
Gars are an ancient group of ray-finned fish in the family Lepisosteidae. They comprise seven living species of fish in two genera that inhabit fresh, brackish, and occasionally marine waters of eastern North America, Central America and Cuba in the Caribbean, though extinct members of the family were more widespread. They are the only surviving members of the Ginglymodi, a clade of fish which first appeared during the Triassic, over 240 million years ago, and are one of only two surviving groups of holosteian fish, alongside the bowfins, which have a similar distribution.
Hemiramphidae is a family of fishes that are commonly called halfbeaks, spipe fish or spipefish. They are a geographically widespread and numerically abundant family of epipelagic fish inhabiting warm waters around the world. The halfbeaks are named for their distinctive jaws, in which the lower jaws are significantly longer than the upper jaws. The similar viviparous halfbeaks have often been included in this family.

Hemiramphus is a genus of schooling marine fish commonly called halfbeaks, garfish, or ballyhoos, and are members of the family Hemiramphidae. They inhabit the surface of warm temperate and tropical sea, and feed on algae, plankton, and smaller fish. Hemiramphus species are edible but are more important as food fish for larger predatory species including dolphinfish and billfish.
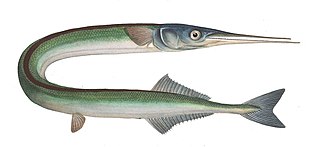
The garfish, also known as the garpike or sea needle, is a pelagic, oceanodromous needlefish found in brackish and marine waters of the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean, Caribbean, Black, and Baltic Seas.

Pompanos are marine fish in the genus Trachinotus in the family Carangidae. Pompano may also refer to various other, similarly shaped members of the Carangidae, or the order Perciformes. Their appearance is of deep-bodied fishes, exhibiting strong lateral compression, with a rounded face and pronounced curve to the anterior portion of their dorsal profile. Their ventral profile is noticeably less curved by comparison, while their anterior profile is straight-edged, tapering sharply to a narrow caudal peduncle. Their dorsal and anal fins are typically sickle-shaped, with very long anterior rays and a succession of much shorter rays behind, with a similarly long & curved, deeply forked tail which has a narrow base. They are typically overall silvery in color, sometimes with dark or yellowish fins, and one or a few black markings on the side of their body. They are toothless and are relatively large fish, up to about 1.2 m (3.9 ft) long, although most species reach no more than half or two-thirds of that size. They are found worldwide in warmer seas, sometimes also entering brackish waters.

Hyporhamphus ihi, the known as the garfish, piper or by its Māori name takeke, is a halfbeak found all around New Zealand in shallow inshore waters.
The snubnosed eel, Simenchelys parasitica, also known as the pug-nosed eel, slime eel, or snub-nose parasitic eel, is a species of deep-sea eel and the only member of its genus. Some authors classify it as the sole member of the subfamily Simenchelyinae of the family Synaphobranchidae, or cutthroat eels, while others place it in its own monotypic family, the Simenchelyidae. It is found in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, typically at a depth of 500–1,800 m (1,600–5,900 ft) near the bottom. Although typically a scavenger, it is better known for using its powerful jaws and teeth to burrow into larger fishes as a parasite. This species is harmless to humans and of no interest to fisheries. The generic name Simenchelys translates literally as "pug-nosed eel".

The snubnose sculpin is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cottidae, the typical sculpins. This fish is found in the eastern Pacific Ocean.

Arrhamphus sclerolepis, the Northern snub-nosed garfish, is a species of halfbeak in the genus Arrhamphus found in coastal waters of the Indo-West Pacific around Papua New Guinea and Australia, and in the freshwaters of adjacent river systems. Considered a good game fish, but of little commercial value either as food or as an aquarium fish. This species is known to anglers in Australia as the snub-nosed gar. The species is distinguished from most other halfbeaks by the lower jaw being only slightly longer than the upper jaw. In coastal wetlands this species feeds mainly on sea grass, with some crustaceans, but in urban waterways it feeds on algae at night and on ants during the day.

Xenentodon is a genus of needlefishes native to Asia. It is one of ten genera in the family Belonidae.

Zenarchopterus is a genus of viviparous halfbeaks. These fish are found in marine, brackish and fresh water of the Indo-Pacific region. Despite being in the viviparous halfbeak family, Zenarchopterus species are oviparous.
Robert's river garfish is a species of viviparous halfbeak endemic to Papua New Guinea where it is only known from the area around Kokoda. This species grows to a length of 13 centimetres (5.1 in) SL.
The Philippine snubnose halfbeak is a species of halfbeak. It is a coastal species that originates from the South China and Sulu Seas around the Philippines and Malaysia. It grows to about 22.7 centimetres (8.9 in) SL. It is the only member of its monotypic genus and was originally described as Oxyporhamphus brevis by Alvin Seale in 1910 with the type locality given as Paawacan, Palawan Island, Philippines.

Belone is a genus of needlefish common in brackish and marine waters. It is one of ten genera in the family Belonidae.

Hyporhamphus is a genus of halfbeaks. The species in this genus are distributed throughout the warmer seas of the world, most species being Indo-Pacific and there are some freshwater species.
The Cumberland snubnose darter is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish, a darter from the subfamily Etheostomatinae, part of the family Percidae, which also contains the perches, ruffes and pikeperches. This species is found in the middle Cumberland River drainage in Tennessee, Kentucky, Virginia, North Carolina, Georgia, and Alabama. It is absent in reaches above the Big South Fork, rare in North Carolina, and absent in western tributaries of the Tennessee River. While research on the ecology of E. atripinne is not extensive, what is known is they are usually found in small to medium freshwater streams in gravel riffle areas where their eggs can attach to the substrate and be left unguarded. E. atripinne can be found within a wide range of depths in its environment, leading its being classified as benthopelagic. While its global status is secure, the American Fisheries Society labels it with a status of “Special Concern”.

The snubnose darter is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish, a darter from the subfamily Etheostomatinae, part of the family Percidae, which also contains the perches, ruffes and pikeperches. It is endemic to the southeastern United States.
The black-tipped halfbeak, Hyporhamphus neglectissimus, is a halfbeak from the family Hemiramphidae.
Arrhamphus krefftii, the snub-nosed garfish, is a species of halfbeak in the genus Arrhamphus found in coastal waters of Australia from south of Rockhampton in Queensland to Sydney. The identity of the person honoured in the specific name is uncertain but it is thought that it may be the Australian zoologist and paleontologist Gerard Krefft (1830–1881). This species was previously classified as a subspecies of Arrhamphus sclerolepis, and remains so according to some authorities. This species is a herbivore and eats seagrass during the day. At night, it is a carnivore, eating mainly crustaceans.
The snubnose eelpout is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Zoarcidae, the eelpouts. This species is found in the deep waters of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans











