
The Allogromiida is an order of single-chambered, mostly organic-walled foraminiferans, including some that produce agglutinated tests (Lagynacea). Genetic studies indicate that some foraminiferans with agglutinated tests, previously included in the Textulariida or as their own order Astrorhizida, may also belong here. Allogromiids produce relatively simple tests, usually with a single chamber, similar to those of other protists such as Gromia. They are found as both marine and freshwater forms, and are the oldest forms known from the fossil record.

The Textulariida are an order of foraminifera that produce agglutinated shells or tests. An agglutinated test is one made of foreign particles glued together with an organic or calcareous cement to form an external shell on the outside of the organism. Commonly, the order had been made up of all species of Foraminifera with these types of shells, but genetic studies indicate these organisms do not form an evolutionary group, and several superfamilies in the order have been moved to the order Allogromiida. The remaining forms are sometimes divided into three orders: the Trochamminida and Lituolida, which have organic cement, and the Textulariida sensu stricto, which use a calcareous cement. All three orders or superfamilies are known as fossils from the Cambrian onwards.
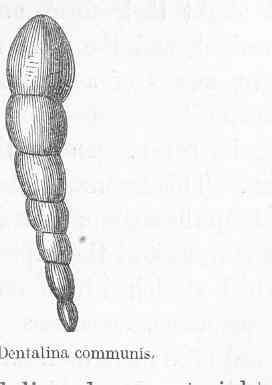
Lagenida is an order of benthic foraminiferal protists in which the tests (shells) are monolamellar, with walls composed of optically and ultra-structurally radiate calcite, with the crystallographic c-axes perpendicular to the surface. Lagenids first appear in the Upper Silurian and continue to the Recent. They are currently divided into two superfamilies, the older Robuloidacea which range from the Upper Silurian to the Lower Cretaceous (Albian) and the younger Nodosariacea, ranging from the Permian to Recent.
Miliamellus is a genus of Cenozoic benthic foraminifera with tests made of imperforate opaline silica. It is the only genus in the order Silicoloculinida and the family Silicoloculinidae. It is sometimes referred to by the junior synonym Silicoloculina.
The Rzehakinidae is a family of Lower Cretaceous to recent formaminifera that resemble the calcareous imperforate Miliolidae but which are constructed of finely agglutinated material that veneers an organic base. Tests are with two, or less commonly three, chambers per whorl, which are commonly added in various planes. In form they are generally ovoid.
The Ammodiscacea is a superfamily of foraminifera in the order Textulariida. tests are made of agglutinated grains and consist of a proloculus followed by an enrolled tubular second chamber open at the distal end, that lacks internal septa but which may have growth constrictions.
The Hormosinacea is a superfamily of agglutinated foraminifera in the Textulariida, with a range that extends from the Middle Ordovician, that unites seven families characterized by multilocular tests,, in a uniserial arrangement.
Sigmoilinopsis is a genus of miliolid Foraminifera, with an ovate test, chambers one-half coil in length, arranged in rapidly changing planes in the early stage resulting in two spiralling series that appear sigmoid in section, gradually becoming planispiral in the adult. Walls are thick, porcelaneous but enclosing a large quantity of agglutinated quartz particles, sponge spicules, and shell fragments; the aperture terminal, rounded, with a small tooth.
Cornuspiracea comprise a superfamily of miliolid forams in which the test may be free or attached, planispiral or trochospiral, evolute or involute, spreading or discoidal. The proloculus, or initial chamber, is followed by undivided spiral passage or enrolled tubular chamber, later may be irregularly coiled, unicoiled, or show zigzag growth pattern and may be distinctly chambered. The test wall is composed of imperforate porcelaneous calcite, a character of the Miliolida
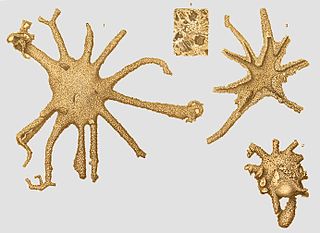
Astrorhizana are a subclass of foraminifera characterized by simple tests composed of agglutinated material that can be irregular, spheroidal, or tubular and straight, branching or enrolled. Tests are non septate and consist of a single chamber following the proloculus. These are the Ammodiscacea of the Textulariina in the Treatise Part C, that range from the Cambrian to Recent.
Lagynana is a subclass of foraminifera which comprises Astrorhizata with membranous or pseudochitinous tests that may have ferruginous encrustations or more rarely small quantities of agglutinated material. The Lagynacea Schultze, 1854, of the Allogriomiina, is fairly equivalent.

Helen Niña Tappan Loeblich was an American micropaleontologist who was a professor of geology at the University of California, Los Angeles, a United States Geological Survey (USGS) biostratigrapher, and a scientific illustrator whose micropaleontology specialty was research on Cretaceous foraminifera.
Miliamminana is a subclass of miliolates established by Mikhalevich, 1980 that combines two groups of foraminifers with agglutinated tests. They are the Rzehakinidae which previously were included in the Texulariina in the Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology although milioline in form, and the milioline Schlumbergerinida which includes genera removed from the Miliolina. The rzehakinids are composed of finely agglutinated material, insoluble in acid, over an organic base. Schlumbergerinids are composed of acid soluble agglutinated material over a porcelenous base. The unifying character is the nature of their coiling in which there are two tubular chambers, or sections, per whorl arranged in various planes and the fact that they are in part all agglutinated.
Spirocyclinidae is a family of foraminifera included in the order Loftusiida.

Cyclamminidae is a family of Foraminifera in the order Loftusiida, ex textulariid subfamily Cyclammininae in the Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology Part C, Protista 2.
Spirocyclina is a genus of large forams, with a flat test as much as 10mm in diameter. Coiling is planispiral to slightly asymmetric and mostly involute, some becoming uncoiled with a straight final stage. The final whorl, or stage, has about 25 strongly arcuate chambers. Composition is of agglutinated matter, the outer layer of the wall imperforate. Chambers are subdivided into secondary chamberlets by internal structures. The aperture consists of a double row of pores on the apertural face. Anchispirocyclina and Martiguesia are among related genera.
Haurania is a genus of elongated, finely agglutinated benthic foraminifera included in the Spirocyclinidae. The test is free, starting with a brief planispiral coil followed by a straight uncoiled stage. The exterior is imperforate, the interior divided by radial septula or beams, perpendicular to the septa and outer wall. The aperture is cribrate, a series of openings on the terminal face.
Martiguesia is a genus of agglutinated benthic forams from the Upper Cretaceous (Santonian) of France. The test is free, the early stage planispirally coiled, becoming nearly straight during later growth. The agglutinated wall is externally imperforate, the interior with a coarse alveolar network. Chambers are subdivided and almost completely filled by irregular radial pillars. The aperture, cribrate.
Pseudospirocyclina is a genus of large planispirally coiled agglutinated benthic forams with a complex interior known from the upper Jurassic (Kimmeridgian) of Portugal and Morocco.
Saudia is a genus of large discoidal to reniform forams, with a relatively thick test and complex interior, composed of agglutinated matter, or microgranular calcite. Saudia is known from the Paleocene to middle Eocene of Saudi Arabia, Iraq and the balkans. Related genera include Vania, Sornayina, and Haurania.






