
Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. It is used by plants to make cellulose, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world, for use in cell walls, and by all living organisms to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used by the cell as energy.
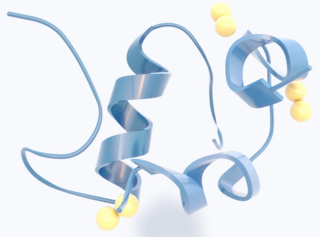
Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (INS) gene. It is the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat, and skeletal muscles. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen, via glycogenesis, or fats (triglycerides), via lipogenesis; in the liver, glucose is converted into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver are strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is thus an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules in the cells. Low insulin in the blood has the opposite effect, promoting widespread catabolism, especially of reserve body fat.
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cells in insulin-sensitive tissues in the body fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin or downregulate insulin receptors in response to hyperinsulinemia.

Beta cells (β-cells) are specialized endocrine cells located within the pancreatic islets of Langerhans responsible for the production and release of insulin and amylin. Constituting ~50–70% of cells in human islets, beta cells play a vital role in maintaining blood glucose levels. Problems with beta cells can lead to disorders such as diabetes.

Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue and unexplained weight loss. Other symptoms include increased hunger, having a sensation of pins and needles, and sores (wounds) that heal slowly. Symptoms often develop slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, stroke, diabetic retinopathy, which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the lower-limbs, which may lead to amputations. The sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon.
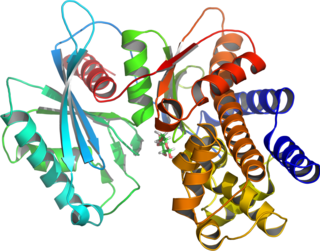
Glucokinase is an enzyme that facilitates phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. Glucokinase occurs in cells in the liver and pancreas of humans and most other vertebrates. In each of these organs it plays an important role in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism by acting as a glucose sensor, triggering shifts in metabolism or cell function in response to rising or falling levels of glucose, such as occur after a meal or when fasting. Mutations of the gene for this enzyme can cause unusual forms of diabetes or hypoglycemia.

Allantoin is a chemical compound with formula C4H6N4O3. It is also called 5-ureidohydantoin or glyoxyldiureide. It is a diureide of glyoxylic acid. Allantoin is a major metabolic intermediate in most organisms including animals, plants and bacteria, though not humans. It is produced from uric acid, which itself is a degradation product of nucleic acids, by action of urate oxidase (uricase). Allantoin also occurs as a natural mineral compound (IMA symbol Aan).

Amylin, or islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), is a 37-residue peptide hormone. It is co-secreted with insulin from the pancreatic β-cells in the ratio of approximately 100:1 (insulin:amylin). Amylin plays a role in glycemic regulation by slowing gastric emptying and promoting satiety, thereby preventing post-prandial spikes in blood glucose levels.
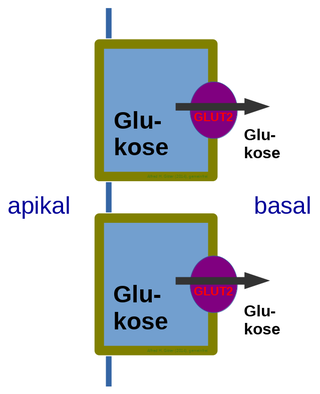
Glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) also known as solute carrier family 2, member 2 (SLC2A2) is a transmembrane carrier protein that enables protein facilitated glucose movement across cell membranes. It is the principal transporter for transfer of glucose between liver and blood Unlike GLUT4, it does not rely on insulin for facilitated diffusion.
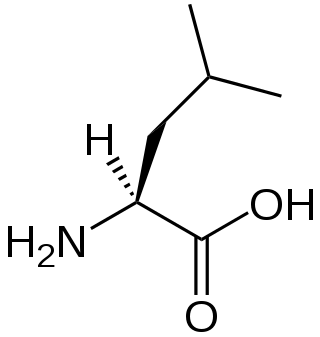
A branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) is an amino acid having an aliphatic side-chain with a branch. Among the proteinogenic amino acids, there are three BCAAs: leucine, isoleucine, and valine. Non-proteinogenic BCAAs include 2-aminoisobutyric acid and alloisoleucine.

Streptozotocin or streptozocin (STZ) is a naturally occurring alkylating antineoplastic agent that is particularly toxic to the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas in mammals. It is used in medicine for treating certain cancers of the islets of Langerhans and used in medical research to produce an animal model for hyperglycemia and Alzheimer's in a large dose, as well as type 2 diabetes or type 1 diabetes with multiple low doses.

Glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4), also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 4, is a protein encoded, in humans, by the SLC2A4 gene. GLUT4 is the insulin-regulated glucose transporter found primarily in adipose tissues and striated muscle. GLUT4 is distinctive because it is predominantly stored within intracellular vesicles, highlighting the importance of its trafficking and regulation as a central area of research. The first evidence for this glucose transport protein was provided by David James in 1988. The gene that encodes GLUT4 was cloned and mapped in 1989.

Biguanide is the organic compound with the formula HN(C(NH)NH2)2. It is a colorless solid that dissolves in water to give a highly basic solution. These solutions slowly hydrolyse to ammonia and urea.

MODY 1 or HNF4A-MODY is a form of maturity onset diabetes of the young.
The insulin transduction pathway is a biochemical pathway by which insulin increases the uptake of glucose into fat and muscle cells and reduces the synthesis of glucose in the liver and hence is involved in maintaining glucose homeostasis. This pathway is also influenced by fed versus fasting states, stress levels, and a variety of other hormones.
Mladen Vranic, MD, DSc, O.C., O.Ont, FRSC, FRCP(C), FCAHS, Canadian Medical Hall of Fame[CMHF] April 3, 1930 – June 18, 2019, was a Croatian-born diabetes researcher, best known for his work in tracer methodology, exercise and stress in diabetes, the metabolic effects of hormonal interactions, glucagon physiology, extrapancreatic glucagon, the role of the direct and indirect metabolic effects of insulin and the prevention of hypoglycemia. Vranic was recognized by a number of national and international awards for his research contributions, mentoring and administration including the Orders of Canada (Officer) and Ontario.

2-NBDG is a fluorescent tracer used for monitoring glucose uptake into living cells; it consists of a glucosamine molecule substituted with a 7-nitrobenzofurazan fluorophore at its amine group. It is widely referred to a fluorescent derivative of glucose, and it is used in cell biology to visualize uptake of glucose by cells. Cells that have taken up the compound fluoresce green.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a type of metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia. It is caused by either defected insulin secretion or damaged biological function, or both. The high-level blood glucose for a long time will lead to dysfunction of a variety of tissues.

Luigi Valentino Brugnatelli was an Italian chemist and inventor who discovered the process for electroplating in 1805.

Glysobuzole is an oral antidiabetic drug, it is taken once daily by oral administration and it is water soluble to become pharmaceutically active within the gastrointestinal tract. It is a sulfonamide derivative that is similar to sulfonylureas. Glysobuzole has antihyperglycemic activity, so it is able to lower blood glucose levels by increasing the release of insulin from the pancreatic beta cells. Glysobuzole functions as a modulator in metabolic processes involving insulin and therefore it is used to treat diabetes.



















