
Gwalior is a major city in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh; it lies in northern part of Madhya Pradesh and is one of the Counter-magnet cities. Located 343 kilometres (213 mi) south of Delhi, the capital city of India, 120 kilometres (75 mi) from Agra and 414 kilometres (257 mi) from Bhopal, the state capital, Gwalior occupies a strategic location in the Gird region of India. The historic city and its fortress have been ruled by several historic Indian kingdoms. From the Kachchhapaghatas in the 10th century, Tomars in the 13th century, it was passed on to the Mughal Empire, then to the Maratha in 1754, and the Scindia Dynasty of Maratha Empire in the 18th century. In April 2021, It was found that Gwalior had the best air quality index amongst the 4 major cities in Madhya Pradesh.

Sheopur District is a district of Madhya Pradesh state in central India. The district is located in the north of the state and forms part of Chambal division. It is situated on the periphery of Rajasthan, which shows in the influence of Rajasthani culture in this district.

Sheopur is a city in Madhya Pradesh state of central India. It is the administrative headquarters of Sheopur District. Sheopur is linked by narrow gauge rail to Gwalior(No longer in operation). The town is traditionally famous for its wood carving. Chambal River is just 25 km, which forms the boundary between Rajasthan and MP states.
Vijaypur is a Town located in district Sheopur, Madhya Pradesh, India. This town is a part of the Vijaypur constituency and Morena constituency. It is located on the bank of the Kwari River. The town is one of the gateways to the Kuno National Park, the site selected as a second home to the Asiatic Lion and also for cheetah reintroduction in India.

Jaura is a town and a nagar panchayat in Morena district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh.
Sabalgarh is a municipality in Morena district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh.
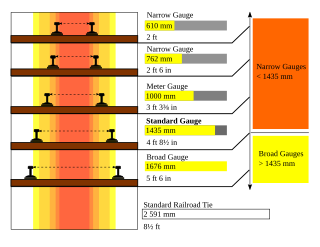
Project Unigauge, started on 1 April 1992, is an ongoing effort by Indian Railways to convert and unify all rail gauges in India to 1,676 mm broad gauge.

Gwalior Junction railway station is the main railway station of Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, India. It is operated by Indian Railways and is part of the Jhansi Division of the North-Central Railways.

Birlanagar Junction railway station is a small railway junction in Gwalior city, Madhya Pradesh. Its code is BLNR. It serves Gwalior city. The station consists of three platforms. The platforms are not well sheltered. It lacks many facilities including water and sanitation.

Pohari Assembly constituency is one of the 230 Vidhan Sabha constituencies of Madhya Pradesh state in central India. This constituency came into existence in 1951, as Sheopur Pohri, one of the 79 Vidhan Sabha constituencies of the erstwhile Madhya Bharat state.

The Agra–Bhopal section is a railway line connecting, Agra, one of large city in Uttar Pradesh, and Bhopal, capital of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. This 508 km (316 mi) track is part of the Delhi–Chennai line. The line is under the jurisdiction of North Central Railway and West Central Railway.

The New Delhi–Chennai main line is a railway line connecting Chennai and Delhi cutting across southern part of the Eastern Coastal Plains of India, the Eastern Ghats, the Deccan Plateau and the Yamuna valley. It covers a distance of 2,182 kilometres (1,356 mi) across Delhi, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. The route is used by the Grand Trunk Express and as such is referred to by many as the Grand Trunk Route.
Ashoknagar railway station is a small railway station in Ashoknagar district, Madhya Pradesh. Its code is ASKN. It serves Ashoknagar city. The station consists of two platforms. The platforms are not well sheltered. It lacks many facilities including water and sanitation. Ashoknagar is the part of Kota–Bina railway section of West Central Railway.

Guna Junction railway station is a main railway station in Guna district, Madhya Pradesh. Its code is GUNA. It serves Guna city. The station consists of three platforms. The platforms are well sheltered. It has many facilities including water and sanitation.
Meghnagar railway station is a small railway station in Jhabua district, Madhya Pradesh. Its code is MGN. It serves Meghnagar city. The station consists of three platforms. The platforms are not well sheltered. It lacks many facilities including water and sanitation.
Malanpu railway station is a small railway station in Bhind district, Madhya Pradesh. Its code is MLAR. It serves Industrial Area of Malanpur. The station consists of two platforms. The platforms are not well sheltered. It lacks many facilities including water and sanitation.
Sheopur Kalan railway station is a railway station in Sheopur district, Madhya Pradesh. Its code is SOE. It serves Sheopur town. The station consists of one platform. The platform is not well sheltered. It lacks many facilities including water and sanitation.
Gwalior West is a development project under National Capital Region. It was started in 1992 to attract the population of Delhi. Gwalior was first city out of 5 Counter Magnets selected by the government. Gwalior West lies 15 km from Gwalior and 8 km east of the Tigra Dam.
Biyavra Rajgarh railway station is a railway station in Rajgarh district, Madhya Pradesh. Its code is BRRG. It serves Biyavra city. The station consists of two platforms. It lacks many facilities including water and sanitation. Passenger, Express, and Superfast trains halt here.

Bhind railway station is a railway station in Bhind city of Madhya Pradesh. Its code is BIX. It serves Bhind city. The station consists of three platforms. Passenger, Express and Superfast trains halt here.










