
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family. It includes the carps, the true minnows, and relatives like the barbs and barbels. Cyprinidae is the largest and most diverse fish family and the largest vertebrate animal family in general with about 3,000 species, of which only 1,270 remain extant, divided into about 370 genera. Cyprinids range from about 12 mm in size to the 3 m (9.8 ft) giant barb. By genus and species count, the family makes up more than two-thirds of the ostariophysian order Cypriniformes. The family name is derived from the Greek word kyprînos.

The family Psittacidae or holotropical parrots is one of three families of true parrots. It comprises the roughly 10 species of subfamily Psittacinae and 157 of subfamily Arinae, as well as several species that have gone extinct in recent centuries. Some of the most iconic birds in the world are represented here, such as the blue-and-gold macaw among the New World parrots and the grey parrot among the Old World parrots.

Ovenbirds or furnariids are a large family of small suboscine passerine birds found from Mexico and Central to southern South America. They form the family Furnariidae. This is a large family containing around 315 species and 70 genera. The ovenbird, which breeds in North America, is not a furnariid – rather it is a distantly related bird of the wood warbler family, Parulidae.

The Leptotyphlopidae are a family of snakes found in North America, South America, Africa and Asia. All are fossorial and adapted to burrowing, feeding on ants and termites. Two subfamilies are recognized.

The Doradidae are a family of catfishes also known as thorny catfishes, raphael catfishes or talking catfishes. These fish are native to South America, primarily the Amazon basin and the Guianas.

Eupterotidae is a family of insects in the order Lepidoptera with more than 300 described species.

Clusiidae or "druid flies" is a family of small, thin, yellow to black acalyptrate flies with a characteristic antenna and with the wing usually partially infuscated. They have a cylindrical body. The head is round, the vertical plate reaches the anterior margin of the frons and the vibrissae on the head are large. The costa is interrupted near subcosta and the latter developed throughout length. Larvae are found in the bark of trees, the flies on trunks. The larvae are notable for their ability to jump. Males of many species in the subfamily Clusiodinae have been observed while engaged in lekking behaviour. There are hundreds of species in 14 genera found in all the Ecoregions, although most species occur in tropical regions. The type genus is Clusia Haliday, 1838.

The Ecnomidae are a family of caddisflies comprising 9 genera with a total of 375 species.
Astrodoras is a monotypic genus with the only species Astrodoras asterifrons of catfish family Doradidae. This species originates from the Amazon basin of Bolivia and Brazil and reaches a length of about 8.0 centimetres (3.1 in) SL. This genus is the type genus of the subfamily Astrodoradinae.
Merodoras nheco is species of freshwater ray-finned fish, it is the only species in the genus Merodoras of the catfish family Doradidae.
Amblydoras is a genus of thorny catfishes native to rivers in tropical South America.

The Perissommatidae are a family of flies (Diptera) that was proposed in 1962 by Donald Colless based on the species Perissomma fusca from Australia. The family now includes five extant species within the single genus Perissomma, four from Australia and one from Chile. The Perissommatidae are unusual as they appear to have four compound eyes. They have a small slender body less than 2 mm in length. Their wings are large in comparison to their bodies and subsequently their flight is weak. Preferring high-altitude forest environments, adults only fly in the winter. The larvae live in decaying leaf litter in wet sclerophyll or cool rain forests. Some species are suspected to be associated with fungi. In the case of Perissomma macalpinei, numbers of adults have been observed congregating in clumps of foliage and rising in short, zigzag flights in the sunlight above the foliage for short periods before descending.

Goniasteridae constitute the largest family of sea stars, included in the order Valvatida. They are mostly deep-dwelling species, but the family also include several colorful shallow tropical species.
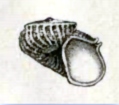
Scissurellidae, sometimes known by the common name little slit snails, are a taxonomic family of minute sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs or micromolluscs in the clade Vetigastropoda.

Lutjanidae, or snappers are a family of perciform fish, mainly marine, but with some members inhabiting estuaries, feeding in fresh water. The family includes about 113 species. Some are important food fish. One of the best known is the red snapper.

Pristimantis is a very large genus of frogs distributed in the southern Caribbean islands and in Central and South America from Honduras to northern Argentina and southern Brazil. With 596 described species, the genus had more species than any other genus of vertebrate animals. Many of these species genus are endemic to the Northwestern Andean montane forests ecoregion in north-western South America.
Trachelostenus is a genus of beetles belonging to Tenebrionoidea. It is native to the Valdivian forests of Chile, and has at least two species, T. inaequalis (Solier) and T. fascicularis (Philipp). It was historically considered the only member of the family Trachelostenidae, but a 2015 study sunk the genus into the tenebrionid subfamily Tenebrioninae.

Gracillariinae are a subfamily of moths which was described by Henry Tibbats Stainton in 1854.

Typhlocybinae is a subfamily of insects in the leafhopper family, Cicadellidae. This is currently the second largest leafhopper subfamily based on the number of described species, but researchers believe there are so many taxa yet undescribed that it is probably the largest subfamily. Approximately 6000 species have been described to science so far.















