
Alternaria is a genus of Deuteromycetes fungi. All species are known as major plant pathogens. They are also common allergens in humans, growing indoors and causing hay fever or hypersensitivity reactions that sometimes lead to asthma. They are present in the human mycobiome and readily cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised people such as AIDS patients.

Rhizoctonia solani is a species of fungus in the order Cantharellales. Basidiocarps are thin, effused, and web-like, but the fungus is more typically encountered in its anamorphic state, as hyphae and sclerotia. The name Rhizoctonia solani is currently applied to a complex of related species that await further research. In its wide sense, Rhizoctonia solani is a facultative plant pathogen with a wide host range and worldwide distribution. It causes various plant diseases such as root rot, damping off, and wire stem. It can also form mycorrhizal associations with orchids.

Thielaviopsis basicola is the plant-pathogen fungus responsible for black root rot disease. This particular disease has a large host range, affecting woody ornamentals, herbaceous ornamentals, agronomic crops, and even vegetable crops. Examples of susceptible hosts include petunia, pansy, poinsettia, tobacco, cotton, carrot, lettuce, tomato, and others. Symptoms of this disease resemble nutrient deficiency but are truly a result of the decaying root systems of plants. Common symptoms include chlorotic lower foliage, yellowing of plant, stunting or wilting, and black lesions along the roots. The lesions along the roots may appear red at first, getting darker and turning black as the disease progresses. Black root lesions that begin in the middle of a root can also spread further along the roots in either direction. Due to the nature of the pathogen, the disease can easily be identified by the black lesions along the roots, especially when compared to healthy roots. The black lesions that appear along the roots are a result of the formation of chlamydospores, resting spores of the fungus that contribute to its pathogenicity. The chlamydospores are a dark brown-black color and cause the "discoloration" of the roots when they are produced in large amounts.

Erysiphe betae is a fungal plant pathogen. It is a form of powdery mildew that can affect crops of sugar beet, that could cause up to a 30% yield loss. The fungus occurs worldwide in all regions where sugar beet is grown and it also infects other edible crops, e.g. beetroot.

Nectria cinnabarina, also known as coral spot, is a plant pathogen that causes cankers on broadleaf trees. This disease is polycyclic and infects trees in the cool temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. N. cinnabarina is typically saprophytic, but will act as a weak parasite if presented with an opportunity via wounds in the tree or other stressors that weaken the tree's defense to the disease. A study published in 2011 showed that this complex consists of at least 4 distinct species. There are only a few ways to manage this disease with techniques such as sanitation and pruning away branches that have the cankers. N. cinnabarina is not as significant a problem as other Nectria spp., some of which are the most important pathogens to infect hardwood trees.

Pyrenophora tritici-repentis (teleomorph) and Drechslera tritici-repentis (anamorph) is a necrotrophic plant pathogen of fungal origin, phylum Ascomycota. The pathogen causes a disease originally named yellow spot but now commonly called tan spot, yellow leaf spot, yellow leaf blotch or helminthosporiosis. At least eight races of the pathogen are known to occur based on their virulence on a wheat differential set.
Cercospora carotae is a fungal plant pathogen.
Alternaria dauci is a plant pathogen. The English name of the disease it incites is "carrot leaf blight".
Pythium sulcatum is a chromalveolate plant pathogen infecting carrots. Because this organism was once thought to be a type of fungus, it is still often treated as such.
Pythium violae is a plant pathogen infecting carrots. It is a soil-borne oomycete that causes the cavity spot disease of carrots. Pythium sulcatum also causes a less serious form of this disease. Pythium violae causes elliptical shaped brown lesions surrounded by a thin yellow halo on the surface of the taproot. These lesions cause a blemished aesthetic appearance on the carrot, reducing their market value while maintaining yield. The lesions are, on average, less than half an inch in diameter and appear near harvest, but can grow as the carrot matures and grow larger on processing varieties of carrots. Low density hyphae are present in early formation of the lesions, but there is little to no presence of Pythium violae spores in the mature lesions making it difficult to diagnose in the field. This disease can be instigated by excessive rainfall, poor soil drainage, cool temperatures, and low Soil pH. Pythium violae has been shown to infect and produce similar necrotic lesions on other hosts such as alfalfa, wheat, and broccoli. However, no economic loss has been reported from these alternate host infections.

