Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic, some are benthic, a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants (phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.

Tantulocarida is a highly specialised group of parasitic crustaceans that consists of about 33 species, treated as a class in superclass Multicrustacea. They are typically ectoparasites that infest copepods, isopods, tanaids, amphipods and ostracods.

Monogeneans, members of the class Monogenea, are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.

The family Argulidae, whose members are commonly known as carp lice or fish lice, are parasitic crustaceans in the class Ichthyostraca. It is the only family in the monotypic subclass Branchiura and the order Arguloida, although a second family, Dipteropeltidae, has been proposed. Although they are thought to be primitive forms, they have no fossil record.

Sea lice are copepods of the family Caligidae within the order Siphonostomatoida. They are marine ectoparasites that feed on the mucus, epidermal tissue, and blood of host fish. The roughly 559 species in 37 genera include around 162 Lepeophtheirus and 268 Caligus species.
Gyrinicola batrachiensis are nematode parasites that are members of the order Oxyurida. Members of this order are also known as pinworms. These organisms are nematodes that feed on micro-particles in the gut of vertebrates and invertebrates. Oxyurida is further separated into two superfamilies: Oxyuroidea and Thelastomatoidea, which are parasites of vertebrates and invertebrates respectively. Oxyuroidea is composed on three families: Pharyngodonidae; parasites of herbivorous vertebrates, and Oxyuridae and Heteroxynematidae; parasites of mammals and some birds.

Schistocephalus solidus is a tapeworm of fish, fish-eating birds and rodents. This hermaphroditic parasite belongs to the Eucestoda subclass, of class Cestoda. This species has been used to demonstrate that cross-fertilization produces a higher infective success rate than self-fertilization.

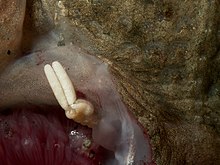
Lernaeocera branchialis, sometimes called cod worm, is a parasite of marine fish, found mainly in the North Atlantic. It is a marine copepod which starts life as a small pelagic crustacean larva. It is among the largest of copepods, ranging in size from 2 to 3 millimetres when it matures as a copepodid larva to more than 40 mm as a sessile adult.
Nicothoë astaci or the 'lobster louse' is an ectoparasitic copepod that parasitises the gills of the European lobster species Homarus gammarus. The lobster louse was first reported in 1826 by Audoin & Milne-Edwards. N. astaci has been found on lobsters inhabiting locations including Scotland, Lundy Island in the Bristol Channel and as far south as France and Portugal. The louse possesses a narrow suctorial mouthpart to feed on host haemolymph. Internally, In its adult form, Nicothoe is barely mobile and most likely remains in the same position for most of its life. The parasite occurs in groups, particularly near the base of the gills, and study has gone into its effects on the lobsters, which are considerably important, commercially. Not much is known about its life cycle, since there are significant gaps in knowledge of certain stages of its growth.
Pennella is a genus of large copepods which are common parasites of large pelagic fishes. They begin their life cycle as a series of free-swimming planktonic larvae. The females metamorphose into a parasitic stage when they attach to a host and enter into its skin. The males are free swimming. Due to their large size and mesoparasitic life history there have been a number of studies of Pennella, the members of which are among the largest of the parasitic Copepoda. All species are found as adults buried into the flesh of marine bony fish, except for a single species, Pennella balaenopterae which can be found in the muscles and blubber of cetaceans and occasionally other marine mammals, and is the largest species of copepod.
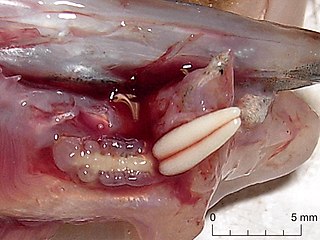
Acanthochondria limandae is a species of copepods in the genus Acanthochondria. They are host-specific ectoparasites of two species of flatfish: the common dab and the European flounder. They attach themselves to the bases of the gill arches of their hosts. They can infest as much as 2 to 30% of fish in a given population.
Choniomyzon is a genus of copepods, containing the following species: One species, C. inflatus, is a parasite of the eggs of the slipper lobster Ibacus novemdentatus.

Acanthochondria is a genus of copepods, containing the following species:
Pennella balaenopterae is a large ectoparasitic copepod specialising in parasitising marine mammals. It is the largest member of the genus Pennella, the other species of which are parasites of larger marine fish.
Caligus musaicus is a sea louse species that parasitises the European flounder ; it was discovered off Portugal.

Lepeophtheirus pectoralis is a species of parasitic copepod from the northeast Atlantic Ocean, and the type species of the genus Lepeophtheirus. It is a parasite of flatfish, with the European flounder, the plaice, and the dab as the most frequent hosts. It feeds on the mucus, skin, and blood of the fish, with egg-producing females infecting the pectoral and pelvic fins of the host, while immature individuals and males are found on the rest of the body.
Cardiodectes bellottii is a species of copepods in the family Pennellidae. It is a parasite of fish. It is found in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans as well as the Mediterranean Sea; specimens from the Pacific were formerly treated as a separate species, Cardiodectes medusaeus.
Temora longicornis is a species of copepod in the family Temoridae. It is found in marine environments on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean.
Pennella exocoeti is a large ectoparasitic copepod, a specialist parasite of flying fish. The adult female copepod clings to the fish's gills or skin and feeds on its body fluids.

Lernaeenicus sprattae is a species of copepod in the family Pennellidae. It is a parasite of the European sprat and certain other fish and is sometimes known as the sprat eye-maggot.