
The Nearctic realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting the Earth's land surface.

The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both regions overlap. The region of overlap is called a vegetation tension zone.

Temperate rainforests are coniferous or broadleaf forests that occur in the temperate zone and receive heavy rain.
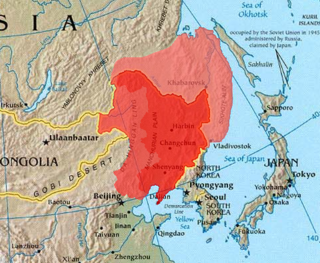
Outer Manchuria, alternatively called Outer Northeast China or Russian Manchuria, refers to a territory in Northeast Asia that is currently part of Russia and had formerly belonged to a series of Chinese dynasties, including the Tang, Liao, Jin, Eastern Xia, Yuan, Northern Yuan, Ming, Later Jin, and Qing dynasties. It is considered part of the larger region of Manchuria. The Russian Empire annexed this territory from Qing China by way of the Treaty of Aigun in 1858 and the Treaty of Peking in 1860. The northern part of the area was disputed by Qing China and the Russian Empire between 1643 and 1689.

Laurel forest, also called laurisilva or laurissilva, is a type of subtropical forest found in areas with high humidity and relatively stable, mild temperatures. The forest is characterized by broadleaf tree species with evergreen, glossy and elongated leaves, known as "laurophyll" or "lauroid". Plants from the laurel family (Lauraceae) may or may not be present, depending on the location.

The Boreal Kingdom or Holarctic Kingdom (Holarctis) is a floristic kingdom identified by botanist Ronald Good, which includes the temperate to Arctic portions of North America and Eurasia. Its flora is inherited from the ancient supercontinent of Laurasia. However, parts of the floristic kingdom were glaciated during the Pleistocene and as a consequence have a very young flora. Cenozoic relicts found refuge in the southern and mountainous parts of the kingdom, especially in the Eastern Asiatic Region and southern North American Atlantic Region.

The California Floristic Province (CFP) is a floristic province with a Mediterranean-type climate located on the Pacific Coast of North America with a distinctive flora similar to other regions with a winter rainfall and summer drought climate like the Mediterranean Basin. This biodiversity hotspot is known for being the home of the Sierran giant sequoia tree and its close relative the coast redwood. In 1996, the Province was designated as a biodiversity hotspot allowing it to join ranks among 33 other areas in the world with many endemic species. To be named a biodiversity hotspot, an area has to contain species and plant life that cannot be found anywhere else in the world. The California Floristic Province is home to over 3,000 species of vascular plants, 60% of which are endemic to the province.

The Cape Floristic Region is a floristic region located near the southern tip of South Africa. It is the only floristic region of the Cape Floristic Kingdom, and includes only one floristic province, known as the Cape Floristic Province.
The World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions (WGSRPD) is a biogeographical system developed by the international Biodiversity Information Standards (TDWG) organization, formerly the International Working Group on Taxonomic Databases. The WGSRPD standards, like other standards for data fields in botanical databases, were developed to promote "the wider and more effective dissemination of information about the world's heritage of biological organisms for the benefit of the world at large". The system provides clear definitions and codes for recording plant distributions at four scales or levels, from "botanical continents" down to parts of large countries. Current users of the system include the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), and the World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP).

