4-trimethylaminobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH9A1 gene. [5] [6] [7]
4-trimethylaminobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH9A1 gene. [5] [6] [7]
This protein belongs to the aldehyde dehydrogenase family of proteins. It has a high activity for oxidation of gamma-aminobutyraldehyde (GABAL) and other amino aldehydes. The enzyme catalyzes the dehydrogenation of GABAL to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). This isozyme is a tetramer of identical 54-kD subunits. [7]

Acetaldehyde dehydrogenases are dehydrogenase enzymes which catalyze the conversion of acetaldehyde into acetyl-CoA. This can be summarized as follows:

Pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase catalytic subunit 1, also known as protein phosphatase 2C, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDP1 gene. PDPC 1 is an enzyme which serves to reverse the effects of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase upon pyruvate dehydrogenase, activating pyruvate dehydrogenase.

Alcohol dehydrogenase 1B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADH1B gene.

Alcohol dehydrogenase 1C is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADH1C gene.

17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 (17β-HSD1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HSD17B1 gene. This enzyme oxidizes or reduces the C17 hydroxy/keto group of androgens and estrogens and hence is able to regulate the potency of these sex steroids

HSD3B1 is a human gene that encodes for a 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta(5)-delta(4)isomerase type I or hydroxy-delta-5-steroid dehydrogenase, 3 beta- and steroid delta-isomerase 1. While it can carry out the same function as HSD3B2, it localizes primarily to different tissues, such as the placenta and nonsteroidogenic tissues. Its requirement for the production of progesterone by the placenta, which has a vital role in pregnancy, may be one reason why no disease based on mutations in this gene has been identified to date, besides prostate cancer.

Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 (AKR1C3), also known as 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5 or 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 (3α-HSD2) is a steroidogenic enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKR1C3 gene.

17-β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase X (HSD10) also known as 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase type-2 is a mitochondrial enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HSD17B10 gene. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified, but the full-length nature of only two transcript variants has been determined. Human HSD10 cDNA was cloned from the brain (NM_004493), and the resulting protein, a homotetramer, was first characterized as a short chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SCHAD). Active sites of this enzyme can accommodate different substrates; 17β-HSD10 is involved in the oxidation of isoleucine, branched-chain fatty acids, and xenobiotics as well as the metabolism of sex hormones and neuroactive steroids.

Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C1 also known as 20α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, and dihydrodiol dehydrogenase 1/2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKR1C1 gene.

Alcohol dehydrogenase [NADP+] also known as aldehyde reductase or aldo-keto reductase family 1 member A1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKR1A1 gene. AKR1A1 belongs to the aldo-keto reductase (AKR) superfamily. It catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of a variety of aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes to their corresponding alcohols and catalyzes the reduction of mevaldate to mevalonic acid and of glyceraldehyde to glycerol. Mutations in the AKR1A1 gene has been found associated with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.

Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C4, also known as 3α-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (3α-HSD1), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKR1C4 gene. It is known to be necessary for the synthesis of the endogenous neurosteroids allopregnanolone, tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone, and 3α-androstanediol. It is also known to catalyze the reversible conversion of 3α-androstanediol (5α-androstane-3α,17β-diol) to dihydrotestosterone and vice versa.

Alcohol dehydrogenase 1A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADH1A gene.

Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit alpha, mitochondrial (IDH3α) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the IDH3A gene.

Succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH5A1 gene.

Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit gamma, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the IDH3G gene.

Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit beta, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the IDH3B gene.
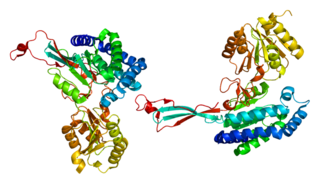
Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase (P5CS) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH18A1 gene. This gene is a member of the aldehyde dehydrogenase family and encodes a bifunctional ATP- and NADPH-dependent mitochondrial enzyme with both gamma-glutamyl kinase and gamma-glutamyl phosphate reductase activities. The encoded protein catalyzes the reduction of glutamate to delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate, a critical step in the de novo biosynthesis of proline, ornithine and arginine. Mutations in this gene lead to hyperammonemia, hypoornithinemia, hypocitrullinemia, hypoargininemia and hypoprolinemia and may be associated with neurodegeneration, cataracts and connective tissue diseases. Alternatively spliced transcript variants, encoding different isoforms, have been described for this gene. As reported by Bruno Reversade and colleagues, ALDH18A1 deficiency or dominant-negative mutations in P5CS in humans causes a progeroid disease known as De Barsy Syndrome.

D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BDH1 gene.

Methylmalonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase [acylating], mitochondrial (MMSDH) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH6A1 gene.
Carnitine biosynthesis is a method for the endogenous production of L-carnitine, a molecule that is essential for energy metabolism. In humans and many other animals, L-carnitine is obtained from both diet and by biosynthesis. The carnitine biosynthesis pathway is highly conserved among many eukaryotes and some prokaryotes.