
Angraecum, also known as comet orchid, is a genus of the family Orchidaceae native to tropical and South Africa, as well as Sri Lanka. It contains 223 species.

Cypripedium acaule is a species of flowering plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae native to eastern North America. It is currently the provincial flower of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and the state wildflower of New Hampshire, United States.

Ramosmania rodriguesi, commonly known as café marron, is a tree native to the Mauritian island of Rodrigues in the Indian Ocean. The plant has an average size of about 5 to 6 feet and features white five-petal star-shaped flowers. Its French common name café marron translates to "brown coffee."

Amesiella is a genus of orchids endemic to the Island of Luzon, in the Philippines.

Phalaenopsis micholitzii is a species of plant in the family Orchidaceae. It is endemic to the Zamboanga peninsula in the island of Mindanao, Philippines.

Angraecum sesquipedale, also known as Darwin's orchid, Christmas orchid, Star of Bethlehem orchid, and king of the angraecums, is an epiphytic orchid in the genus Angraecum endemic to Madagascar. The orchid was first discovered by the French botanist Louis-Marie Aubert du Petit-Thouars in 1798, but was not described until 1822. It is noteworthy for its long spur and its association with the naturalist Charles Darwin, who surmised that the flower was pollinated by a then undiscovered moth with a proboscis whose length was unprecedented at the time. Darwin's prediction went unverified for 21 years after his death, until just such a moth was discovered and his conjecture vindicated. The story of its postulated pollinator has come to be seen as one of the celebrated predictions of the theory of evolution.

Aerangis fastuosa, commonly known as the 'magnificent Aerangis', is a species of epiphytic orchid endemic to Madagascar. It is widespread across Madagascar, stretching from the eastern coastal forests across to the south and along the central plateau. Aerangis fastuosa belongs to the family Orchidaceae, subtribe Aerangidinae.

Epidendrum ciliare, synonyms including Coilostylis ciliaris is a species of orchid. It is known as the fringed star orchid. It has a wide distribution from Mexico through Central America and the Caribbean to northern and western South America.

Cattleya gaskelliana is a labiate Cattleya species of orchid. The diploid chromosome number of C. gaskelliana has been determined as 2n = 40.

Encyclia patens is a species of orchid native to east and south Brazil. Encyclia flava is a synonym of Encyclia patens var. patens.

Epidendrum rigidum is an epiphytic reed-stemmed Epidendrum orchid common throughout the Neotropical lowlands, below 600 m (2,000 ft).

Paphiopedilum sanderianum is a rare species of orchid endemic to northwestern Borneo. First discovered in 1885 by F. Sander's collector, J. Foerstermann, the orchid became renowned for the remarkable length of its petals, which can measure over 1 meter long. Although P. sanderianum has been used as a parent in a number of crosses, none of the resulting hybrids have so far matched the extraordinary lengths of this species' petals. However, soon after the turn of the 20th century, this rare orchid was lost to cultivation and thought to be extinct in the wild, until its rediscovery in 1978 by Ivan Nielson. The wild population of Paphiopedilum sanderianum grows protected in Gunung Mulu National Park.

Epidendrum calanthum is a terrestrial reed-stemmed Epidendrum orchid from the montane Tropical rainforest of Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Venezuela, and the West Indies.

Cyrtorchis is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family Orchidaceae native to Africa.

Microsaccus is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to Southeast Asia.

Gilbertiodendron dewevrei is a species of tree in the family Fabaceae, native to tropical rain forests in Central Africa. It is often the dominant tree species of the Guineo-Congolian rainforest. The timber is traded as limbali, and is used for construction, flooring and railway sleepers. It is also used for making boats, furniture, tool handles and joinery and for making charcoal.
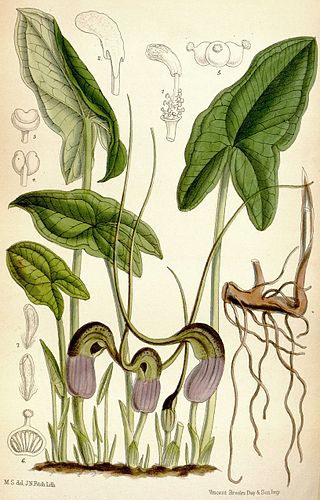
Arisarum proboscideum, also known as the mouse plant or mouse-tail plant, is a flowering plant in the family Araceae.

Phalaenopsis venosa, is a species of orchid endemic to Sulawesi, Indonesia. The specific epithet venosa, from the Latin venosus meaning veiny, refers to the floral colouration.

Pamianthe peruviana, also known as the giant Peruvian daffodil, is a species of epiphytic plant native to seasonally dry areas of Peru and Bolivia.

Nymphaea dimorpha is a species of waterlily endemic to Madagascar.






