North American Atlantic Region is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom identified by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne, spanning from the Atlantic and Gulf coasts to the Great Plains and comprising a major part of the United States and southeastern portions of Canada. It is bordered by the Circumboreal floristic region in the north, by the Rocky Mountain and Madrean floristic regions in the west and by the Caribbean floristic region of the Neotropical Kingdom in the south of Florida. The flora of the region comprises two endemic monotypic families, Hydrastidaceae and Leitneriaceae, and is characterized by about a hundred of endemic genera. The degree of species endemism is very high, many species are Tertiary relicts, which survived the Wisconsin glaciation and are now concentrated in the Appalachians and the Ozarks. A number of genera are shared only with the Canadian floristic province of the Circumboreal region. Moreover, as has long been noted, a large number of relict genera are shared with the relatively distant Eastern Asiatic Region and sometimes Southeast Asia. R. F. Thorne counted at least 74 genera restricted to eastern North America and Asia. The fossil record indicates that during the Tertiary period a warm temperate zone extended across much of the Northern Hemisphere, linking America to Asia.
The native flora of the United States includes about 17,000 species of vascular plants, plus tens of thousands of additional species of other plants and plant-like organisms such as algae, lichens and other fungi, and mosses. About 3,800 additional non-native species of vascular plants are recorded as established outside of cultivation in the U.S., as well as a much smaller number of non-native non-vascular plants and plant relatives. The United States possesses one of the most diverse temperate floras in the world, comparable only to that of China.

The Antarctic Floristic Kingdom, also the Holantarctic Kingdom, is a floristic kingdom that includes most areas of the world south of 40°S latitude. It was first identified by botanist Ronald Good, and later by Armen Takhtajan. The Antarctic Floristic Kingdom is a classification in phytogeography, different from the Antarctic realm classification in biogeography, and from Antarctic flora genera/species classifications in botany.

The Rocky Mountain Floristic Region, also known as the Rocky Mountain Floristic Province, is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in western North America delineated by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne. The region extends from Kodiak Island in Alaska to the San Francisco Bay Area and Sierra Nevada in California. The Vancouverian Province comprises the coastal part of the region for its entire length, including the Pacific Coast Ranges, and the Rocky Mountain Province includes the Rocky Mountains and associated ranges. There are no endemic plant families in the region but many endemic genera and species.

The Madrean Region is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in North America, as delineated by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne. It occupies arid or semiarid areas in the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico and is bordered by the Rocky Mountain Region and North American Atlantic Region of the Holarctic Kingdom in the north and in the east, Caribbean Region of the Neotropical Kingdom in the south.

The Circumboreal Region in phytogeography is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in Eurasia and North America, as delineated by such geobotanists as Josias Braun-Blanquet and Armen Takhtajan.

The Paleotropical Kingdom (Paleotropis) is a floristic kingdom comprising tropical areas of Africa, Asia and Oceania, as proposed by Ronald Good and Armen Takhtajan. Part of its flora, inherited from the ancient supercontinent of Gondwana or exchanged later, is shared with the Neotropical Kingdom, comprising tropical areas of Central and South America. Moreover, the Paleotropical flora influenced the tropical flora of the Australian Kingdom. The Paleotropical Kingdom is subdivided into five floristic subkingdoms according to Takhtajan and about 13 floristic regions. In this article the floristic subkingdoms and regions are given as delineated by Takhtajan.

All of the animals living in Asia and its surrounding seas and islands are considered the fauna of Asia. Since there is no natural biogeographic boundary in the west between Europe and Asia, the term "fauna of Asia" is somewhat elusive. Temperate Asia is the eastern part of the Palearctic realm, and its south-eastern part belongs to the Indomalayan realm. Asia shows a notable diversity of habitats, with significant variations in rainfall, altitude, topography, temperature and geological history, which is reflected in its richness of animal life.
The Saharo-Arabian Region is a floristic region of the Holarctic Kingdom proposed by Armen Takhtajan. The region is covered by hot deserts, semideserts and savanna.

The flora of China consists of a diverse range of plant species including over 39,000 vascular plants, 27,000 species of fungi and 3000 species of bryophytes. More than 30,000 plant species are native to China, representing nearly one-eighth of the world's total plant species, including thousands found nowhere else on Earth. China's land, extending over 9.6 million km, contains a variety of ecosystems and climates for plants to grow in. Some of the main climates include shores, tropical and subtropical forests, deserts, elevated plateaus and mountains. The events of the continental drift and early Paleozoic Caledonian movement also play a part in creating climatic and geographical diversity resulting in high levels of endemic vascular flora. These landscapes provide different ecosystems and climates for plants to grow in, creating a wide variety of different flora spanning over not just China but different parts of the world now.



















