
Baby corn is a cereal grain taken from corn (maize) harvested early while the stalks are still small and immature. It typically is eaten whole – cob included – in contrast to mature corn, whose cob is too tough for human consumption. It is eaten both raw and cooked. Baby corn is common in stir fry dishes.

Senegalia senegal is a small thorny deciduous tree from the genus Senegalia, which is known by several common names, including gum acacia, gum arabic tree, Sudan gum and Sudan gum arabic. In parts of India, it is known as Kher or Khor. It is native to semi-desert regions of Sub-Saharan Africa, as well as Oman, Pakistan, west coastal India. It grows to a height of 5–12 metres (16-40'), with a trunk up to 30 cm (1') in diameter. Sudan is the source of the world's highest quality gum arabic, known locally as hashab gum in contrast to the related, but inferior, gum arabic from Red acacia or talah gum.

Quercus glauca, commonly called ring-cupped oak or Japanese blue oak, is a tree in the beech family (Fagaceae). It is native to eastern and southern Asia, where it is found in Afghanistan, Bhutan, China, northern and eastern India, southern Japan, Kashmir, Korea, Myanmar, Nepal, and Vietnam.

Erythrina variegata, commonly known as tiger's claw or Indian coral tree, is a species of Erythrina native to the tropical and subtropical regions of eastern Africa, the Indian Subcontinent, northern Australia, and the islands of the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean east to Fiji.
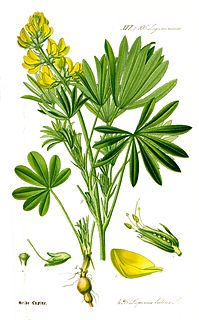
Lupinus luteus is known as annual yellow-lupin, European yellow lupin or yellow lupin. It is native to the Mediterranean region of Southern Europe.
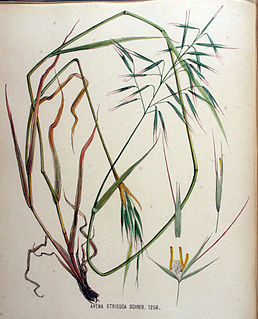
Avena strigosa is a species of grass native to Europe, and its seeds are edible. This plant is often cultivated as animal feed in the south Brazil, and it is sometimes reported as a weed.

Psidium guajava, the common guava, yellow guava, or lemon guava, is an evergreen shrub or small tree native to the Caribbean, Central America and South America. It is easily pollinated by insects; when cultivated, it is pollinated mainly by the common honey bee, Apis mellifera.

Senegalia catechu is a deciduous, thorny tree which grows up to 15 m (50 ft) in height. The plant is called khair in Hindi, and kachu in Malay, hence the name was Latinized to "catechu" in Linnaean taxonomy, as the type-species from which the extracts cutch and catechu are derived. Common names for it include kher, catechu, cachou, cutchtree, black cutch, and black catechu.

Senegalia laeta, the gay acacia or daga, is a legume found in the family Fabaceae. It was formerly included in the genus Acacia.

Senegalia mellifera is a common thorn tree in Africa. The name mellifera refers to its sweet-smelling blossoms and honey. Its lumber turns pitch black when oiled. Common names of the tree include Blackthorn and Swarthaak (Afrikaans). It is listed as being not threatened.

Vachellia oerfota is a perennial shrub or tree which is native to Africa, Asia and the Middle East. Among other things, it is used in making beverages. It grows 1–5m high. It is an important legume tree commonly browsed by goats and camels in Africa. It is valued as a fodder by pastoralists.

Tephrosia purpurea is a species of flowering plant in the pea family, Fabaceae, that has a pantropical distribution. It is a common wasteland weed. In many parts it is under cultivation as green manure crop. It is found throughout India and Sri Lanka in poor soils.

Cenchrus biflorus is a species of annual grass in the family Poaceae. Common names include Indian sandbur, Bhurat or Bhurut in India, Haskaneet in Sudan, Aneeti in the Arabic dialect of Mauritania, K 'arangiya in the Hausa language of Nigeria, and Ngibbi in the Kanuri language of Nigeria. In the francophone countries of the Sahel, it is usually referred to as "cram-cram".

Luffa cylindrica, the sponge gourd, Egyptian cucumber or Vietnamese luffa, is an annual species of vine cultivated for its fruit, native to South and Southeast Asia.

Arachis pintoi is a forage plant native to Cerrado vegetation in Brazil. It is native to the valleys of the upper São Francisco and the Jequitinhonha rivers of Minas Gerais. It has been named after the Brazilian botanist Geraldo Pinto, who first collected the plant at the locality of Boca do Córrego, município de Belmonte in 1954 and suggested its potential as a forage. The species has been first described by A. Krapovickas and W. Gregory in 1994.

Setaria sphacelata is a tall African grass, also known as South African pigeon grass and African bristlegrass. It is native to tropical and subtropical Africa, and is extensively cultivated globally as a pasture grass and for cut fodder. This is a rhizomatous perennial grass producing flattened, hairless, blue-green stems up to 2 m tall. The inflorescence is a dense, narrow panicle of bristly, orange-tinged spikelets up to 25 cm long.

Aeschynomene americana is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae (legume) known by many common names, including shyleaf, forage aeschynomene, American joint vetch, thornless mimosa, bastard sensitive plant (Jamaica), pega pega, pega ropa, antejuela, ronte, cujicillo, and dormilonga. It is native to Central America, parts of South America, the West Indies, and Florida. It is now found in the USA, in Australia and in South-East Asia.

Albizia chinensis is a species of legume in the genus Albizia, native to south and southeast Asia, from India to China and Indonesia.

Trichanthera is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the acanthus family containing the single species Trichanthera gigantea, which is known by many common names, including madre de agua, suiban, cenicero, tuno, naranjillo, and palo de agua. It is native to Central America and northern South America. It has also been introduced to other tropical regions such as Vietnam, Cambodia, and the Philippines.

Brachiaria nigropedata is a perennial grass belonging to the grass family (Poaceae). It is native to Southern Africa the tropical regions of South Africa and East Africa. Brachiaria nigropedata is used as fodder grass in Namibia. As a pioneering grass, it has also environmental uses such as revegetation and soil binding.




















