Year 2 BC was a common year starting on Thursday or Friday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Silvanus. The denomination 2 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Sextus Julius Frontinus was a prominent Roman civil engineer, author, soldier and senator of the late 1st century AD. He was a successful general under Domitian, commanding forces in Roman Britain, and on the Rhine and Danube frontiers. A novus homo, he was consul three times. Frontinus ably discharged several important administrative duties for Nerva and Trajan. However, he is best known to the post-Classical world as an author of technical treatises, especially De aquaeductu, dealing with the aqueducts of Rome.

The Janiculum, occasionally known as the Janiculan Hill, is a hill in western Rome, Italy. Although it is the second-tallest hill in the contemporary city of Rome, the Janiculum does not figure among the proverbial Seven Hills of Rome, being west of the Tiber and outside the boundaries of the ancient city.
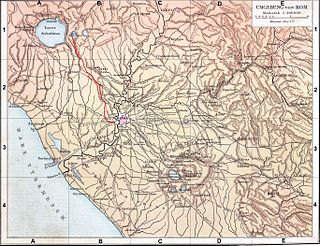
The Aniene, formerly known as the Teverone, is a 99-kilometer (62 mi) river in Lazio, Italy. It originates in the Apennines at Trevi nel Lazio and flows westward past Subiaco, Vicovaro, and Tivoli to join the Tiber in northern Rome. It formed the principal valley east of ancient Rome and became an important water source as the city's population expanded. The falls at Tivoli were noted for their beauty. Historic bridges across the river include the Ponte Nomentano, Ponte Mammolo, Ponte Salario, and Ponte di San Francesco, all of which were originally fortified with towers.

The Aqua Appia was the first Roman aqueduct, constructed in 312 BC by the co-censors Gaius Plautius Venox and Appius Claudius Caecus, the same Roman censor who also built the important Via Appia.

The Aqua Augusta, or Serino Aqueduct, was one of the largest, most complex and costliest aqueduct systems in the Roman world; it supplied water to at least eight ancient cities in the Bay of Naples including Pompeii and Herculaneum. This aqueduct was unlike any other of its time, being a regional network rather than being focused on one urban centre.

The Romans constructed aqueducts throughout their Republic and later Empire, to bring water from outside sources into cities and towns. Aqueduct water supplied public baths, latrines, fountains, and private households; it also supported mining operations, milling, farms, and gardens.

Aqua Anio Novus was an ancient Roman aqueduct supplying the city of Rome. Like the Aqua Claudia, it was begun by emperor Caligula in 38 AD and completed in 52 AD by Claudius, who dedicated them both on August 1.

Aqua Claudia was an ancient Roman aqueduct that, like the Aqua Anio Novus, was begun by Emperor Caligula in 38 AD and finished by Emperor Claudius in 52 AD.

The Aqueduct of the Miracles is a Roman aqueduct in the Roman colonia of Emerita Augusta –present-day Mérida, Spain–, capital of the Roman province of Lusitania. It was built during the first century AD to supply water from the Proserpina Dam into the city. After the fall of the Roman Empire, the aqueduct fell into decay and today it is in ruins with only a relatively small section of the aqueduct bridge standing. It is part of the Archaeological Ensemble of Mérida, which is one of the largest and most extensive archaeological sites in Spain and that was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1993.

The Aqua Julia is a Roman aqueduct built in 33 BC by Agrippa under Augustus to supply the city of Rome. It was repaired and expanded by Augustus from 11–4 BC.

The Acqua Felice is one of the aqueducts of Rome, completed in 1586 by Pope Sixtus V, whose birth name, which he never fully abandoned, was Felice Peretti. The first new aqueduct of early modern Rome, its source is at the springs at Pantano Borghese, off Via Casilina. Its length is fifteen miles (24 km), running underground for eight miles (13 km) from its source, first in the channel of Aqua Alexandrina, then alternating on the arches of the Aqua Claudia and the Aqua Marcia for seven miles (11 km) to its terminus at the Fontana dell'Acqua Felice on the Quirinal Hill, standing to one side of the Strada Pia, so as to form a piazza in this still new part of Rome. The engineer was Giovanni Fontana, brother of Sixtus' engineer-architect Domenico Fontana, who recorded that the very day the new pope entered the Lateran, he decided that he would bring water once again to the hills of Rome, which had remained waterless and sparsely inhabited, largely by monasteries, since the original ancient aqueducts had been destroyed in the sixth century. From the source, which Sixtus purchased, there was only a very small fall, and the work required an underground conduit as well as an aqueduct carried on arches.
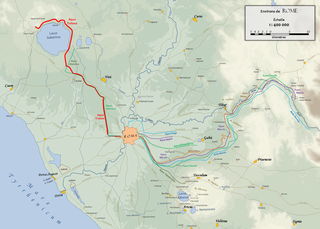
The Aqua Traiana was a 1st-century Roman aqueduct built by Emperor Trajan and inaugurated in 109 AD. It channelled water from sources around Lake Bracciano, 40 km (25 mi) north-west of Rome, to ancient Rome. It joined the earlier Aqua Alsietina to share a common lower route into Rome.

The Aqua Tepula is an ancient Roman aqueduct completed in 125 BC by censors Gnaeus Servilius Caepio, who had served as consul in 141 BC, and Lucius Cassius Longinus Ravilla.

In Ancient Rome, the Aqua Alsietina was the earlier of the two western Roman aqueducts, erected sometime around 2 BC, during the reign of emperor Augustus. It was the only water supply for the Transtiberine region, on the right bank of the river Tiber until the Aqua Traiana was built.
The Via Sublacensis was a Roman road constructed to connect Nero's palace in present-day Subiaco to Rome, splitting off from the Via Valeria near Varia, about 10 km northeast of Tivoli.

The Aqua Marcia is one of the longest of the eleven aqueducts that supplied the city of Rome. The aqueduct was built between 144–140 BC, during the Roman Republic. The still-functioning Acqua Felice from 1586 runs on long stretches along the route of the Aqua Marcia.

Aqua Crabra was a Roman aqueduct supplying villas in the hinterland of the ancient town of Tusculum.

The Tor Fiscale park in Rome is located between the 3rd and 4th miles of the Roman Via Latina and forms part of the Appian Way Regional Park. It is connected by a short path to Rome's Aqueduct Park and is dominated by a 30 m-high tower, which gives the park its name. Several aqueducts traversed the area and their remains are still visible.

















