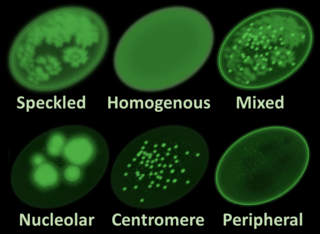
Antinuclear antibodies are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human proteins (autoantigens). In some cases, antibodies to human antigens are produced.

Autoimmune hepatitis, formerly known as lupoid hepatitis, plasma cell hepatitis, or autoimmune chronic active hepatitis, is a chronic, autoimmune disease of the liver that occurs when the body's immune system attacks liver cells, causing the liver to be inflamed. Common initial symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, muscle aches, or weight loss or signs of acute liver inflammation including fever, jaundice, and right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Individuals with autoimmune hepatitis often have no initial symptoms and the disease may be detected by abnormal liver function tests and increased protein levels during routine bloodwork or the observation of an abnormal-looking liver during abdominal surgery.

Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is an autoimmune disease of the liver. It results from a slow, progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver, causing bile and other toxins to build up in the liver, a condition called cholestasis. Further slow damage to the liver tissue can lead to scarring, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis.
In medicine, specifically gastroenterology, the Child–Pugh score is used to assess the prognosis of chronic liver disease, mainly cirrhosis. Although it was originally used to predict mortality during surgery, it is now used to determine the prognosis, as well as the required strength of treatment and the necessity of liver transplantation.
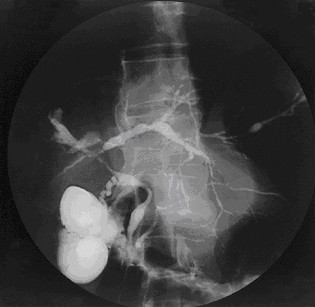
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a long-term progressive disease of the liver and gallbladder characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, which normally allow bile to drain from the gallbladder. Affected individuals may have no symptoms or may experience signs and symptoms of liver disease, such as yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes, itching, and abdominal pain.
The oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (OGDC) or α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex is an enzyme complex, most commonly known for its role in the citric acid cycle.
An autoantibody is an antibody produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases are associated with such antibodies.

Cholestasis is a condition where bile cannot flow from the liver to the duodenum. The two basic distinctions are an obstructive type of cholestasis where there is a mechanical blockage in the duct system that can occur from a gallstone or malignancy, and metabolic types of cholestasis which are disturbances in bile formation that can occur because of genetic defects or acquired as a side effect of many medications. Classification is further divided into acute or chronic and extrahepatic or intrahepatic.
The branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex is a multi-subunit complex of enzymes that is found on the mitochondrial inner membrane. This enzyme complex catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of branched, short-chain alpha-ketoacids. BCKDC is a member of the mitochondrial α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex family comprising pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, key enzymes that function in the Krebs cycle.

Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase is an enzyme component of the multienzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is responsible for the pyruvate decarboxylation step that links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle. This involves the transformation of pyruvate from glycolysis into acetyl-CoA which is then used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. The conversion requires the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate.

E3 binding protein also known as pyruvate dehydrogenase protein X component, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDHX gene. The E3 binding protein is a component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex found only in eukaryotes. Defects in this gene are a cause of pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency which results in neurological dysfunction and lactic acidosis in infancy and early childhood. This protein is also a minor antigen for antimitochondrial antibodies. These autoantibodies are present in nearly 95% of patients with primary biliary cholangitis, an autoimmune disease of the liver. In primary biliary cholangitis, activated T lymphocytes attack and destroy epithelial cells in the bile duct where this protein is abnormally distributed and overexpressed. Primary biliary cholangitis eventually leads to liver failure.

Nuclear pore glycoprotein-210 (gp210) is an essential trafficking regulator in the eukaryotic nuclear pore complex. Gp-210 anchors the pore complex to the nuclear membrane. and protein tagging reveals its primarily located on the luminal side of double layer membrane at the pore. A single polypeptide motif of gp210 is responsible for sorting to nuclear membrane, and indicate the carboxyl tail of the protein is oriented toward the cytoplasmic side of the membrane.
Anti-glycoprotein-210 antibodies are directed at gp210 and are found within primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) patients in high frequency. AGPA recognize the cytoplasmic-oriented carboxyl terminus (tail) of the protein. While AGPA is found as a prognostic marker in only a minority of PBC patients, those that did had higher mortality and were predicted a poor outcome. In addition, patients that responded to ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) therapy and, therefore, had AGPA reductions failed to develop end-stage liver disease relative to untreated cohort with anti-gp210 Ab. PBC patients with potentially destructive AGPA have increased expression of Nup210 in the bile duct, a potential immune tolerance-escaping factor.
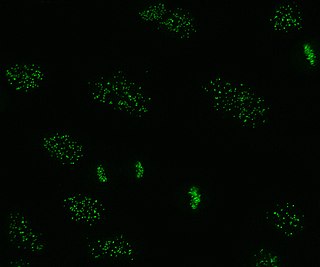
Anti-centromere antibodies are autoantibodies specific to centromere and kinetochore function. They occur in some autoimmune diseases, frequently in limited systemic scleroderma, and occasionally in the diffuse form of scleroderma. They are rare in other rheumatic conditions and in healthy persons.

Anti-sp100 antibodies are found in association with primary biliary cirrhosis. The autoimmune target of anti-sp100 is the sp100 nuclear antigen which was identified by its association with primary biliary cirrhosis. 20-30% of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis have sp100 Abs. The sera of these patients exhibit a characteristic "nuclear dots" pattern in indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) on Hep-2 cells.

Anti-thrombin antibodies are autoantibodies directed against thrombin that may constitute a fraction of lupus anticoagulant and are seen an increased levels in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Anti-histone antibodies are autoantibodies that are a subset of the anti-nuclear antibody family, which specifically target histone protein subunits or histone complexes. They were first reported by Henry Kunkel, H.R. Holman, and H.R.G. Dreicher in their studies of cellular causes of lupus erythematosus in 1959–60. Today, anti-histone antibodies are still used as a marker for systemic lupus erythematosus, but are also implicated in other autoimmune diseases like Sjögren syndrome, dermatomyositis, or rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-histone antibodies can be used as a marker for drug-induced lupus.

Anti-SSA autoantibodies are a type of anti-nuclear autoantibodies that are associated with many autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), SS/SLE overlap syndrome, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), neonatal lupus and primary biliary cirrhosis. They are often present in Sjögren's syndrome (SS). Additionally, Anti-Ro/SSA can be found in other autoimmune diseases such as systemic sclerosis (SSc), polymyositis/dermatomyositis (PM/DM), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), and are also associated with heart arrhythmia.













