
Abies balsamea or balsam fir is a North American fir, native to most of eastern and central Canada and the northeastern United States.

Symphyotrichum novae-angliae is a species of flowering plant in the aster family (Asteraceae) native to central and eastern North America. Commonly known as New England aster, hairy Michaelmas-daisy, or Michaelmas daisy, it is a perennial, herbaceous plant usually between 30 and 120 centimeters tall and 60 to 90 cm wide.

Claytonia virginica, the Virginia springbeauty, eastern spring beauty, grass-flowernarrowleaf springbeauty or fairy spud, is an herbaceous perennial plant in the family Montiaceae. Its native range is eastern North America. Its scientific name honors Colonial Virginian botanist John Clayton (1694–1773).

Persicaria pensylvanica is a species of flowering plant in the buckwheat family, Polygonaceae. It is native to parts of North America, where it is widespread in Canada and the United States. It has also been noted as an introduced species in parts of Europe and South America. Common names include Pennsylvania smartweed and pinkweed.

Waldsteinia fragarioides (syn. Dalibarda fragarioides Michx. and Geum fragarioides, also called Appalachian barren strawberry, or just barren strawberry, is a low, spreading plant with showy yellow flowers that appear in early spring. This plant is often used as an underplanting in perennial gardens.

Ranunculus acris is a species of flowering plant in the family Ranunculaceae, and is one of the more common buttercups across Europe and temperate Eurasia. Common names include meadow buttercup, tall buttercup, common buttercup and giant buttercup.

Eurybia macrophylla, commonly known as the bigleaf aster, large-leaved aster, largeleaf aster or bigleaf wood aster, is an herbaceous perennial in the family Asteraceae that was formerly treated in the genus Aster. It is native to eastern North America, with a range extending from eastern and central Canada through the northeastern deciduous and mixed forests of New England and the Great Lakes region and south along the Appalachians as far as the northeastern corner of Georgia, and west as far as Minnesota, Missouri and Arkansas. The flowers appear in the late summer to early fall and show ray florets that are usually either a deep lavender or violet, but sometimes white, and disc florets that are cream-coloured or light yellow, becoming purple as they mature. It is one of the parent species of the hybrid Eurybia × herveyi.

Epigaea repens, the mayflower, trailing arbutus, or ground laurel, is a low, spreading shrub in the family Ericaceae. It is found from Newfoundland to Florida, west to Kentucky and the Northwest Territories.

Jeffersonia, also known as twinleaf or rheumatism root, is a small genus of herbaceous perennial plants in the family Berberidaceae. They are uncommon spring wildflowers and grow in limestone soils of rich deciduous forests. Jeffersonia was named for United States President Thomas Jefferson by his contemporary Benjamin Smith Barton. This genus was formerly grouped in genus Podophyllum. Twinleaf is protected by state laws as a threatened or endangered plant in Georgia, Iowa, New York, and New Jersey.

Senna hebecarpa, with the common names American senna and wild senna, is a species of legume native to eastern North America.

Cardamine diphylla is a flowering plant in the family Brassicaceae. It is a spring flowering woodland plant that is native to eastern North America.

Solidago rugosa, commonly called the wrinkleleaf goldenrod or rough-stemmed goldenrod, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to North America, where it is widespread across eastern and central Canada and the eastern and central United States. It is usually found in wet to mesic habitats.

Strophostyles is monophyletic three-species genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae. Common names for the genus include wild bean and fuzzybean. It consists of annual and perennial herbaceous vines, ranging in their native distribution from Nevada, east to Florida, and north to the Great Lakes and eastern Canada. The etymology of the name is strophe (turning) + stylos (style), referring to the curve of the style within the keel petal.
This is a list of plants used by the indigenous people of North America. For lists pertaining specifically to the Cherokee, Iroquois, Navajo, and Zuni, see Cherokee ethnobotany, Iroquois ethnobotany, Navajo ethnobotany, and Zuni ethnobotany.
See also Zuni ethnobotany, and Native American ethnobotany.
This is a list of plants and how they are used in Zuni culture.
This is a list of plants documented to have been traditionally used by the Cherokee, and how they are used.

Potentilla canadensis, the dwarf cinquefoil, is a species of cinquefoil native to North America.

Agastache nepetoides, commonly known as yellow giant hyssop, is a perennial flowering plant native to the central and eastern United States and Canada. It is a member of the Lamiaceae (mint) family.
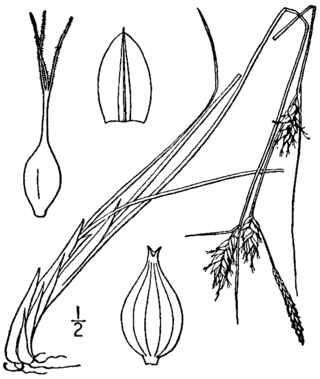
Carex oligosperma, common name fewseed sedge, few-seeded sedge, and few-fruited sedge, is a perennial plant in the Carex genus. A distinct variety, Carex oligosperma var. oligosperma, exists.















