
The ticto barb or twospot barb is a species of subtropical freshwater fish belonging to the family Cyprinidae. It is a native of the upper Mekong, Salwen, Irrawaddy, Meklong and upper Charo Phraya basins in the countries of Nepal, India, Pakistan, Myanmar, Bangladesh, Thailand, and Sri Lanka. It has frequently been confused with the Odessa barb in the aquarium trade, but in that species the male is reddish-orange.

Channa is a genus of predatory fish in the family Channidae, commonly known as snakehead, native to freshwater habitats in Asia. This genus contains more than 45 scientifically described species. The genus has a wide natural distribution extending from Iraq in the west, to Indonesia and China in the east, and parts of Siberia in the Far East. A particularly high richness exists in Myanmar (Burma) and northeastern India, and many Channa species live nowhere else. In contrast, a few widespread species have been introduced to several regions outside their natural range where they often become invasive. The large and medium-sized Channa species are among the most common staple food fish in several Asian countries and they are extensively cultured. Apart from their importance as a food fish, snakeheads are consumed in some regions as a traditional medicine for wound healing and reducing post-operative pain and discomfort, and collected for the international aquarium pet trade.

Devario is a genus of fish in the family Cyprinidae native to the rivers and streams of South and Southeast Asia. These fishes have short barbels and many species having vertical or horizontal stripes. These species consume various small, aquatic insects, crustaceans and worms, as well as, in the case of fry, plankton.
The black-barred danio is a species of Danio discovered in Myanmar by Tin Win in 2005 and described in 2015 by Sven Oscar Kullander and Ralf Britz.

Danio is a genus of small freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae found in South and Southeast Asia, commonly kept in aquaria. They are generally characterised by a pattern of horizontal stripes, rows of spots or vertical bars. Some species have two pairs of long barbels. Species of this genus consume various small aquatic insects, crustaceans and worms.

Glyptothorax is a genus of catfishes order Siluriformes of the family Sisoridae. It is the most species-rich and widely distributed genus in the family with new species being discovered on a regular basis. These species are distributed in the Black Sea basin, northern Turkey, south and east to the Yangtze River drainage in China and south throughout Indo-China to Java, Indonesia. They are found in Asia Minor and southwards to Southeast Asia. The genus is very diverse in the Indian subcontinent. Southeast Asian species tend to have restricted distributions.

Horabagrus is a genus of catfish in the family Horabagridae endemic to rivers in the Western Ghats in Kerala and Karnataka, India. H. brachysoma is an important food fish and members of this genus can be found in the aquarium trade.

Schistura is a genus of fish in the stone loach family Nemacheilidae native to the streams and rivers of the southern and eastern Asia. Some of these species are troglobitic.
Amblyceps is a genus of fish in the family Amblycipitidae. The genera Amblyceps and Liobagrus are sister group pair that is, in turn, sister to Xiurenbagrus. These species are easily distinguished by the presence of pinnate processes along the median caudal-fin rays, a prominent cup-like skin flap above the base of the pectoral spine and the adipose fin largely separate from the caudal fin. In most species the caudal fin is deeply forked; A. apangi and A. murraystuarti differ in having their caudal fin truncate. Amblyceps species may reach about 100 millimetres (3.94 in) SL.

Channa marulius is a large species of snakehead native to South and Southeast Asia, as well as southern China. It has been introduced to the United States, where it is considered an invasive species.

Psilorhynchus is a genus of fish in the family Psilorhynchidae native to South Asia. This genus is the only member of its family. The members of Psilorhynchus are small benthic fishes which occur in rivers and streams with fast to swift currents, hence they are often referred to a torrent minnows. They are distributed in southern Asia, in the Indo-Burma region and the Western Ghats. The genus is the sister group to the family Cyprinidae, and with that family the Psilorhynchidae makes up the superfamily Cyprinoidea, with all the other cypriniform families in the superfamily Cobitoidea.

Nemacheilus rueppelli, also known as the mongoose loach is a species of stone loach from rivers in India. It includes Nemachilichthys shimogensis, which frequently is recognized as a valid species from the Thunga River in Karnataka, but Keskar et al. 2015 treat them as synonyms, while Fishbase says the name is misapplied and should not be used as N. shimgoensis is treated as a separate species by Fishbase and the IUCN. According to Keskar et al, 2015 this species is placed in the monotypic genus Nemachilichthys but Fishbase retains it in Nemacheilus., although Catalog of Fishes follows treatment outlined by Keskar et al.
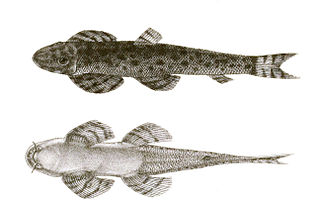
Balitora is a genus of fish in the family Balitoridae endemic to Asia.
Pethia muvattupuzhaensis is a species of cyprinid fish found in Muvattupuzha and Periyar Rivers, Kerala, India. It is sometimes considered conspecific with Pethia punctata. Day, 1865 This species can be found over sand or gravel substrates. This species reaches a length of 4.5 centimetres (1.8 in) SL.

Pethia is a genus of small freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae native to South Asia, East Asia(only Pethia stoliczkana recorded)and Mainland Southeast Asia. Some species are commonly seen in the aquarium trade. The name Pethia is derived from the Sinhalese "pethia", a generic word used to describe any of several small species of cyprinid fishes. Members of this genus were formerly included in Puntius.

The Badidae are a small family of anabantiforme fishes. Members of this family are small freshwater fish that are found in Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Laos, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan and Thailand. The largest is Badis assamensis that reaches a standard length of up to 7.5 cm (3 in), while the smallest, Dario dario, does not exceed 2 cm (0.8 in).

Dario is a genus of very small chameleonfishes native to streams and freshwater pools in China (Yunnan), India and Myanmar. Depending on exact species, they are up to 1.5–3 cm (0.6–1.2 in) in standard length, and reddish or brownish in colour.

Badis khwae is a species of freshwater fish native to Thailand.

Pristolepis is a genus of fish in the family Pristolepididae native to freshwater habitats in Southeast Asia and India's Western Ghats. This genus is the only member of its family, but the common name "leaffish" is shared with the families Nandidae and Polycentridae.

The Anabantiformes are an order of freshwater ray-finned fish with seven families and having at least 252 species. This group of fish are found in Asia and Africa, with some species introduced in United States of America.




















