
Sarracenia is a genus comprising 8 to 11 species of North American pitcher plants, commonly called trumpet pitchers. The genus belongs to the family Sarraceniaceae, which also contain the closely allied genera Darlingtonia and Heliamphora.

The Drosophilidae are a diverse, cosmopolitan family of flies, which includes species called fruit flies, although they are more accurately referred to as vinegar or pomace flies. Another distantly related family of flies, Tephritidae, are true fruit flies because they are frugivorous, and include apple maggot flies and many pests. The best known species of the Drosophilidae is Drosophila melanogaster, within the genus Drosophila, also called the "fruit fly." Drosophila melanogaster is used extensively for studies concerning genetics, development, physiology, ecology and behaviour. Many fundamental biological mechanisms were discovered first in D. melanogaster. The fruit fly is mostly composed of post-mitotic cells, has a very short lifespan, and shows gradual aging. As in other species, temperature influences the life history of the animal. Several genes have been identified that can be manipulated to extend the lifespan of these insects. Additionally, Drosophila subobscura, also within the genus Drosophila, has been reputed as a model organism for evolutionary-biological studies, along with D. sechellia for the evolution of host specialization on the toxic noni fruit and Scaptomyza flava for the evolution of herbivory and specialist on toxic mustard leaves.

Sarracenia flava, the yellow pitcherplant, is a carnivorous plant in the family Sarraceniaceae. Like all the Sarraceniaceae, it is native to the New World. Its range extends from southern Alabama, through Florida and Georgia, to the coastal plains of southern Virginia, North Carolina and South Carolina. Populations also exist in the Piedmont, Mendocino County, California and mountains of North Carolina.

Anamirta is a genus of woody vines in the family of Menispermaceae, native to southern Asia. It has a single extant species, which is Anamirta cocculus.

Syncarpha is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. The flowers are known by the common name: everlastings. The genus is endemic to the fynbos of the Eastern and Western Cape in South Africa.

Monopyle is a genus of plants in the family Gesneriaceae.
Triclisia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Menispermaceae. It is native to tropical Africa.

Micromyrtus flava is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a slender, erect shrub with spreading stems, narrowly-elliptic leaves and yellow flowers.

Aeginetia is a genus of plants in the broomrape family Orobanchaceae, native mostly to tropical Asia and also Cameroon.
Aeginetia flava is a plant in the broomrape family Orobanchaceae, native to Thailand. The specific epithet flava means 'yellow' or 'golden yellow', referring to the flowers.

Lachenalia flava, the golden opal flower, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Lachenalia native to the southwest Cape Provinces of South Africa. It has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.

Carex flava, called hedgehog grass or large yellow sedge, is a widespread species of sedge, native to the northern United States, Canada, Iceland, Europe, the Atlas Mountains in Africa, the Transcaucasus area, and parts of Siberia. It is a synonym of the Carex flava species complex.
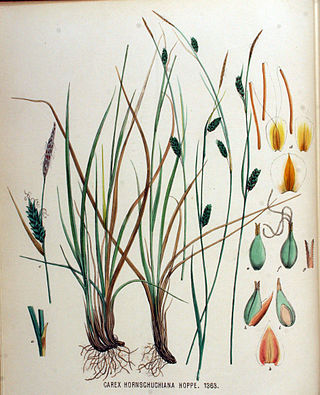
Carex hostiana, the tawny sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to Europe and northeast Canada, and extinct in Massachusetts. It is a member of the Carex flava species complex.

Carex lepidocarpa, called the long-stalked yellow-sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to eastern Canada, Morocco, and most of Europe. It is a member of the Carex flava species complex.
Andreadoxa is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Rutaceae.
Aspidonepsis is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Apocynaceae.
Dauresia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Asteraceae.

Pseudomussaenda is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Rubiaceae.
Phlyctidocarpa is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Apiaceae. It contains a single species, Phlyctidocarpa flava. Its native range is Namibia.

Oxalis flava is a species of succulent that is native to Cape Province in South Africa. This plant was first described in 1753.













