
Wolf spiders are members of the family Lycosidae. They are robust and agile hunters with excellent eyesight. They live mostly in solitude, hunt alone, and usually do not spin webs. Some are opportunistic hunters, pouncing upon prey as they find it or chasing it over short distances; others wait for passing prey in or near the mouth of a burrow.

The Artoriinae are a subfamily of wolf spiders. The monophyly of the subfamily has been confirmed in a molecular phylogenetic study, although the relationships among the subfamilies was shown to be less certain.

Artoriopsis is a genus of wolf spiders first described by Volker W. Framenau in 2007. It is endemic to Australia and is most diverse in the southern half of the continent, though A. anacardium is found in the tropical north of Australia. Its body size ranges from 3 to 11 mm, with males smaller than females. It appears to prefer open, vegetated or sandy areas of moderate humidity.

Artoria is a genus of spiders in the family Lycosidae. It was first described in 1877 by Tamerlan Thorell, and the type species is Artoria parvula. In 1960, Roewer erected the genera Artoriella and Trabeola. However, in 2002, Volker Framenau reviewed Artoria and synonymised both these genera with Artoria.
Dingosa is a genus of spiders in the family Lycosidae. It was first described in 1955 by Roewer. As of 2017, it contains 6 species from Australia and from South America.

Tasmanicosa is a genus of spiders in the family Lycosidae. It was first described in 1959 by Roewer. As of 2017, it contains 14 species, all from Australia.

Tetralycosa is a genus of Australian spiders in the family Lycosidae first described by Roewer in 1960, later revised by Framenau & Hudson to include thirteen species. Genetic studies show that these spiders all diverged from a common ancestor who likely wandered into the salty area and remained. They live exclusively in certain saline environments of Australia's interior, including coastal beaches, mound springs, clay pans, and salt lakes. There haven't been enough studies to establish a conservation status, but some species have only been found in solitary salt lakes, suggesting that the increase of mining, agriculture, recreational, and similar disturbances of these unique ecosystems may eventually lead to their extinction if not properly regulated.

Venatrix is a genus of wolf spiders first described by Carl Friedrich Roewer in 1960.
Barbara Baehr is a German research scientist, entomologist, arachnologist, and spider taxonomist. She has described over 400 new spider species, mostly from Australia. She is originally from Pforzheim, Germany.

Portacosa is a genus of wolf spiders containing the single species, Portacosa cinerea. It was first described by V. W. Framenau in 2017, and is only found in Australia.

Venator is a genus of Australian wolf spiders first described by Henry Roughton Hogg in 1900. As of April 2019 it contains only three species.

Venatrix furcillata, one of the wolf spiders, is a mid sized spider found in eastern Australia. The body length of the female is up to 13 mm, the male 9 mm. The abdomen has distinctive tapering markings. Sometimes noted in suburban gardens and lawns. It lives in a simple burrow, but may be seen migrating in large numbers to a communal web, an unusual feature for wolf spiders. The grey coloured spherical egg sac is around 6 mm in diameter, carried by the female. Eggs are 45 to 60 in number, 0.8 mm in diameter. Prey is ground dwelling insects. The spider has been identified as occurring in Queensland, New South Wales, and Victoria.

Venator immansuetus is a wolf spider, endemic to Australia and found in the south-west of Western Australia.

Venator marginatus is a wolf spider, endemic to Australia and found in Victoria.
Volker W. Framenau is a German-born Australian arachnologist and entomologist.
Anomalosa oz is a spider in the Lycosidae family. It was first described in 2006 by Volker Framenau.
Anomalosa kochi is a spider in the Lycosidae family. It was first described in 1898 by Eugène Simon as Anomalomma kochi. In 1960, it was transferred to the genus Anomalosa by Carl Friedrich Roewer. The current description is given by Volker Framenau.
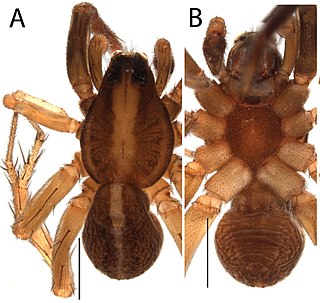
Artoria barringtonensis is a spider in the Lycosidae (wolf-spider) family. It was first described in 2018 by Volker Framenau and Barbara Baehr.

Artoria belfordensis is a spider in the Lycosidae (wolf-spider) family. It was first described in 2018 by Volker Framenau and Barbara Baehr.














