
Edward Lewis "Bob" Bartlett, was an American politician and a member of the Democratic Party. He served as a U.S. Senator. A key fighter for Alaska statehood, Bartlett served as the Secretary of Alaska Territory from 1939 to 1945, in Congress from 1945 to 1959 as a Delegate, and from 1959 until his death in 1968 as a U.S. senator. He was opposed to U.S. involvement in Vietnam, along with his fellow Senator Ernest Gruening, and also worked to warn people about the dangers of radiation. Many acts bear his name, including a major law known as the Bartlett Act, mandating handicap access in all federally-funded buildings.

The 1936 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 75th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 3, 1936, while Maine held theirs on September 14. They coincided with President Franklin D. Roosevelt's landslide re-election. Roosevelt's Democratic Party gained twelve net seats from the Republican Party, bringing them above a three-fourths majority. This was the largest majority since Reconstruction, as the last time a party won so decisively was in 1866. To date, this was the last time that any party held three-quarters of all House seats, as well as the last time that a party won more than 300 House seats.

The 1932 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 73rd United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 8, 1932, while Maine held theirs on September 12. They coincided with the landslide election of President Franklin D. Roosevelt.

1916 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 65th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 7, 1916, while Maine held theirs on September 11. They coincided with the re-election of President Woodrow Wilson.
The 1910 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 8, 1910, while Maine and Vermont held theirs early in September, in the middle of President William Howard Taft's term. Elections were held for all 391 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 46 states, to the 62nd United States Congress.
The 1908 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 3, 1908, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the 1908 United States presidential election, which William Howard Taft won. Elections were held for all 391 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 46 states, to serve in the 61st United States Congress.
The 1906 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 6, 1906, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They occurred in the middle of President Theodore Roosevelt's second term. Elections were held for 386 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 60th United States Congress.
The 1902 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 4, 1902, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They occurred in the middle of President Theodore Roosevelt's first term, about a year after the assassination of William McKinley in September 1901. Elections were held for 386 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 58th United States Congress.

The 1882 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 7, 1882, with five states holding theirs early between June and October. They occurred during President Chester A. Arthur's term. Elections were held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 48th United States Congress. They were the first elections after reapportionment following the 1880 United States census, increasing the size of the House. Special elections were also held throughout the year.
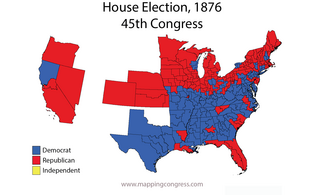
The 1876–77 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 5, 1876, and March 13, 1877. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 45th United States Congress convened on October 15, 1877. The size of the House increased to 293 seats with the addition of the new state of Colorado.

The 1868–69 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 1, 1868, to August 2, 1869. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 41st United States Congress convened on March 4, 1869. They coincided with the 1868 United States presidential election, which was won by Ulysses S. Grant. Elections were held for all 243 seats, representing 37 states. All of the former Confederate states were represented in Congress for the first time since they seceded from the Union.

The 1864–65 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 5, 1864, and November 7, 1865, in the midst of the American Civil War and President Abraham Lincoln's reelection. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. Members were elected before the first session of the 39th United States Congress convened on December 4, 1865, including the at-large seat from the new state of Nevada, and the 8 from Tennessee, the first secessionist state to be readmitted. The other 10 secessionist states had not yet been readmitted, and therefore were not seated.

The 1854–55 United States House of Representatives elections were held in 31 states for all 234 seats between August 4, 1854, and November 6, 1855, during President Franklin Pierce's term. Each state legislature separately set a date to elect representatives to the House of Representatives before the 34th Congress convened its first session on December 3, 1855.

The 1846–47 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 2, 1846, and November 2, 1847. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. 228 elected members representing 29 states took their seats when the first session of the 30th United States Congress convened December 6, 1847. The new states of Iowa and Texas elected their first representatives during this election cycle. These elections were held during President James K. Polk's term.

The 1830–31 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 5, 1830, and October 3, 1831. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 22nd United States Congress convened on December 5, 1831. Elections were held for all 213 seats, representing 24 states.

In 1798, the Northwest Territory became eligible to send a non-voting delegate to the U.S. Congress. The Assembly elected this representative.
The Oklahoma Territory's at-large congressional district is a defunct congressional district that was created by the Organic Act of 1890 and ended with Oklahoma statehood. One delegate was to be sent to the U.S. House of Representatives from Oklahoma Territory.

Hawaii Territory's at-large congressional district was the congressional district for the Territory of Hawaii, which was established by the Newlands Resolution of 1898.

The 1958 United States Senate elections in Alaska were held November 25, 1958. The elections were held in anticipation of Alaska's admission as the forty-ninth state in the union, effective January 3, 1959. The state held two simultaneous elections to determine their first senators.
There were four special elections to the United States House of Representatives in 1919, during the 65th United States Congress and 66th United States Congress.






















