Abdulaziz ibn Abdul Rahman ibn Faisal ibn Turki ibn Abdullah ibn Muhammad Al Saud, usually known within the Arab world as Abdulaziz and in the West as Ibn Saud, was the first monarch and founder of Saudi Arabia, the "third Saudi state".

Diriyah, formerly romanized as Dereyeh and Dariyya, is a town in Saudi Arabia located on the north-western outskirts of the Saudi capital, Riyadh. Diriyah was the original home of the Saudi royal family, and served as the capital of the Emirate of Diriyah under the first Saudi dynasty from 1744 to 1818. Today, the town is the seat of the Diriyah Governorate, which also includes the villages of Uyayna, Jubayla, and Al-Ammariyyah, among others, and is part of Ar Riyad Province.

Juhayman ibn Muhammad ibn Sayf al-Otaybi was a Saudi militant and former Saudi Arabian soldier who in 1979 led the Grand Mosque seizure of the Masjid al Haram in Mecca, Islam's holiest site, to protest against the Saudi monarchy and the House of Saud.
The Banu Bakr bin Wa'il or simply Banu Bakr were an Arabian tribe belonging to the large Rabi'ah branch of Adnanite tribes, which also included Abdul Qays, Anazzah, Taghlib, Banu Shayban and Bani Hanifa. The tribe is reputed to have engaged in a 40-year war before Islam with its cousins from Taghlib, known as the War of Basous. The pre-Islamic poet, Tarafah was a member of Bakr.
Almutairi is one of the largest predominantly Sunni Arab tribes in the Arabian Peninsula, especially Saudi Arabia and Kuwait.

Banu Yam are a large tribe native to Najran Province in Saudi Arabia and the principal tribe of that area. They belong to the Qahtanite branch of Arabian tribes, specifically the group known as Banu Hamdan, and are, therefore, native to southwestern Arabia.
Banu Hanifa were an ancient Arab tribe inhabiting the area of al-Yamama in the central region of modern-day Saudi Arabia. The tribe belonged to the great Rabi'ah branch of North Arabian tribes, which also included Abdul Qays, Bakr, and Taghlib. Though counted by the classical Arab genealogists as a Christian branch of Bani Bakr, they led an independent existence prior to Islam.

Anazzah is an Arab tribe in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, and the Levant.
Al-Ajman or al-'Ijman العجمي is an Arabian tribal confederation in Mid-Eastern Arabian Peninsula, with members spread across Saudi Arabia, Qatar, U.A.E. and the Kuwait.

Faisal bin Sultan al-Duwaish was a Prince of the Mutair tribe and one of the Ikhwan leaders, who assisted Ibn Saud in the unification of Saudi Arabia.

The unification of Saudi Arabia was a military and political campaign, by which the various tribes, sheikhdoms, city-states, emirates, and kingdoms of most of the Arabian Peninsula were conquered by the House of Saud, or Al Saud, between 1902 and 1932, when the modern-day Kingdom of Saudi Arabia was proclaimed under the leadership of Ibn Saud, creating what is sometimes referred to as the Third Saudi State, to differentiate it from the Emirate of Diriyah, the First Saudi State and the Emirate of Nejd, the Second Saudi State, also House of Saud states.
Al-Mutairi or Almutairi or Mutairi s a powerful Arabic tribe in the Arabian Peninsula and prominent in the Middle East.
The Ghamd is an Arab tribe and one of the largest tribes of Azd tribe in Hejaz Region.

The Ikhwan Revolt began in 1927, when the tribesmen of the Otaibah and Mutayr and Ajman rebelled against the authority of Ibn Saud and engaged in cross-border raids into parts of Trans-Jordan, Mandatory Iraq and the Emirate of Kuwait. The relationship between the House of Saud and the Ikhwan deteriorated into an open bloody feud in December 1928. The main instigators of the rebellion were defeated in the Battle of Sabilla, on 29 March 1929. Ikhwan tribesmen and troops loyal to Abd al-Aziz Ibn Saud clashed again in the Jabal Shammar region in August 1929, and Ikhwan tribesmen attacked the Awazim tribe on 5 October 1929. Faisal al-Dawish, the main leader of the rebellion and the Mutair tribe, fled to Kuwait in October 1929 before being detained by the British and handed over to Ibn Saud. Faisal Al-Dawish would die in Riyadh on 3 October 1931 from what appears to have been a heart condition. Government troops had finally suppressed the rebellion on 10 January 1930, when other Ikhwan rebel leaders surrendered to the British. In the aftermath, the Ikhwan leadership was slain, and the remains were eventually incorporated into regular Saudi units. Sultan bin Bajad, one of the three main Ikhwan leaders, was killed in 1931, while al-Dawish died in prison in Riyadh on 3 October 1931.
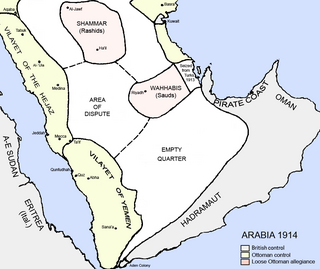
The Ottoman era in the history of Arabia lasted from 1517 to 1918. Ottoman degree of control over these lands varied over the four centuries with the fluctuating strength or weakness of the Empire's central authority.
Muhammad ibn Saud, also known as Ibn Saud, was the emir of Ad-Diriyyah and is considered the founder of the First Saudi State and the Saud dynasty, which are technically named for his father – Saud ibn Muhammad ibn Muqrin. Ibn Saud's family traced its descent to the tribe of Banu Audi and Hanifa tribes but, despite popular misconceptions, Muhammad ibn Saud was neither a nomadic bedouin nor was he a tribal leader. Rather, he was the chief (emir) of an agricultural settlement near modern-day Riyadh, called Diriyah. Furthermore, he was a competent and ambitious desert warrior.

Not to be confused with the Qahtanite peoples