
Jewellery consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a western perspective, the term is restricted to durable ornaments, excluding flowers for example. For many centuries metal such as gold often combined with gemstones, has been the normal material for jewellery, but other materials such as glass, shells and other plant materials may be used.

Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Historically, flint was widely used to make stone tools and start fires.
The culture of Egypt has thousands of years of recorded history. Ancient Egypt was among the earliest civilizations in the world. For millennia, Egypt developed strikingly unique, complex and stable cultures that influenced other cultures of Europe, Africa and the Middle East.

Egyptology is the scientific study of ancient Egypt. The topics studied include ancient Egyptian history, language, literature, religion, architecture and art from the 5th millennium BC until the end of its native religious practices in the 4th century AD.

Knapping is the shaping of flint, chert, obsidian, or other conchoidal fracturing stone through the process of lithic reduction to manufacture stone tools, strikers for flintlock firearms, or to produce flat-faced stones for building or facing walls, and flushwork decoration. The original Germanic term knopp meant to strike, shape, or work, so it could theoretically have referred equally well to making statues or dice. Modern usage is more specific, referring almost exclusively to the hand-tool pressure-flaking process pictured. It is distinguished from the more general verb "chip" and is different from "carve", and "cleave".
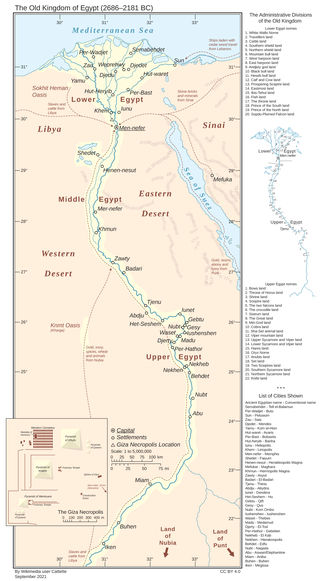
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynasty, such as King Sneferu, who perfected the art of pyramid-building, and the kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who constructed the pyramids at Giza. Egypt attained its first sustained peak of civilization during the Old Kingdom, the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods, which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley.

The Museum of Egyptian Antiquities, commonly known as the Egyptian Museum, located in Cairo, Egypt, houses the largest collection of Egyptian antiquities in the world. It houses over 120,000 items, with a representative amount on display. Located in Tahrir Square in a building built in 1901, it is the largest museum in Africa. Among its masterpieces are Pharaoh Tutankhamun's treasure, including its iconic gold burial mask, widely considered one of the best-known works of art in the world and a prominent symbol of ancient Egypt.

Zahi Abass Hawass is an Egyptian archaeologist, Egyptologist, and former Minister of State for Antiquities Affairs, serving twice. He has also worked at archaeological sites in the Nile Delta, the Western Desert and the Upper Nile Valley.

A bracelet is an article of jewellery that is worn around the wrist. Bracelets may serve different uses, such as being worn as an ornament. When worn as ornaments, bracelets may have a supportive function to hold other items of decoration, such as charms. Medical and identity information are marked on some bracelets, such as allergy bracelets, hospital patient-identification tags, and bracelet tags for newborn babies. Bracelets may be worn to signify a certain phenomenon, such as breast cancer awareness, or for religious/cultural purposes.

The Fitzwilliam Museum is the art and antiquities museum of the University of Cambridge. It is located on Trumpington Street opposite Fitzwilliam Street in central Cambridge. It was founded in 1816 under the will of Richard FitzWilliam, 7th Viscount FitzWilliam (1745–1816), and comprises one of the best collections of antiquities and modern art in western Europe. With over half a million objects and artworks in its collections, the displays in the museum explore world history and art from antiquity to the present. The treasures of the museum include artworks by Monet, Picasso, Rubens, Vincent van Gogh, Rembrandt, Cézanne, Van Dyck, and Canaletto, as well as a winged bas-relief from Nimrud. Admission to the public is always free.
Djer is considered the third pharaoh of the First Dynasty of ancient Egypt in current Egyptology. He lived around the mid 31st century BC and reigned for c. 40 years. A mummified forearm of Djer or his wife was discovered by Egyptologist Flinders Petrie, but was discarded by Émile Brugsch.

