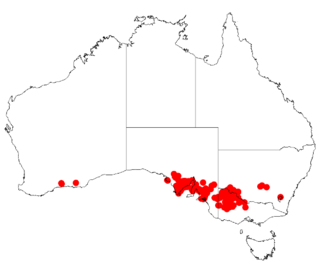
Acacia halliana is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to parts of south eastern Australia.

Acacia perangusta, commonly known as eprapah wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.

Acacia polifolia is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to parts of eastern Australia.

Acacia rivalis, commonly known as silver wattle or creek wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to southern Australia.
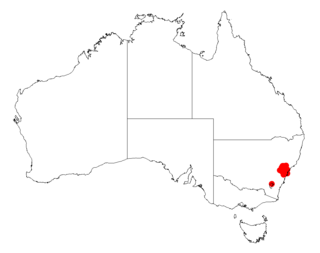
Acacia saliciformis is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.

Acacia siculiformis, commonly known as dagger wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to south eastern Australia.

Acacia linearifolia, commonly known as stringybark wattle or narrow-leaved wattle, is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia sericoflorais a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to northern Australia.

Acacia subporosa, also commonly known as river wattle, bower wattle, narrow-leaf bower wattle and sticky bower wattle, is a tree or shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south eastern Australia. It is considered to be rare in Victoria




















