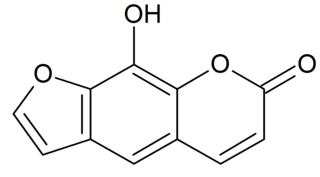Lepidoptera is an order of insects that includes butterflies and moths. About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera are described, in 126 families and 46 superfamilies, 10 percent of the total described species of living organisms. It is one of the most widespread and widely recognizable insect orders in the world. The Lepidoptera show many variations of the basic body structure that have evolved to gain advantages in lifestyle and distribution. Recent estimates suggest the order may have more species than earlier thought, and is among the four most speciose orders, along with the Hymenoptera, Diptera, and Coleoptera.

Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species.

The domestic silk moth is an insect from the moth family Bombycidae. It is the closest relative of Bombyx mandarina, the wild silk moth. The silkworm is the larva or caterpillar of a silk moth. It is an economically important insect, being a primary producer of silk. A silkworm's preferred food are white mulberry leaves, though they may eat other mulberry species and even the osage orange. Domestic silk moths are entirely dependent on humans for reproduction, as a result of millennia of selective breeding. Wild silk moths are not as commercially viable in the production of silk.

The Sphingidae are a family of moths (Lepidoptera) called sphinx moths, also colloquially known as hawk moths, with many of their caterpillars known as “hornworms”; it includes about 1,450 species. It is best represented in the tropics, but species are found in every region. They are moderate to large in size and are distinguished among moths for their agile and sustained flying ability, similar enough to that of hummingbirds as to be reliably mistaken for them. Their narrow wings and streamlined abdomens are adaptations for rapid flight. The family was named by French zoologist Pierre André Latreille in 1802.

A pupa is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in their life cycle, the stages thereof being egg, larva, pupa, and imago. The processes of entering and completing the pupal stage are controlled by the insect's hormones, especially juvenile hormone, prothoracicotropic hormone, and ecdysone. The act of becoming a pupa is called pupation, and the act of emerging from the pupal case is called eclosion or emergence.

The Arctiinae are a large and diverse subfamily of moths with around 11,000 species found all over the world, including 6,000 neotropical species. This subfamily includes the groups commonly known as tiger moths, which usually have bright colours, footmen, which are usually much drabber, lichen moths, and wasp moths. Many species have "hairy" caterpillars that are popularly known as woolly bears or woolly worms. The scientific name Arctiinae refers to this hairiness. Some species within the Arctiinae have the word "tussock"' in their common names because they have been misidentified as members of the Lymantriinae subfamily based on the characteristics of the larvae.

The de Havilland DH.82 Tiger Moth is a 1930s British biplane designed by Geoffrey de Havilland and built by the de Havilland Aircraft Company. It was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and other operators as a primary trainer aircraft. In addition to the type's principal use for ab initio training, the Second World War had RAF Tiger Moths operating in other capacities, including maritime surveillance and defensive anti-invasion preparations; some aircraft were even outfitted to function as armed light bombers.

The Tortricidae are a family of moths, commonly known as tortrix moths or leafroller moths, in the order Lepidoptera. This large family has over 11,000 species described, and is the sole member of the superfamily Tortricoidea, although the genus Heliocosma is sometimes placed within this superfamily. Many of these are economically important pests. Olethreutidae is a junior synonym. The typical resting posture is with the wings folded back, producing a rather rounded profile.

The Crambidae are the grass moth family of lepidopterans. They are variable in appearance, the nominal subfamily Crambinae taking up closely folded postures on grass stems where they are inconspicuous, while other subfamilies include brightly coloured and patterned insects which rest in wing-spread attitudes.

The Pyralidae, commonly called pyralid moths, snout moths or grass moths, are a family of Lepidoptera in the ditrysian superfamily Pyraloidea. In many classifications, the grass moths (Crambidae) are included in the Pyralidae as a subfamily, making the combined group one of the largest families in the Lepidoptera. The latest review by Eugene G. Munroe and Maria Alma Solis retain the Crambidae as a full family of Pyraloidea.
A carminative, also known as carminativum, is a herb or preparation intended to either prevent formation of gas in the gastrointestinal tract or facilitate the expulsion of said gas, thereby combatting flatulence.
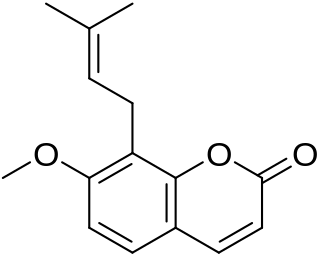
Osthol, or osthole, is a chemical compound which is a derivative of coumarin. It is found in a variety of plants including Cnidium monnieri, Angelica archangelica and Angelica pubescens.

The Botanischer Garten der Universität Karlsruhe is a botanical garden maintained by the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology directorate of Peter Nick. It is located at Am Fasanengarten 2, Karlsruhe, Baden-Württemberg, Germany, and is open weekdays and Sundays; admission is free.

Cnidium cnidiifolium is a species of flowering plant in the parsley family, Apiaceae. Its common names include northern hemlock-parsley and Jakutsk snowparsley, after the Russian town Jakutsk. It is native to Russia, Alaska, and the Northwest Territories, Yukon, and British Columbia in Canada.

The Erebidae are a family of moths in the superfamily Noctuoidea. The family is among the largest families of moths by species count and contains a wide variety of well-known macromoth groups. The family includes the underwings (Catocala); litter moths (Herminiinae); tiger, lichen, and wasp moths (Arctiinae); tussock moths (Lymantriinae), including the arctic woolly bear moth ; piercing moths ; micronoctuoid moths (Micronoctuini); snout moths (Hypeninae); and zales, though many of these common names can also refer to moths outside the Erebidae. Some of the erebid moths are called owlets.
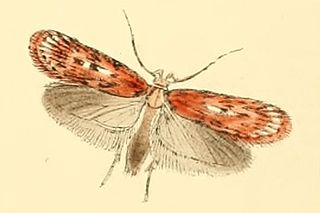
Depressaria pulcherrimella is a moth of the family Depressariidae. It is found in most of Europe, except the Balkan Peninsula.
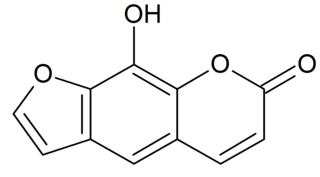
Xanthotoxol is a furanocoumarin. It is one of the major active ingredients in Cnidium monnieri.
Cnidium monnieri (L.) Cusson ex Juss., Monnier's snowparsley, is a flowering plant species in the genus Cnidium. Also known as Shechuangzi, Osthole, Jashoshi, Cnidii Fructus . It may be confused with Bacopa monnieri, Ligusticum officinale, both similar but different plants. The coumarins osthol, imperatorin and xanthotoxol can be found in C. monnieri.
Lozotaenia cupidinana is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in France, Portugal, Spain and Italy.

Kadenia dubia is a species of flowering plant belonging to the family Apiaceae.