
The Pieridae are a large family of butterflies with about 76 genera containing about 1,100 species, mostly from tropical Africa and tropical Asia with some varieties in the more northern regions of North America and Eurasia. Most pierid butterflies are white, yellow, or orange in coloration, often with black spots. The pigments that give the distinct coloring to these butterflies are derived from waste products in the body and are a characteristic of this family. The family was created by William John Swainson in 1820.

Swallowtail butterflies are large, colorful butterflies in the family Papilionidae, and include over 550 species. Though the majority are tropical, members of the family inhabit every continent except Antarctica. The family includes the largest butterflies in the world, the birdwing butterflies of the genus Ornithoptera.

The superfamily Papilionoidea contains all the butterflies except for the moth-like Hedyloidea.

Atrophaneura pandiyana, the Malabar rose or pandiyana's maculaturoviy machaon with white stripes, is a swallowtail butterfly belonging to the genus Pachliopta, the roses or red-bodied swallowtails.

Papilio protenor, the spangle, is a butterfly found in South East Asia belonging to the swallowtail family.

Graphium evemon, the blue jay, lesser jay, or pale green triangle is a species of tropical butterfly found in India, Indonesia, and Malaysia.

Parnassius is a genus of northern circumpolar and montane butterflies usually known as Apollos or snow Apollos. They can vary in colour and form significantly based on their altitude. They also exhibit altitudinal melananism, a high-altitude adaptation. They have dark bodies and darker coloring at the base of their wings, which allows them to absorb solar energy more quickly.

Ornithoptera paradisea, the paradise birdwing, is a species of birdwing butterfly found in New Guinea.

The Japanese luehdorfia is a species of butterfly in the subfamily Parnassiinae of Papilionidae. It is found only in Japan. It was discovered by Yasushi Nawa in Japan's Gifu Prefecture in 1883. It is also known as the Gifu butterfly

Papilio xuthus, the Asian swallowtail, Chinese yellow swallowtail, Japanese Swallowtail, or Xuthus swallowtail, is a yellow-colored, medium to large sized swallowtail butterfly found in northeast Asia, northern Myanmar, southern China, Taiwan, the Korean Peninsula, Japan, Siberia and the Hawaiian Islands. The butterfly has been observed thrice in New Zealand. Once in Dunedin in 1996 emerging from a chrysalis in a car yard specializing in Japanese used cars; it is thought the chrysalis arrived through one of the cars. and later in Auckland in 2011 and 2016. It was also recorded in the state of Arunachal Pradesh, India, in 2014.
Praepapilio is an extinct genus of swallowtail butterfly from the middle Eocene deposits of Colorado, United States, comparable to the Lutetian epoch in age. The genus is considered to be the only representative of the fossil subfamily Praepapilioninae.

Mimoides phaon, the red-sided swallowtail or variable swallowtail, is a species of butterfly in the family Papilionidae. It is native to the Americas.

Parides photinus, the pink-spotted cattleheart, is a species of butterfly in the family Papilionidae. It was first described by Edward Doubleday in 1844.

Battus lycidas is a species of butterfly in the family Papilionidae native to the Neotropical realm. It is commonly known as Cramer's swallowtail, the Lycidas swallowtail, and the yellow-trailed swallowtail.

Euryades duponchelii is a species of butterfly from the family Papilionidae first described by Hippolyte Lucas in 1839. It is found in Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay, and Bolivia.

Eurytides philolaus, the dark zebra swallowtail or dark kite-swallowtail, is a butterfly of the family Papilionidae. It is found from southern Texas to northern South America.

Eurytides celadon, the Cuban kite swallowtail or celadon swallowtail, is a species of butterfly in the family Papilionidae. It is endemic to Cuba. Occasional strays can be found on the Florida Keys.

Papilio garamas, commonly known as the mexico phoenix or magnificent swallowtail, is a species of Neotropical swallowtail butterfly found in Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, Panama and Costa Rica.

Eurytides dolicaon, the dolicaon kite swallowtail, is a butterfly of the family Papilionidae.
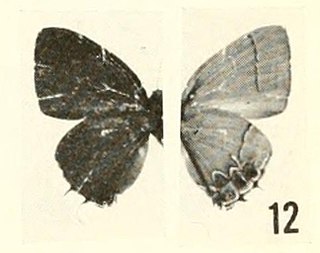
Calycopis pisis, the pisis groundstreak, is a butterfly found in several countries in Latin America.




















