
Desidae is a family of spiders, some of which are known as intertidal spiders. The family is named for the genus Desis, members of which live in a very unusual location — between the tides. The family has been reevaluated in recent years and now includes inland genera and species as well, such as Badumna and Phryganoporus. In 2017, the family Amphinectidae was merged into Desidae. The family Toxopidae has been separated off. Those intertidal spiders that are truly marine commonly live in barnacle shells, which they seal up with silk; this allows them to maintain an air bubble during high tide. They emerge at night to feed on various small arthropods that live in the intertidal zone.

Dwarf sheet spiders (Hahniidae) is a family of araneomorph spiders, first described by Philipp Bertkau in 1878. Their bodies are about 2 millimetres (0.079 in) long, and they build extremely delicate webs in the form of a sheet. Unlike many spiders the web does not lead to a retreat. The silk used in these webs is so fine that they are difficult to spot unless they are coated with dew. They greatly favor locations near water or near moss, and are often found in leaf litter and detritus or on the leaves of shrubs and trees.

Arthur Gardiner Butler F.L.S., F.Z.S. was an English entomologist, arachnologist and ornithologist. He worked at the British Museum on the taxonomy of birds, insects, and spiders.

Nepenthes tenuis is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to the Indonesian island of Sumatra. The species was first collected in 1957, from a remote mountain in the western part of the island. It remained undescribed until 1994, and was only rediscovered in the wild in 2002. Prior to this, N. tenuis was known solely from a single photograph and dried herbarium specimen.

Eurema is a widespread genus of grass yellow butterflies in the family Pieridae.

Banksia tenuis is a species of shrub that is endemic to the southwest of Western Australia. It has pinnatifid, serrated or smooth-edges leaves, golden brown and cream-coloured flowers in heads of about fifty-five and glabrous, egg-shaped follicles.
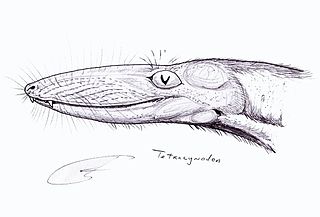
Tetracynodon is an extinct genus of therocephalian. Fossils of Tetracynodon have been found in the Karoo Basin of South Africa. Two species are known: the type species T. tenuis from the Late Permian and the species T. darti from the Early Triassic. Both species were small-bodied and probably fed on insects and small vertebrates. Although Tetracynodon is more closely related to mammals than to reptiles, its braincase is very primitive and more resembles that of modern amphibians and reptiles than of mammals.

Athetis is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1821.

Machaeroprosopus is an extinct genus of mystriosuchin leptosuchomorph phytosaur from the Late Triassic of the southwestern United States. M. validus, once thought to be the type species of Machaeroprosopus, was named in 1916 on the basis of three complete skulls from Chinle Formation, Arizona. The skulls have been lost since the 1950s, and a line drawing in the original 1916 description is the only visual record of the specimen. Another species, M. andersoni, was named in 1922 from New Mexico, and the species M. adamanensis, M. gregorii, M. lithodendrorum, M. tenuis, and M. zunii were named in 1930. Most species have been reassigned to the genera Smilosuchus, Rutiodon, or Phytosaurus. Until recently, M. validus was considered to be the only species that has not been reassigned. Thus, Machaeroprosopus was considered to be a nomen dubium or "doubtful name" because of the lack of diagnostic specimens that can support its distinction from other phytosaur genera. However, a taxonomic revision of Machaeroprosopus, conducted by Parker et al. in 2013, revealed that UW 3807, the holotype of M. validus, is not the holotype of Machaeroprosopus, while the species Machaeroprosopus buceros, Machaeroprosopus being a replacement name, with a fixed type species, for Metarhinus, is the combinatio nova of the type species of the genu: Belodon buceros. Therefore, the name Pseudopalatus must be considered a junior synonym of Machaeroprosopus, and all species of the former must be reassigned to the latter. This revised taxonomy was already accepted in several studies, including Stocker and Butler (2013). Stocker and Butler (2013) also treated M. andersoni as a valid species, and not a junior synonym of Machaeroprosopus buceros as was previously suggested by Long and Murry (1995).

Athetis thoracica is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found all over the Indo-Australian and Pacific tropics. It was first recorded from Hawaii in the early 1900s. It is believed to have been accidentally introduced from Fiji. It is now present on Kauai, Oahu, Molokai, Maui and Hawaii.

Athetis maculatra is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in Australia.
Athetis striolata is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1886. It is found on Fiji and in Australia.

Gadirtha pulchra is a moth of the family Nolidae first described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1886. It is found from the Indian subregion to the Ryukyu Islands in Japan and Thailand, Singapore, New Guinea and Queensland in Australia.

Concinnia is a genus of skinks in the subfamily Lygosominae.

Athetis lepigone is a species of moth, belonging to the genus Athetis.

















