| Ankothrips | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Thysanoptera |
| Family: | Melanthripidae |
| Genus: | Ankothrips Crawford, 1909 |
Ankothrips is a genus of thrip in the family Melanthripidae. [1]
| Ankothrips | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Thysanoptera |
| Family: | Melanthripidae |
| Genus: | Ankothrips Crawford, 1909 |
Ankothrips is a genus of thrip in the family Melanthripidae. [1]
Catalogue of Life shows the following species as accepted within Ankothrips: [1]

Biological databases are libraries of biological sciences, collected from scientific experiments, published literature, high-throughput experiment technology, and computational analysis. They contain information from research areas including genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, microarray gene expression, and phylogenetics. Information contained in biological databases includes gene function, structure, localization, clinical effects of mutations as well as similarities of biological sequences and structures.

The Cupedidae are a small family of beetles, notable for the square pattern of "windows" on their elytra, which give the family their common name of reticulated beetles.
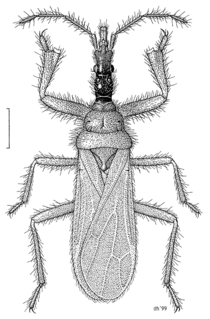
Enicocephalidae, also called unique-headed bugs and gnat bugs, are a family of around 300 species of the suborder heteroptera. They are typically 4 mm long, and found throughout the world. They have an elongated head, constricted in places, hence their head is 'unique'.

Ochodaeidae, also known as the sand-loving scarab beetles, is a small family of scarabaeiform beetles occurring in many parts of the world.

Ripiphoridae is a cosmopolitan family of some 450 described species of beetles sometimes called "wedge-shaped beetles". Ripiphoridae are unusual among beetle families in that many species are hypermetamorphic parasitoids, an attribute that they share with the Meloidae. Members of the family differ in their choice of hosts, but most attack various species of bees or wasps, while some others attack cockroaches. Many species of Ripiphoridae have abbreviated elytra, and flabellate or pectinate antennae.

Evaniidae is a family of parasitoid wasps also known as ensign wasps, nightshade wasps, hatchet wasps, or cockroach egg parasitoid wasps. They number around 20 extant genera containing over 400 described species, and are found all over the world except in the polar regions. The larvae of these solitary wasps are parasitoids that feed on cockroaches and develop inside the egg-cases, or oothecae, of their hosts.

Hybotidae, the typical dance flies, are a family of true flies. They belong to the superfamily Empidoidea and were formerly included in the Empididae as a subfamily.

Gaeanini is a tribe of cicadas in the family Cicadidae, found in the Palearctic and Indomalaya. There are about 10 genera and at least 50 described species in Gaeanini.

The Lycidae are a family in the beetle order Coleoptera, members of which are commonly called net-winged beetles. These beetles are cosmopolitan, being found in Nearctic, Palearctic, Neotropical, Afrotropical, Oriental, and Australian ecoregions.

Compsocidae is a family of Psocodea belonging to the suborder Troctomorpha. The family comprises two extant species in two genera, both found in Mesoamerica. Compsocus elegans is found in Mexico and Central America, while Electrentomopsis variegata is found in Mexico. The antennae of each species have 13 or 14 segments. Two extinct genera, Burmacompsocus and Paraelectrentomopsis are known from the Cenomanian aged Burmese amber of Myanmar.
Pachytroctidae is a family of thick barklice in the order Psocodea. There are about 15 genera and at least 90 described species in Pachytroctidae.

Rhachiberothidae, sometimes called thorny lacewings, are a family of winged insects in the order Neuroptera. The family has only 14 extant species in 4 genera found in Sub-Saharan Africa, but has a diverse fossil record extending back to the Early Cretaceous in Lebanon, Eurasia and North America. Like the closely related Mantispidae members of the group possess raptorial forelegs, which probably only evolved once in the common ancestor of the groups.

Kateretidae is a family of short-winged flower beetles in the suborder Polyphaga. There are about 11 genera and at least 40 described species in Kateretidae. They are found worldwide except in New Zealand. Adults are anthophagous, feeding on flowers, while the larvae are spermatophagous inside the flower corolla.

Schizopteridae is the largest family in the infraorder Dipsocoromorpha and comprises 56 genera and approximately 255 species. Schizopterids are some of the smallest (0.5–2.0 mm) true bugs. Members of this family can be distinguished by their small size, enlarged forecoxae and varying degree of abdominal and genitalic asymmetry in males. Schizopteridae exhibit a wide range of simple and complex wing venation patterns. The group is currently divided into three subfamilies: Schizopterinae, Ogeriinae and Hypselosomatinae.
Psilothrips is a genus of thrips in the family Thripidae. There are at least two described species in Psilothrips.

Mesoveliidae is a family of water treaders in the order Hemiptera. There are about 16 genera and at least 50 described species in Mesoveliidae.

Aeolothrips is a genus of predatory thrips in the family Aeolothripidae. There are more than 80 described species in Aeolothrips.

Winnertziinae is a subfamily of gall midges and wood midges in the family Cecidomyiidae.

Leptopsaltriini is a tribe of cicadas in the family Cicadidae. There are at least 200 described species in Leptopsaltriini, found in the Palearctic, Nearctic, and Indomalaya.
Manicapsocidae is a family of Psocodea. It contains 8 extant species in 4 genera, with most of the species being found in the Neotropics, with one species in the Afrotropics. The extinct family Electrentomidae has been suggested to be a synonym of this family, though this has been considered premature by other scholars in the absence of cladistic analysis. Confirmed fossil species of the family are nearly as numerous as living ones, extending back to the Mid-Cretaceous.