Typhula variabilis is a species of clavarioid fungus in the family Typhulaceae. It is a plant pathogen that infects carrots.

Mycocentrospora acerina is a deuteromycete fungus that is a plant pathogen.
Pyrenochaeta terrestris is a fungal plant pathogen that infects maize, sweet potatoes, and strawberries. This plant pathogen causes a disease in onion that is commonly called pink root. P. terrestris is also known to infect shallots, garlic, leeks, chives, cantaloupe, carrots, cauliflower, cowpea, cucumbers, eggplants, lima beans, millet, oats, peas, peppers, potatoes, spinach, sugarcane, and tomatoes.

Dibotryon morbosum or Apiosporina morbosa is a plant pathogen, which is the causal agent of black knot. It affects members of the Prunus genus such as; cherry, plum, apricot, and chokecherry trees in North America. The disease produces rough, black growths that encircle and kill the infested parts, and provide habitat for insects.

Atheliaceae is a family of corticioid fungi placed under the monotypic order Atheliales. Both the order and the family were described by Walter Jülich in 1981. According to a 2008 estimate, the family contains 20 genera and approximately 100 species. However, many genera formerly considered to belong in the Atheliaceae have since been moved to other families, including Amylocorticiaceae, Albatrellaceae, and Hygrophoraceae. Despite being a relatively small group with inconspicuous forms, Atheliaceae members show great diversity in life strategies and are widespread in distribution. Additionally, being a group strictly composed of corticioid fungi, they may also provide insights on the evolution of fruiting body forms in basidiomycetes.

Athelia is a genus of corticioid fungi in the family Atheliaceae. Some species are facultative parasites of plants and of lichens. The widespread genus contains 28 species. However, Athelia rolfsii was found to belong in the Amylocorticiales in a molecular phylogenetics study and renamed Agroathelia rolfsii.

Rhizoctonia is a genus of fungi in the order Cantharellales. Species form thin, effused, corticioid basidiocarps, but are most frequently found in their sterile, anamorphic state. Rhizoctonia species are saprotrophic, but some are also facultative plant pathogens, causing commercially important crop diseases. Some are also endomycorrhizal associates of orchids. The genus name was formerly used to accommodate many superficially similar, but unrelated fungi.

Telium, plural telia, are structures produced by rust fungi as part of the reproductive cycle. They are typically yellow or orange drying to brown or black and are exclusively a mechanism for the release of teliospores which are released by wind or water to infect the alternate host in the rust life-cycle. The telial stage provides an overwintering strategy in the life cycle of a parasitic heteroecious fungus by producing teliospores; this occurs on cedar trees. A primary aecial stage is spent parasitizing a separate host plant which is a precursor in the life cycle of heteroecious fungi. Teliospores are released from the telia in the spring. The spores can spread many kilometers through the air, however most are spread near the host plant.
Fibularhizoctonia is a genus of fungus in the Atheliaceae family. The genus, circumscribed in 1996, contains three widespread species that are anamorphs of Athelia. One species of Fibularhizoctonia is commonly known as the cuckoo fungus because it makes sclerotia, also called termite balls, which mimic termite eggs. The name Athelia termitophila sp. nov. has been proposed for the teleomorph of termite balls. The generic name had been incorrectly modified to "Fibulorhizoctonia" in some publications but this change is not a nomenclaturally supportable spelling correction. The genome sequences of two species of Fibularhizoctonia have been described.
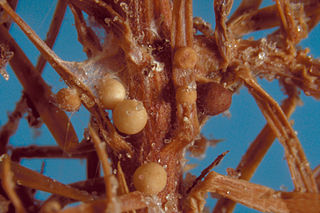
Agroathelia rolfsii is a corticioid fungus in the order Amylocorticiales. It is a facultative plant pathogen and is the causal agent of "southern blight" disease in crops.















