
Ammophila arenaria is a species of grass in the family Poaceae. It is known by the common names marram grass and European beachgrass. It is one of two species of the genus Ammophila. It is native to the coastlines of Europe and North Africa where it grows in the sands of beach dunes. It is a perennial grass forming stiff, hardy clumps of erect stems up to 1.2 metres (3.9 ft) in height. It grows from a network of thick rhizomes which give it a sturdy anchor in its sand substrate and allow it to spread upward as sand accumulates. These rhizomes can grow laterally by 2 metres in six months. One clump can produce 100 new shoots annually.

Eudonia philerga is a species of moth of the family Crambidae. This species was first described by Edward Meyrick. It is endemic to New Zealand, found throughout the country, and regarded as common. Larvae feed on moss. Adult moths have been observed on the wing more frequently from October to April, and are attracted to light.

Kupea is a monotypic moth genus of the family Crambidae described by Alfred Philpott in 1930. It contains only one species, Kupea electilis, also known as Kupe's grassmoth, which is endemic to New Zealand. This species has only been recorded at Kaitorete Spit. The larvae feed on Zoysia minima and exist in a cocoon constructed of silk and sand. Adults are on the wing from March to April. It has been hypothesised that the adults are active at twilight. It is classified as Nationally Vulnerable by the Department of Conservation. The female of the species was first discovered in 2012.

Philocryptica is a monotypic genus of moths belonging to the subfamily Tortricinae of the family Tortricidae. It contains only one species, Philocryptica polypodii, the leather-leaf star-miner, which is endemic to New Zealand. This species has been recorded in both the North Island and the South Island, as far south as Banks Peninsula. The preferred habitat of this species is native forest where the species' larval host is present. The larvae feed on Pyrrosia eleagnifolia, mining the host plant leaves. P. polypodii pupates within the final blotch-mine. Adults are on the wing in November and December.

Metacrias huttoni is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. This species is endemic to New Zealand where it is known from the eastern areas of the South Island. The female of the species is flightless and buff coloured where as the male is brightly coloured and flies during the day.

Pterophorus monospilalis, the white plume moth, is a moth of the family Pterophoridae. It is endemic to New Zealand and occurs throughout the country. It inhabits native forest, parks and domestic gardens. Larvae are active during the day, are slow moving, and feed exposed. They feed on Araliaceae species as well as on Hedera helix, Meryta sinclairii, and Schefflera digitata. There are several broods in a year. Adult moths are on the wing from November until May and are attracted to light.

Chalastra ochrea is a moth of the family Geometridae. It is endemic to New Zealand. It has been observed in both the North and South Islands and inhabits native forest. Larvae of C. ochrea feed on the leaves of species in the genus Sophora including Sophora chathamica. Adults are on the wing from February until April. They have been collected via sugar traps.

Epiphryne undosata, also known as the lacebark looper, is a moth of the family Geometridae. It is endemic to New Zealand and is found on both the North and South Islands. It inhabits native forest. The larvae feed on plant species in the genera Hoheria and Plagianthus. They pupate amongst dead leaves in a silk cocoon. The adult moths have been observed on the wing all year round but are most commonly seen from November until February. The adult moths are extremely variable in both their colour intensity and wing pattern.

Ichneutica steropastis, or the flax notcher moth, is a species of moth in the family Noctuidae. It is endemic to New Zealand and can be found throughout the country from the Three Kings Islands to Stewart Island as well as in the Chatham Islands. The larvae of this species feed on a variety of native and introduced plants however the New Zealand flax is one of the more well known host plants for the larvae of this moth. The larvae are nocturnal, hiding away in the base of the plants and coming out to feed at night. They create a distinctive notch in the leaf when they feed. The adults of this species are on the wing from October to March. Although adult specimens of I. steropastis are relatively easy to recognise they might possibly be confused with I. inscripta, I. theobroma or with darker forms of I. arotis. However I. steropastis can be distinguished as it has a long dark basal forewing streak that these three species lack.

