
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion. The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west.
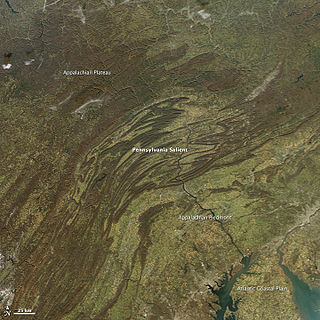
The geology of the Appalachians dates back to more than 480 million years ago. A look at rocks exposed in today's Appalachian Mountains reveals elongate belts of folded and thrust faulted marine sedimentary rocks, volcanic rocks and slivers of ancient ocean floor – strong evidence that these rocks were deformed during plate collision. The birth of the Appalachian ranges marks the first of several mountain building plate collisions that culminated in the construction of the supercontinent Pangaea with the Appalachians and neighboring Anti-Atlas mountains near the center. These mountain ranges likely once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before they were eroded.

The Piedmont is a plateau region located in the Eastern United States. It is situated between the Atlantic coastal plain and the main Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New York in the north to central Alabama in the south. The Piedmont Province is a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division which consists of the Gettysburg-Newark Lowlands, the Piedmont Upland and the Piedmont Lowlands sections.

The geography of North Carolina falls naturally into three divisions — the Appalachian Mountains in the west, the central Piedmont Plateau, and the eastern Atlantic Coastal Plain. North Carolina covers 53,821 square miles (139,396 km2) and is 503 miles (810 km) long by 150 miles (241 km) wide. The physical characteristics of the state vary from the summits of the Smoky Mountains, an altitude of near seven thousand feet (2,130 m) in the west, sloping eastward to sea level along the coast and beaches of the Atlantic Ocean.
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both regions overlap. The region of overlap is called a vegetation tension zone.
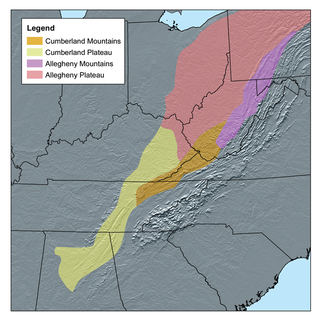
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau in the Appalachian Mountains of the United States. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and Tennessee, and portions of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia. The terms "Allegheny Plateau" and the "Cumberland Plateau" both refer to the dissected plateau lands lying west of the main Appalachian Mountains. The terms stem from historical usage rather than geological difference, so there is no strict dividing line between the two. Two major rivers share the names of the plateaus, with the Allegheny River rising in the Allegheny Plateau and the Cumberland River rising in the Cumberland Plateau in Harlan County, Kentucky.

The Allegheny Front is the major southeast- or east-facing escarpment in the Allegheny Mountains in southern Pennsylvania, western Maryland, eastern West Virginia, and western Virginia, USA. The Allegheny Front forms the boundary between the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians to its east and the Appalachian Plateau to its west. The Front is closely associated with the Appalachian Mountains' Eastern Continental Divide, which in this area divides the waters of the Ohio/Mississippi river system, flowing to the Gulf of Mexico, from rivers flowing into Chesapeake Bay and from there into the Atlantic Ocean.
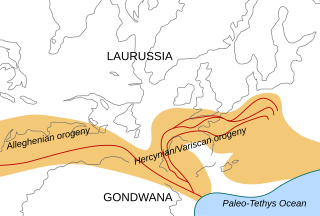
The Alleghanian orogeny or Appalachian orogeny is one of the geological mountain-forming events that formed the Appalachian Mountains and Allegheny Mountains. The term and spelling Alleghany orogeny was originally proposed by H.P. Woodward in 1957.

The Appalachian Plateau is a series of rugged dissected plateaus located on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. The Appalachian Mountains are a mountain range that run down the Eastern United States. The Appalachian Plateau is the northwestern part of the Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New York to Alabama. The plateau is a second level United States physiographic region, covering parts of the states of New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Maryland, West Virginia, Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama, and Georgia.

The California Floristic Province (CFP) is a floristic province with a Mediterranean-type climate located on the Pacific Coast of North America with a distinctive flora similar to other regions with a winter rainfall and summer drought climate like the Mediterranean Basin. This biodiversity hotspot is known for being the home of the Sierran giant sequoia tree and its close relative the coast redwood. In 1996, the Province was designated as a biodiversity hotspot allowing it to join ranks among 33 other areas in the world with many endemic species. To be named a biodiversity hotspot, an area has to contain species and plant life that cannot be found anywhere else in the world. The California Floristic Province is home to over 3,000 species of vascular plants, 60% of which are endemic to the province.