Sekhemkhet was an ancient Egyptian king (pharaoh) of the 3rd Dynasty during the Old Kingdom. His reign is thought to have been from about 2648 BC until 2640 BC. He is also known under his later traditioned birth name Djoser-tety and under his Hellenized name Tyreis. Sekhemkhet was probably the brother or eldest son of king Djoser. Little is known about this king, since he ruled for only a few years. However, he erected a step pyramid at Saqqara and left behind a well known rock inscription at Wadi Maghareh.
In ancient Egypt, cats were represented in social and religious scenes dating as early as 1980 BC. Several ancient Egyptian deities were depicted and sculptured with cat-like heads such as Mafdet, Bastet and Sekhmet, representing justice, fertility, and power, respectively. The deity Mut was also depicted as a cat and in the company of a cat.
Lisht or el-Lisht is an Egyptian village located south of Cairo. It is the site of Middle Kingdom royal and elite burials, including two pyramids built by Amenemhat I and Senusret I. The two main pyramids were surrounded by smaller pyramids of members of the royal family, and many mastaba tombs of high officials and their family members. They were constructed throughout the Twelfth and Thirteenth Dynasties. The site is also known for the tomb of Senebtisi, found undisturbed and from which a set of jewelry has been recovered. The pyramid complex of Senusret I is the best preserved from this period. The coffins in the tomb of Sesenebnef present the earliest versions of the Book of the Dead.

The Oxus treasure is a collection of about 180 surviving pieces of metalwork in gold and silver, most relatively small, and around 200 coins, from the Achaemenid Persian period which were found by the Oxus river about 1877–1880. The exact place and date of the find remain unclear, but is often proposed as being near Kobadiyan. It is likely that many other pieces from the hoard were melted down for bullion; early reports suggest there were originally some 1500 coins, and mention types of metalwork that are not among the surviving pieces. The metalwork is believed to date from the sixth to fourth centuries BC, but the coins show a greater range, with some of those believed to belong to the treasure coming from around 200 BC. The most likely origin for the treasure is that it belonged to a temple, where votive offerings were deposited over a long period. How it came to be deposited is unknown.

The Gebel el-Arak Knife, also Jebel el-Arak Knife, is an ivory and flint knife dating from the Naqada II period of Egyptian prehistory, showing Mesopotamian influence. The knife was purchased in 1914 in Cairo by Georges Aaron Bénédite for the Louvre, where it is now on display in the Sully wing, room 633. At the time of its purchase, the knife handle was alleged by the seller to have been found at the site of Gebel el-Arak, but it is today believed to come from Abydos.

The Gebelein predynastic mummies are six naturally mummified bodies, dating to approximately 3400 BC from the Late Predynastic period of Ancient Egypt. They were the first complete predynastic bodies to be discovered. The well-preserved bodies were excavated at the end of the nineteenth century by Wallis Budge, the British Museum Keeper for Egyptology, from shallow sand graves near Gebelein in the Egyptian desert.

Ancient Roman jewelry was characterized by an interest in colored gemstones and glass, in contrast with their Greek predecessors who focused primarily on the production of high-quality metalwork by practiced artisans. Extensive control of Mediterranean territories provided an abundance of natural resources to utilize in jewelry making. Participation in trade allowed access to both semi-precious and precious stones that traveled down the Persian Silk Road from the East.
Robert Grenville Gayer-Anderson, known as John to his friends, was an Irish surgeon, soldier, colonial administrator and collector, perhaps best known for his connection with Egypt and Egyptian antiquities. The Gayer-Anderson Museum in Cairo, and the Gayer-Anderson cat, an Ancient Egyptian bronze figurine of the goddess Bastet in the form of a cat, now in the collections of the British Museum, are both named after him.
















