
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era during the Phanerozoic eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at 419.2 million years ago (Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding Carboniferous period at 358.9 Ma. It is named after Devon, South West England, where rocks from this period were first studied.

The Silurian is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at 443.8 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, 419.2 Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out.

Placodermi is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches.

Alfisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy. Alfisols form in semi-arid to humid areas, typically under a hardwood forest cover. They have a clay-enriched subsoil and relatively high native fertility. "Alf" refers to aluminium (Al) and iron (Fe). Because of their productivity and abundance, Alfisols represent one of the more important soil orders for food and fiber production. They are widely used both in agriculture and forestry, and are generally easier to keep fertile than other humid-climate soils, though those in Australia and Africa are still very deficient in nitrogen and available phosphorus. Those in monsoonal tropical regions, however, have a tendency to acidify when heavily cultivated, especially when nitrogenous fertilizers are used.

Pterygotus is a genus of giant predatory eurypterid, a group of extinct aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Pterygotus have been discovered in deposits ranging in age from Middle Silurian to Late Devonian, and have been referred to several different species. Fossils have been recovered from four continents; Australia, Europe, North America and South America, which indicates that Pterygotus might have had a nearly cosmopolitan (worldwide) distribution. The type species, P. anglicus, was described by Swiss naturalist Louis Agassiz in 1839, who gave it the name Pterygotus, meaning "winged one". Agassiz mistakenly believed the remains were of a giant fish; he would only realize the mistake five years later in 1844.

A fossil track or ichnite is a fossilized footprint. This is a type of trace fossil. A fossil trackway is a sequence of fossil tracks left by a single organism. Over the years, many ichnites have been found, around the world, giving important clues about the behaviour of the animals that made them. For instance, multiple ichnites of a single species, close together, suggest 'herd' or 'pack' behaviour of that species.

Phyllolepida is an extinct taxon of flattened placoderms found throughout the world, with fossils being found in Devonian strata. Like other flattened placoderms, the phyllolepids were bottom-dwelling predators that ambushed prey. Unlike other flattened placoderms, the phyllolepids were inhabitants of freshwater environments.
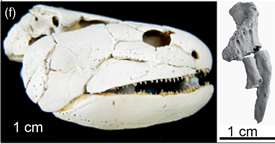
Gogonasus was a lobe-finned fish known from three-dimensionally preserved 380-million-year-old fossils found from the Gogo Formation in Western Australia. It lived in the Late Devonian period, on what was once a 1,400-kilometre coral reef off the Kimberley coast surrounding the north-west of Australia. Gogonasus was a small fish reaching 30–40 cm (1 ft) in length.
Luckeus is an extinct genus of prehistoric lobe-finned fish. Luckeus belonged to the order Onychodontida. It lived during the Early Devonian to Middle Devonian period in what os now central Australia.

The Gogo Formation in the Kimberley region of Western Australia is a Lagerstätte that exhibits exceptional preservation of a Devonian reef community. The formation is named after Gogo Station, a cattle station where outcrops appear and fossils are often collected from, as is nearby Fossil Downs Station.
Huginaspis is an extinct genus of placoderm arthrodire fish which lived during the Middle Devonian period of Spitsbergen, Norway.

Strepsodus is a genus of rhizodont lobe-finned fish that lived throughout the Carboniferous period. Fossils have been found in eastern Canada, Britain, and Queensland, Australia; indeterminate species of Strepsodus have also been found in the late Devonian deposits of Turkey, Iran and Colombia. A large individual is measured up to 3.5 metres (11.5 ft) long.
† Bembexia is a genus of fossil sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks. This genus is placed in the subfamily Eotomariinae, of the family Eotomariidae. The shell characters resemble those of Balbinipleura. These snails have been interpreted as herbivorous, probably grazing on algae.

Osteolepididae is a family of primitive, fish-like tetrapodomorphs that lived during the Devonian period. The family is generally thought to be paraphyletic, with the traits that characterise the family being widely distributed among basal tetrapodomorphs and other osteichthyans. Some of genera historically placed in Osteolepididae have more recently been assigned to the family Megalichthyidae, which appears to be a monophyletic group.

Eastmanosteus is a fossil genus of dunkleosteid placoderms. It was closely related to the giant Dunkleosteus, but differed from that genus in size, in possessing a distinctive tuberculated bone ornament, a differently shaped nuchal plate and a more zig-zagging course of the sutures of the skull roof.

Incisoscutum is an extinct genus of arthrodire placoderm from the Early Frasnian Gogo Reef, from Late Devonian Australia. The genus contains two species I. ritchiei, named after Alex Ritchie, a palaeoichthyologist and senior fellow of the Australian Museum, and I. sarahae, named after Sarah Long, daughter of its discoverer and describer, John A. Long.
Muranjilepis is an extinct genus of prehistoric sarcopterygians or lobe-finned fish.

Marsdenichthys is an extinct genus of Devonian tetrapodomorph. Fossils have been found from Mount Howitt in Victoria, Australia from strata that are Givetian-Frasnian in age. Mount Howitt is an important site that has been the source of many tetrapodomorph fossils, including Beelarongia and Howittichthys, both of which were first described from the locality.

Mcnamaraspis is an extinct monospecific genus of arthrodire placoderm that inhabited the ancient reef system of north Western Australia during the Frasnian epoch of the Late Devonian period. The type specimen was found and described by John A. Long from the Gogo Formation near Fitzroy Crossing. This fossil fish showed new anatomical features in arthrodires, like the well-preserved annular (ring-shaped) cartilages of the snout, previously inferred to be present by Erik Stensiö of Sweden. It is occasionally referred to as "The Gogo Fish" after the locale the holotype was excavated from.
Yarravia is a genus of extinct vascular plants mainly known from fossils found in Victoria, Australia. Originally the rocks in which they were found were considered to be late Silurian in age; more recently they have been found to be Early Devonian. Specimens consist only of incomplete leafless stems, some of which bore groups of spore-forming organs or sporangia which were fused, at least at the base.
