New Jersey is a state within the United States of America that lies on the north eastern edge of the North American continent. It shares a land border with the state of New York along the north, ratified by both states after the New York – New Jersey Line War, which is its only straight line border. New Jersey is slightly larger than the country of Kuwait.

North American Atlantic Region is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom identified by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne, spanning from the Atlantic and Gulf coasts to the Great Plains and comprising a major part of the United States and southeastern portions of Canada. It is bordered by the Circumboreal floristic region in the north, by the Rocky Mountain and Madrean floristic regions in the west and by the Caribbean floristic region of the Neotropical Kingdom in the south of Florida. The flora of the region comprises two endemic monotypic families, Hydrastidaceae and Leitneriaceae, and is characterized by about a hundred of endemic genera. The degree of species endemism is very high, many species are Tertiary relicts, which survived the Wisconsin glaciation and are now concentrated in the Appalachians and the Ozarks. A number of genera are shared only with the Canadian floristic province of the Circumboreal region. Moreover, as has long been noted, a large number of relict genera are shared with the relatively distant Eastern Asiatic Region and sometimes Southeast Asia. R. F. Thorne counted at least 74 genera restricted to eastern North America and Asia. The fossil record indicates that during the Tertiary period a warm temperate zone extended across much of the Northern Hemisphere, linking America to Asia.
The native flora of the United States includes about 17,000 species of vascular plants, plus tens of thousands of additional species of other plants and plant-like organisms such as algae, lichens and other fungi, and mosses. About 3,800 additional non-native species of vascular plants are recorded as established outside of cultivation in the U.S., as well as a much smaller number of non-native non-vascular plants and plant relatives. The United States possesses one of the most diverse temperate floras in the world, comparable only to that of China.

The Rocky Mountain Floristic Region, also known as the Rocky Mountain Floristic Province, is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in western North America delineated by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne. The region extends from Kodiak Island in Alaska to the San Francisco Bay Area and Sierra Nevada in California. The Vancouverian Province comprises the coastal part of the region for its entire length, including the Pacific Coast Ranges, and the Rocky Mountain Province includes the Rocky Mountains and associated ranges. There are no endemic plant families in the region but many endemic genera and species.

The Madrean Region is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in North America, as delineated by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne. It occupies arid or semiarid areas in the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico and is bordered by the Rocky Mountain Region and North American Atlantic Region of the Holarctic Kingdom in the north and in the east, Caribbean Region of the Neotropical Kingdom in the south.

The Circumboreal Region in phytogeography is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in Eurasia and North America, as delineated by such geobotanists as Josias Braun-Blanquet and Armen Takhtajan.

Pochuck Mountain is a ridge in the New York-New Jersey Highlands region of the Appalachian Mountains. Pochuck Mountain's summit and most of its peaks lie within Vernon Township, Sussex County, New Jersey, although the south-western portion of the ridge lies within Hardyston Township, and the north-eastern tip of the ridge extends over the New York state line into Orange County. The ridge marks the eastern edge of the Great Appalachian Valley, and it divides the watersheds of the Wallkill River and its tributary Pochuck Creek. The two rivers meet at Pochuck Neck, marking the terminus of the ridge.
The North American Prairies Province is a large grassland floristic province within the North American Atlantic Region, a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom. It lies between the Appalachian Province and the Rocky Mountains and includes the prairies of the Great Plains. It is bounded by the Canadian coniferous forests on the north and the arid semideserts to the southwest. The province itself is occupied by temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands. Endemism is rather limited in this province, and its boundaries are vague. During the Pleistocene much of the province was glaciated.
The Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plain Province is a coastal plain floristic province within the North American Atlantic Region, a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom. It lies to the east and south of the Appalachian Province. It encompasses the Atlantic coastal plain minus central and southern Florida, and the Gulf coastal plain. Although the precise definition varies, it extends as far north as Long Island or southern Nova Scotia, and as far south as eastern Texas or northeastern Mexico. Additionally, at the Mississippi Embayment the province stretches up to the confluence of the Ohio and Mississippi rivers in Cairo, Illinois.













