
Grand Chord is part of the Howrah–Gaya–Delhi line and Howrah–Prayagraj–Mumbai line. It acts as a link between Sitarampur, (Asansol), and Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyay Junction,, previously known as Mughalsarai Junction, and covers a stretch of 450.7 km (280.1 mi). The Coal India Corridor line that branches off from Dhanbad Junction and rejoins the Grand Chord at Son Nagar Junction is another major coal loading hub. It is a fully electrified, triple line section from Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyay to Son Nagar and double line section from Son Nagar to Sitarampur. There are plans to triple the lines from Son Nagar to Dhanbad to accommodate the increasing traffic.. The entire line lies under the jurisdiction of three divisions, Mughalsarai railway division, Dhanbad railway division and Asansol railway division. The Grand chord section is the lifeline of the country, 2nd busiest railway section of India after Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh to Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyay Junction, Uttar Pradesh Main Line section, on which coal, steel and other important goods are moved from Eastern section to Western and Northern sections of the country. In the down direction, the traffic consists of mostly food grains, fertilizers and empty wagons for coal loading in the Jharkhand and West Bengal coal fields. Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyay Junction is a transit division and the main objective is to maintain mobility of high density traffic. The present capacity of the Grand Chord is being optimally utilized. Traversing through Chota Nagpur Plateau of Jharkhand as well as parts of the fertile Gangetic plains of Bihar, the Grand Chord covers a stretch of 450.7 km (280.1 mi). The Grand Chord is renowned for its remarkable controlling of passenger traffic, despite being burdened with freight traffic.

Chakradharpur is a city in West Singhbhum district in the state of Jharkhand, India. It is the railway divisional headquarters of Chakradharpur (CKP) division of the South Eastern Railway. The city stands at an elevation of 227 metres and has urban area of 10 square kilometres bounded on the east by Jamshedpur (Tatanagar), on the west by Rourkela (Odisha), on the north by Ranchi and on the south by Chaibasa. Chakradharpur is close to boundaries of two neighbouring states, Odisha and West Bengal.

Noamundi is a census town in West Singhbhum district in the Indian state of Jharkhand. It is also an administrative block. It is a small mining town located close to the Odisha border. It lies near Jamshedpur and 64 km (40 mi) from Chaibasa. Nearby towns include Padapahar, Barajamda, jagannathpur, Kharsawan, Gua and Kiriburu.
Barbil is a city and a Municipal Council in the Kendujhar district of the state of Odisha, India. The region around Barbil has one of the largest deposits of iron ore and manganese ore in the world. It is a major source of revenue generation for both the central and the state governments.
Danguwapasi is a census town in Pashchimi Singhbhum district in the state of Jharkhand, India.

The Tatanagar–Bilaspur section is part of the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line and connects Tatanagar in the Indian state of Jharkhand and Bilaspur in Chhattisgarh. Part of one of the major trunk lines in the country, it passes through an industrial-mining area and handles high volumes of freight, particularly coal and iron ore.

The Jharsuguda–Vizianagaram line is a railway line in eastern India. It connects Jharsuguda,516 km (321 mi) from Howrah on the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line, and Titlagarh, which in turn is connected with Vizianagaram, 820 km (510 mi) from Howrah on the Howrah–Chennai main line, and Raipur Junction, 830 km (516 mi) from Howrah on the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line. There are several branch lines, like the 176 km (109 mi) line connecting Rayagada with Koraput on the Kothavalasa–Kirandul line. The line traverses Western Odisha and connects the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line with the Howrah–Chennai main line. It covers small portions of Chhattisgarh and Andhra Pradesh.

Rourkela Junction railway station is a railway junction located in the north-western part of the Indian state of Odisha and serves Rourkela in Sundergarh district. Rourkela is the third-largest urban agglomeration in Odisha.
Kendujhargarh railway station, located in the Indian state of Odisha, serves Kendujhar in Kendujhar district. It is on the Padapahar–Jakhapura branch line.
Purulia railway station serves Purulia City the headquarters of Purulia district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is situated at the eastern side of the city with railway owned colonies which is home for working staffs. The station is under NSG4 category.

The Kharagpur–Puri Line is a railway line connecting Kharagpur in the Indian state of West Bengal and Puri in Odisha. The total line can be divided into sections. The Kharagpur–Khurda Road portion of this line, which is a part of the Howrah–Chennai main line and Khurda Road - Puri portion.
The 12021/22 Howrah–Barbil Jan Shatabdi Express is a superfast express train of the Jan Shatabdi Express series belonging to Indian Railways – South Eastern Railway zone that runs between Howrah Junction and Barbil in India. This Jan Shatabdi Express replaced the Shatabdi Express running between Howrah Junction and Tatanagar Junction. The Departure of Shatabdi from Howrah Junction was at 06.45 AM, and it reached Tatanagar Junction at 10.30 AM. Reverse, the Shatabdi used to depart Tatanagar Junction at 5.00 PM, reaching Howrah Junction at 8.45 PM. The Shatabdi was replaced by this train due to low patronage with extension up till Barbil in Odisha. Now it operates as train number 12021 from Howrah Junction to Barbil and as train number 12022 in the reverse direction serving the states of West Bengal, Jharkhand and Odisha due to the fact that Barbil cuts across the state line between Jharkhand and Odisha.
Chakradharpur railway division is one of the four railway divisions under South Eastern Railway zone of Indian Railways. This railway division was formed on 14 April 1952 and its headquarter is located at Chakradharpur in West Singhbhum district of the state of Jharkhand of India.

Chhatrapur railway station is one of two railway stations in Chatrapur, this being the main railway station in Ganjam district, Odisha. Its code is CAP. It serves Chhatrapur city and another one is Chatrapur Court halt, which code is CAPC. It is situated in the heart of the town, where only DMU, EMU, and passenger trains are stopping.
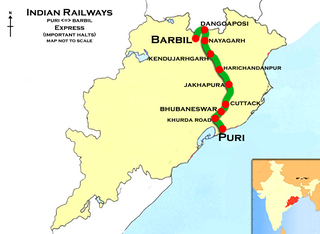
The 18416 / 15 Puri–Barbil Express is an Express train belonging to Indian Railways East Coast Railway zone that runs between Puri and Barbil in India.
The 18403 / 04 Rourkela - Barbil Intercity Express is an Express train belonging to Indian Railways East Coast Railway zone that runs between Rourkela Junction and Barbil in India.

Balugaon railway station is a railway station on the East Coast Railway network in the state of Odisha, India. It serves Balugaon town. Its code is BALU. It has four platforms. Passenger, MEMU, Express and Superfast trains halt at Balugaon railway station.
Rajgangpur railway station is a railway station on the South Eastern Railway network in the state of Odisha, India. It serves Rajgangpur town. Its code is GP. It has three platforms. Passenger, Express trains halt at Rajgangpur railway station.
Delang railway station is a railway station on the East Coast Railway network in the state of Odisha, India. It serves Delang town. Its code is DEG. It has three platforms. Passenger, MEMU, Express trains halt at Delang railway station.
Sakhigopal railway station is a railway station on the East Coast Railway network in the state of Odisha, India. It serves Sakhigopal village. Its code is SIL. It has four platforms. Passenger, MEMU, Express trains halt at Sakhigopal railway station.