Hierodoris atychioides is a moth of the family Oecophoridae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1877. The female holotype specimen held at the Natural History Museum, London. This species is endemic to New Zealand, and can be found in the North, South and Stewart Islands. The larvae form webs of silk attached to frass and leaves on their hosts in which they shelter, often in the company of other larvae in their species. Their feeding habits have not been observed in detail but Hoare hypothesises the larvae may feed on dead or dying leaves. The larvae feed on a wide range of trees and shrubs, including Dacrydium cupressinum, Prumnopitys taxifolia, Dacrycarpus dacrydioides, Libocedrus bidwillii, Cupressus macrocarpa, Leptospermum scoparium, Kunzea ericoides, Ozothamnus leptophyllus, Abies, Picea, Pinus and Thuja species. Although they are regarded as a pest of exotic forests in New Zealand, the economic damage the larvae cause is minimal and they tend to be controlled only by their natural enemies. Larval enemies include the parasitic flies Trigonospila brevifacies and Pales funesta as well as parasitic wasps including Xanthopimpla rhopaloceros. The adult moths are day flying and are most common during the months of December and January. This species is variable in appearance as larvae, pupa and as adults, and it has been hypothesised that it is in the process of speciation.
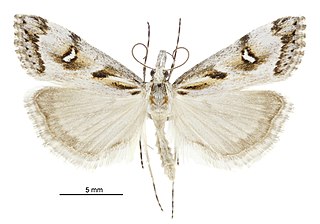
Gadira leucophthalma, the beaked moss moth, is a moth in the family Crambidae. It is endemic to New Zealand. It is found in the south eastern side of the South Island down to Banks Peninsula. G. leucophthalma inhabits the foredunes of coastal areas. The larval host is unknown but it has been hypothesised that the larvae feed on moss. The adult moths are day flying although some specimens have been trapped at night via light traps. Adults are commonly on the wing from March to April. This species has been classified as Nationally Vulnerable by the Department of Conservation.
Kiwaia jeanae, also known as the Kaitorete jumper or mat daisy jumper, is a species of moth in the family Gelechiidae. It is endemic to New Zealand. This species is classified as "At Risk, Naturally Uncommon" by the Department of Conservation. Both the males and females of this species are brachypterous.

Helastia siris is a moth of the family Geometridae. This species is endemic to New Zealand and is found in the Wellington region as well as on Stephens and the Chatham Islands. It is classified as "At Risk, Relict'" by the Department of Conservation. H. siris inhabits coastal tussock grassland. Little is known of the biology of this species. Adults have been observed on the wing in March and September. Adults are nocturnal and are attracted to light.

Euxoa ceropachoides, commonly known as Fereday's cutworm, is a species of moth in the family Noctuidae. It is endemic to New Zealand. It is classified as Not Threatened by the Department of Conservation.

Ichneutica ceraunias is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is endemic to New Zealand. This species is found from the central North Island to the bottom of the South Island. Hosts of the larvae are species of Chionochloa and Festuca. This colourful moth is variable in appearance and can be mistaken for Ichneutica dione. Adults are on the wing from October to February.

Physetica homoscia is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae. It is endemic to New Zealand and is found throughout New Zealand including in the Auckland Islands. This species inhabits places where its host plants are common and this includes costal dune habitat. It lives at a wide range of altitudes from sea-level up to at least 1750 m. The larvae of P. homoscia feed on Ozothamnus leptophyllus and Ozothamnus vauvilliersii. They are very active and drop to the ground when disturbed. Larvae are parasitised by a species of fly. This species pupates in the soil and the pupa life stage lasts for approximately 6 weeks. The adult moths are on the wing from September to June and are attracted to light. The adults of P. homoscia might possibly be confused with Ichneutica moderata however this latter species lacks the small white dots on the forewing veins of P. homoscia. Adults might also be confused with P. temperata but P. homoscia is significantly larger in size.

Xanthorhoe occulta is a species of moth in the family Geometridae. It is endemic to New Zealand and was first described by Alfred Philpott in 1903. It is found in the North, South and Stewart Islands. The adult moths are on the wing from

Pseudocoremia lupinata is a species of moth in the family Geometridae. It is endemic to New Zealand and can be found in both the North and South Islands. The favoured habitat of this species is Kānuka scrubland as its larval hosts are species in the genus Kunzea. Both the larvae and adults of this species are nocturnal. Adult moths are commonly on the wing from December to June and are attracted to light.

Atomotricha chloronota is a moth in the family Oecophoridae first described by Edward Meyrick in 1914. It is endemic to New Zealand and is found in the eastern side of the South Island and at the Antipodes Islands. It inhabits clearings with native tussocks and ferns. The larvae feed on leaf litter from silk tunnels in soil. The male adults of this species are on the wing from July to September and have been trapped via sugar traps and are attracted to light. The female of this species is brachypterous.

Chrysorthenches porphyritis is a species of moth of the family Plutellidae. It was first described by Edward Meyrick in 1885 and is endemic to New Zealand. This species can be found on both the North and South Islands in open native forest and scrub at altitudes from sea level up to 1370 m. The larvae feed on Podocarpus laetus, P. totara, P. nivalis, and Phyllocladus alpinus. The larvae create a shelter by loosely spinning together the leaves of its host plant and can be found feeding in groups. The pupa is formed inside a thin cocoon. Hudson was of the opinion that this species had two broods a year. Adult moths are on the wing all year round. The adults of this species, particularly the female, are variable in colouration and in forewing pattern.






















