
Alexander Emmanuel Rodolphe Agassiz, son of Louis Agassiz and stepson of Elizabeth Cabot Agassiz, was an American scientist and engineer.
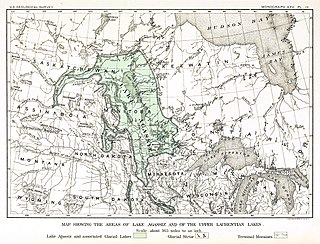
Lake Agassiz was a large proglacial lake that existed in central North America during the late Pleistocene, fed by meltwater from the retreating Laurentide Ice Sheet at the end of the last glacial period. At its peak, the lake's area was larger than all of the modern Great Lakes combined. It eventually drained into what is now Hudson Bay, leaving behind Lake Winnipeg, Lake Winnipegosis, Lake Manitoba, and Lake of the Woods.

The Hexanchiformes are a primitive order of sharks, numbering just seven extant species in two families. Fossil sharks that were apparently very similar to modern sevengill species are known from Jurassic specimens.

The Lamniformes are an order of sharks commonly known as mackerel sharks. It includes some of the most familiar species of sharks, such as the great white as well as less familiar ones, such as the goblin shark and megamouth shark.

The beardfishes consist of a single extant genus, Polymixia, of deep-sea marine ray-finned fish named for their pair of long hyoid barbels. They are classified in their own order Polymixiiformes. But as Nelson says, "few groups have been shifted back and forth as frequently as this one, and they were recently added to Paracanthoptergii". For instance, they have previously been classified as belonging to the Beryciformes, and are presently considered either paracanthopterygians or the sister group to acanthopterygians. They are of little economic importance.

Carcharodon is a genus of sharks within the family Lamnidae, colloquially called the "white sharks." The only extant member is the great white shark. The extant species was preceded by a number of fossil (extinct) species including C. hubbelli and C. hastalis. The first appearance of the genus may have been as early as the Early Miocene or Late Oligocene. Carcharocles megalodon is still argued by some paleontologists to be a close relative of Carcharodon carcharias - as well as being in the same genus. The megalodon's scientific name was originally "Carcharodon" megalodon, but more recently, the giant shark has been assigned by most scientists to either the genus Carcharocles or Otodus.
Highway 7, known for most of its length as the Lougheed Highway and Broadway, is an alternative route to Highway 1 through the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. Whereas the controlled-access Highway 1 follows the southern bank of the Fraser River, Highway 7 follows the northern bank.

Louis Agassiz Fuertes was an American ornithologist, illustrator and artist who set the rigorous and current-day standards for ornithological art and naturalist depiction and is considered one of the most prolific American bird artists, second only to his guiding professional predecessor John James Audubon.

Alpheus Hyatt was an American zoologist and palaeontologist.

Isurus is a genus of mackerel sharks in the family Lamnidae, commonly known as the mako sharks. They are largely pelagic, and are fast, predatory fish capable of swimming at speeds of up to 50 km/h (31 mph).

Belonostomus is a genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish that was described by Louis Agassiz in 1844. It is a member of the order Aspidorhynchiformes, a group of fish known for their distinctive elongated rostrums.

Amblypterus is an extinct genus of freshwater ray-finned fish that lived during the Gzhelian and Cisuralian epoch in what is now Europe and possibly India and Argentina. Potential indeterminate records stretch as far back as the early Carboniferous.

Elophila is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae described by Jacob Hübner in 1822.

Alatinidae is a family of box jellyfish within class Cubozoa, containing the following genera and species:

Palaeoniscidae is an extinct family of "palaeoniscoid" ray-finned fishes (Actinopterygii). The family includes the genus Palaeoniscum and potentially other Palaeozoic and Mesozoic early actinopterygian genera. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek words παλαιός and ὀνίσκος.

Ectopleura is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Tubulariidae.

The Bridger Formation is a geologic formation in southwestern Wyoming. It preserves fossils dating back to the Bridgerian and Uintan stages of the Paleogene Period. The formation was named by American geologist Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden for Fort Bridger, which had itself been named for mountain man Jim Bridger. The Bridger Wilderness covers much of the Bridger Formation's area.

Alatina is a genus of box jellyfish within class Cubozoa. It is the largest of the three known genera in the family Alatinidae, and the only one which is not monotypic. It contains the following ten species:

Cladodus is an extinct genus of cartilaginous fishes in the family Ctenacanthidae. As the name implies, they are a type of cladodont, primitive sharks with teeth designed to snag fish and swallow them whole, instead of sawing off chunks to swallow.

Amblypneustes is a genus of sea urchins, belonging to the family Temnopleuridae.



















