
Congo may refer to either of two countries that border the Congo River in central Africa:
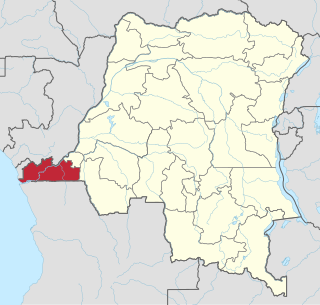
Kongo Central, formerly Bas-Congo is one of the 26 provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Its capital is Matadi.

Ocimum is a genus of aromatic annual and perennial herbs and shrubs in the family Lamiaceae, native to the tropical and warm temperate regions of all 6 inhabited continents, with the greatest number of species in Africa. It is the genus of basil and the name is from the Ancient Greek word for basil, ὤκιμον (ṓkimon). Its best known species are the cooking herb cooking basil, O. basilicum and the medicinal herb tulsi, O. tenuiflorum.

The Army for the Liberation of Rwanda was a rebel group largely composed of members of the Interahamwe and Armed Forces of Rwanda. Operating mostly in the eastern regions of the Democratic Republic of the Congo along the border with Rwanda, it carried out attacks throughout the Second Congo War against forces aligned with Rwanda and Uganda. In 2000, the ALiR agreed to merge with the Hutu resistance movement based in Kinshasa into the new Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR). ALiR was largely supplanted by the FDLR by 2001.
The Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Brazzaville or the Congo, is a country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Gabon, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Angolan exclave province of Cabinda, and the Gulf of Guinea.
Articles related to the Democratic Republic of the Congo include:

Angraecopsis is a genus of plants in the family Orchidaceae. It was first described by Fritz Kraenzlin in 1900 and given its name on account with the genus' similarity to Angraecum species. Angraecopsis are native to Africa, Madagascar, Réunion, Mauritius and the Comoros. The growth habit is rather small and the leaves emerge from a woody stem.

Palisota is a genus of plant in family Commelinaceae, first described in 1828. It is native to sub-Saharan Africa.
The Province of the Anglican Church of the Congo is a province of the Anglican Communion, stretching over the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo.
Eremospatha is a genus of climbing flowering plants in the palm family found in tropical Africa. These rattans are uncommon in cultivation and poorly understood by taxonomists;. Closely related to Laccosperma, they differentiated by the near complete absence of bracts and bracteoles. The name is from Greek meaning "without a spathe".
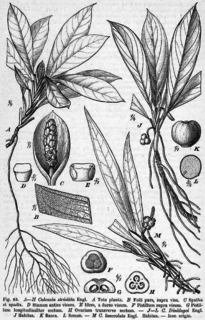
Culcasia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to tropical Africa. Most of its species are climbers and resemble Cercestis except for the fact that they don't produce flagella.
- Culcasia angolensisWelw. ex Schott - western + central Africa from Senegal to Angola
- Culcasia annetiiNtépé-Nyamè - Ivory Coast, Cameroon, Liberia
- Culcasia bosiiNtépé-Nyamè - Cameroon, Gabon, Congo-Brazzaville
- Culcasia brevipetiolataBogner - Gabon
- Culcasia caudataEngl. - Zaïre
- Culcasia dinklageiEngl - western + central Africa from Liberia to Zaïre
- Culcasia ekongoloiNtépé-Nyamè - central Africa from Nigeria to Zaïre
- Culcasia falcifoliaEngl. - central Africa from Gabon east to Tanzania and south to Mozambique
- Culcasia glandulosaHepper - Ivory Coast, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Congo-Brazzaville
- Culcasia insulanaN.E.Br. - Zaïre, Cameroon, Gulf of Guinea Islands
- Culcasia lanceolataEngl. - Cameroon, Gabon
- Culcasia libericaN.E.Br. - Ivory Coast, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Togo
- Culcasia linearifoliaBogner - Cameroon, Gabon
- Culcasia loukandensisPellegr - Cameroon, Gabon, Congo-Brazzaville, Zaïre, Central African Republic
- Culcasia mannii(Hook.f.) Engl. - Cameroon, Gabon, Congo-Brazzaville, Nigeria, Equatorial Guinea
- Culcasia obliquifoliaEngl. - Cameroon, Gabon
- Culcasia orientalisMayo - Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique, Zambia
- Culcasia panduriformisEngl. & K.Krause - Cameroon, Gabon
- Culcasia parvifloraN.E.Br. - western + central Africa from Liberia to Zaïre
- Culcasia rotundifoliaBogner - Gabon
- Culcasia sanagensisNtépé-Nyamè - Cameroon
- Culcasia scandensP.Beauv. - western + central Africa from Liberia to Angola
- Culcasia seretiiDe Wild - western + central Africa from Liberia to Zaïre
- Culcasia simiarumNtépé-Nyamè - western Africa from Ivory Coast to Cameroon
- Culcasia striolataEngl. - western + central Africa from Liberia to Congo-Brazzaville
- Culcasia tenuifoliaEngl. - western + central Africa from Liberia to Zaïre
- Culcasia yangambiensisLouis & Mullend. - Congo-Brazzaville, Zaïre

