
Mites are small arachnids. Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as each other's closest relative within Arachnida, rendering the group non-monophyletic. Most mites are tiny, less than 1 mm (0.04 in) in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others are predators or parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive Varroa parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases.

Trombicula, known as chiggers, red bugs, scrub-itch mites, or berry bugs, are small arachnids in the Trombiculidae family. In their larval stage, they attach to various animals, including humans, and feed on skin, often causing itching and trombiculosis. These relatives of ticks are nearly microscopic, measuring 0.4 mm (0.01 in) and have a chrome-orange hue. A common species of harvest mite in North America is Trombicula alfreddugesi.
Poultry diseases occur in poultry, which are domesticated birds kept for their meat, eggs or feathers. Poultry species include the chicken, turkey, duck, goose and ostrich.
Acariasis is an infestation with mites.

The Acaridae are a family of mites in order Sarcoptiformes.

Dermanyssus gallinae is a haematophagous ectoparasite of poultry. It has been implicated as a vector of several major pathogenic diseases. Despite its common names, it has a wide range of hosts including several species of wild birds and mammals, including humans, where the condition it causes is called gamasoidosis. In both size and appearance, it resembles the northern fowl mite, Ornithonyssus sylviarum.

Mesostigmata is an order of mites belonging to the Parasitiformes. They are by far the largest group of Parasitiformes, with over 8,000 species in 130 families. Mesostigmata includes parasitic as well as free-living and predatory forms. They can be recognized by the single pair of spiracles positioned laterally on the body.

Oribatida, also known as oribatid mites, moss mites or beetle mites, are an order of mites, in the "chewing Acariformes" clade Sarcoptiformes. They range in size from 0.2 to 1.4 millimetres. There are currently 12,000 species that have been identified, but researchers estimate that there may be anywhere from 60,000 to 120,000 total species. Oribatid mites are by far the most prevalent of all arthropods in forest soils, and are essential for breaking down organic detritus and distributing fungi.
Human parasites include various protozoa and worms.

Trombiculidae, commonly referred to in North America as chiggers and in Britain as harvest mites, but also known as berry bugs, bush-mites, red bugs or scrub-itch mites, are a family of mites. Chiggers are often confused with jiggers – a type of flea. Several species of Trombiculidae in their larva stage bite their animal or human host and by embedding their mouthparts into the skin cause "intense irritation" or "a wheal, usually with severe itching and dermatitis".
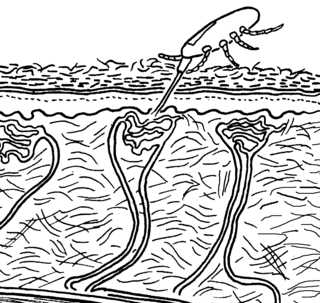
Gamasoidosis, also known as dermanyssosis, is a frequently unrecognized form of dermatitis, following human infestation with avian mites of the genera Dermanyssus or Ornithonyssus. It is characterized by pruritic erythematous papules, macules and urticaria, with itching and irritation resulting from the saliva the mites secrete while feeding. These bites are commonly found around the neck and areas covered by clothing, but can be found elsewhere on the body. The avian mite Dermanyssus gallinae can also infest various body parts, including the ear canal and scalp.

Ornithonyssus bacoti is a hematophagous parasite. It feeds on blood and serum from many hosts. O. bacoti can be found and cause disease on rats and wild rodents most commonly, but also small mammals and humans when other hosts are scarce. Outbreaks tend to occur in older, less maintained buildings. The mite, however, can travel several hundred feet on its own if necessary to find a host and can survive for extended periods of time without a host. This, along with the nonspecific dermatitis it causes, can prevent accurate and fast diagnosis of rat mite dermatitis. The scarcity of reports, due in part to misdiagnosis and also the mildness of its symptoms, makes the disease seem less common than it is. The tropical rat mite can be found in both temperate and tropical regions or rather all continents except the Arctic and Antarctic.

Pyemotes tritici is a species of mite known as the grain itch mite or straw itch mite. It is a cosmopolitan species that is found on straw, hay and stored grain. It is a parasite of small arthropods and is being investigated as a possible biological control of stored product pests. It is associated with dermatitis in humans, and it causes an itchy rash.

The Laelapidae are a family of mites in the order Mesostigmata. The family is also referred to in the literature as Laelaptidae, which may be the correct spelling.

Dermanyssidae is a family of mites in the order Mesostigmata.

Dermanyssoidea is a superfamily of mites, including most of the mites which parasitise vertebrates.
Atoxoplasma is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. The species in this genus infect birds. They are spread by the orofaecal route.
Lankesterella is a genus in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this genus infect amphibians, reptiles and birds.

Mites that infest and parasitize domestic animals cause disease and loss of production. Mites are small invertebrates, most of which are free living but some are parasitic. Mites are similar to ticks and both comprise the order Acari in the phylum Arthropoda. Mites are highly varied and their classification is complex; a simple grouping is used in this introductory article. Vernacular terms to describe diseases caused by mites include scab, mange, and scabies. Mites and ticks have substantially different biology from, and are classed separately from, insects. Mites of domestic animals cause important types of skin disease, and some mites infest other organs. Diagnosis of mite infestations can be difficult because of the small size of most mites, but understanding how mites are adapted to feed within the structure of the skin is useful.

Mites are small crawling animals related to ticks and spiders. Most mites are free-living and harmless. Other mites are parasitic, and those that infest livestock animals cause many diseases that are widespread, reduce production and profit for farmers, and are expensive to control.















