
The golden eagle is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known birds of prey in the Northern Hemisphere. These birds are dark brown, with lighter golden-brown plumage on their napes. Immature eagles of this species typically have white on the tail and often have white markings on the wings. Golden eagles use their agility and speed combined with powerful feet and large, sharp talons to hunt a variety of prey, mainly hares, rabbits, and marmots and other ground squirrels. Golden eagles maintain home ranges or territories that may be as large as 200 km2 (77 sq mi). They build large nests in cliffs and other high places to which they may return for several breeding years. Most breeding activities take place in the spring; they are monogamous and may remain together for several years or possibly for life. Females lay up to four eggs, and then incubate them for six weeks. Typically, one or two young survive to fledge in about three months. These juvenile golden eagles usually attain full independence in the fall, after which they wander widely until establishing a territory for themselves in four to five years.

Aquila is a constellation on the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for 'eagle' and it represents the bird that carried Zeus/Jupiter's thunderbolts in Greek-Roman mythology.

Priscilla and Aquila were a first-century Christian missionary married couple described in the New Testament. Aquila is traditionally listed among the Seventy Disciples. They lived, worked, and traveled with the Apostle Paul, who described them as his "fellow workers in Christ Jesus".
Apamea or Apameia is the name of several Hellenistic cities in western Asia, after Apama, the Sogdian wife of Seleucus I Nicator, several of which are also former bishoprics and Catholic titular see.
Aquilaof Sinope was a translator of the Hebrew Bible into Greek, a proselyte, and disciple of Rabbi Akiva.

Apamea sordens, the rustic shoulder-knot or bordered apamea, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Johann Siegfried Hufnagel in 1766. It is distributed throughout Europe, east across the Palearctic to Central Asia and to China and Japan. It also occurs in North America.
Apamea Myrlea was an ancient city and bishopric on the Sea of Marmara, in Bithynia, Anatolia; its ruins are a few kilometers south of Mudanya, Bursa Province in the Marmara Region of Asian Turkey.

Apamea Cibotus, Apamea ad Maeandrum, Apamea or Apameia was an ancient city in Anatolia founded in the 3rd century BC by Antiochus I Soter, who named it after his mother Apama. It was in Hellenistic Phrygia, but became part of the Roman province of Pisidia. It was near, but on lower ground than, Celaenae (Kelainai).

Apamea or Apameia was a Hellenistic city on the left bank of the Euphrates, opposite the famous city of Zeugma, at the end of a bridge of boats connecting the two, founded by Seleucus I Nicator. The city was rebuilt by Seleucus I. The site, once partially covered by the village of Tilmusa, Şanlıurfa Province, Turkey, is now flooded by the lake formed by the Birecik Dam.

Apamea, on the right bank of the Orontes River, was an ancient Greek and Roman city. It was the capital of Apamene under the Macedonians, became the capital and Metropolitan Archbishopric of late Roman province Syria Secunda, again in the crusader period.

Apamea is a genus of moths in the family Noctuidae first described by Ferdinand Ochsenheimer in 1816.
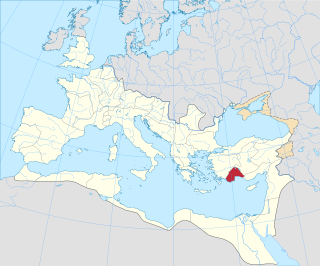
Lycia and Pamphylia was the name of a province of the Roman empire, located in southern Anatolia. It was created by the emperor Vespasian, who merged Lycia and Pamphylia into a single administrative unit. In 43 AD, the emperor Claudius had annexed Lycia. Pamphylia had been a part of the province of Galatia.

Apamea zeta is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It has a Holarctic distribution, and can be found throughout the Northern Hemisphere. It occurs throughout Europe and the northern half of North America.

Apamea furva, the confused, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. It is found throughout Europe. In southwestern Europe it is primarily montane. It is found as far north as the Arctic Circle. From Europe its range extends to Siberia, Turkey, Iran, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia and Xinjiang in China.

The Battle of Apamea was fought on 19 July 998 between the forces of the Byzantine Empire and the Fatimid Caliphate. The battle was part of a series of military confrontations between the two powers over control of northern Syria and the Hamdanid emirate of Aleppo, which in turn were part of the larger series of regional conflicts known as the Arab–Byzantine wars. The Byzantine regional commander, Damian Dalassenos, had been besieging Apamea, until the arrival of the Fatimid relief army from Damascus, under Jaysh ibn Samsama. In the subsequent battle, the Byzantines were initially victorious, but a lone Kurdish rider managed to kill Dalassenos, throwing the Byzantine army into panic. The fleeing Byzantines were then pursued, with much loss of life, by the Fatimid troops. This defeat forced the Byzantine emperor Basil II to personally campaign in the region the next year, and was followed in 1001 by the conclusion of a ten-year truce between the two states.

Apamea epomidion, the clouded brindle, is a moth of the family Noctuidae, sub-family Hadeninae. The species was first described by Adrian Hardy Haworth in 1809. It is found throughout continental Europe, the British Isles, Sweden and Central Asia. It is also found in the Altai Mountains, west Siberia, and in Amur.

Qalaat al-Madiq is a town and medieval fortress in northwestern Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate, located northeast of Hama. It is situated in the al-Ghab plain, on the eastern bank of the Orontes River. Nearby localities include the district center al-Suqaylabiyah to the south, Bureij and Karnaz to the southeast, Kafr Nabudah to the east, al-Huwash to the north, Huwayjah al-Sallah and Shathah to the northwest and Al-Tuwayni and Ennab to the west. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), Qalaat al-Madiq had a population of 12,925 in the 2004 census. It is the administrative center and second largest locality in the Qalaat al-Madiq nahiyah ("subdistrict") which consisted of 40 localities with a collective population of 85,597 in 2004. The town's inhabitants are predominantly Sunni Muslims.

The Facebook Aquila is an experimental solar-powered drone developed by Facebook for use as an atmospheric satellite, intended to act as relay stations for providing internet access to remote areas. The Aquila first flew on 28 June 2016 with a second aircraft successfully flying in 2017. Internal development of the Aquila aircraft was stopped in June 2018.