Aerangis fastuosa, commonly known as the 'Magnificent Aerangis', is a species of epiphytic orchid endemic to Madagascar. It is widespread across Madagascar, stretching from the eastern coastal forests across to the south and along the central plateau. Aerangis fastuosa belongs to the family Orchidaceae, substribe Aerangidinae.

Aerangis ugandensis is a species of epiphytic orchid native to Uganda, Kenya, Rwanda, Burundi, and Congo-Kinshasa.

Ancistrorhynchus is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family Orchidaceae. It contains 16 species native to tropical Africa.

Microcoelia is a genus of orchids native to sub-Saharan Africa as well as to Madagascar and other islands of the Indian Ocean.
- Microcoelia aphylla(Thouars) Summerh. - from Kenya and Uganda south to KwaZulu-Natal, plus Madagascar, Mauritius and Réunion
- Microcoelia aurantiaca(Schltr.) Summerh. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia bispiculataL.Jonss. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia bulbocalcarataL.Jonss. - Príncipe, Cameroon, Gabon, Uganda, Rwanda
- Microcoelia caespitosa(Rolfe) Summerh. in J.Hutchinson & J.M.Dalziel - western and central Africa from Liberia to Zaïre and Uganda
- Microcoelia corallinaSummerh. - Tanzania, Mozambique, Malawi
- Microcoelia cornuta(Ridl.) Carlsward - Madagascar, Comoros
- Microcoelia decaryanaL.Jonss. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia dolichorhiza(Schltr.) Summerh. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia elliotii(Finet) Summerh. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia exilisLindl. - from Kenya and Uganda south to KwaZulu-Natal, plus Madagascar
- Microcoelia gilpinae(Rchb.f. & S.Moore) Summerh. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia globulosa(Hochst.) L.Jonss. - from Nigeria east to Eritrea, south to Angola and Zimbabwe
- Microcoelia hirschbergiiSummerh. - Zaïre, Zambia
- Microcoelia jonssoniiSzlach. & Olszewski - Central African Republic
- Microcoelia koehleri(Schltr.) Summerh. - from Nigeria to Tanzania, south to Zimbabwe
- Microcoelia konduensis(De Wild.) Summerh - western and central Africa
- Microcoelia leptostele(Summerh.) L.Jonss. - Central African Republic, Zaïre
- Microcoelia macrantha(H.Perrier) Summerh. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia macrorhynchia(Schltr.) Summerh. in J.Hutchinson & J.M.Dalziel - central Africa
- Microcoelia megalorrhiza(Rchb.f.) Summerh. - Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi
- Microcoelia microglossaSummerh. - central Africa
- Microcoelia moreauaeL.Jonss - Kenya, Tanzania, Zimbabwe
- Microcoelia nyungwensisL.Jonss. - Rwanda
- Microcoelia obovataSummerh. - from Kenya south to KwaZulu-Natal
- Microcoelia ornithocephalaP.J.Cribb - Malawi
- Microcoelia perrieri(Finet) Summerh. - Madagascar
- Microcoelia physophora(Rchb.f.) Summerh. - Kenya, Tanzania, Madagascar
- Microcoelia sanfordiiL.Jonss - Cameroon
- Microcoelia smithii(Rolfe) Summerh. - Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi
- Microcoelia stolzii(Schltr.) Summerh. - Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, Zimbabwe

Angraecinae is a subtribe in the family Orchidaceae. The subtribe consists of approximately 18 genera and about 360 species. The type genus is Angraecum. Most of the genera are endemic to Africa, Madagascar and other Indian Ocean Islands, a few genera can also be found in the Americas.
Cuviera is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae native to tropical Africa. It was originally described by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1807 and is named after the French naturalist Georges Cuvier.
Belonophora coriacea is a species of flowering plant in the family Rubiaceae. It is found in Nigeria, Central African Republic, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Congo-Brazzaville, and Congo-Kinshasa.
Craterispermum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It contains 16 species that occur in tropical Africa and Seychelles. It is the only genus in the tribe Craterispermeae, of which the divergence time is estimated at 34.8 million years ago.













