
Q fever or query fever is a disease caused by infection with Coxiella burnetii, a bacterium that affects humans and other animals. This organism is uncommon, but may be found in cattle, sheep, goats, and other domestic mammals, including cats and dogs. The infection results from inhalation of a spore-like small-cell variant, and from contact with the milk, urine, feces, vaginal mucus, or semen of infected animals. Rarely, the disease is tick-borne. The incubation period can range from 9 to 40 days. Humans are vulnerable to Q fever, and infection can result from even a few organisms. The bacterium is an obligate intracellular pathogenic parasite.

Bartonella henselae, formerly Rochalimæa henselae, is a bacterium that is the causative agent of cat-scratch disease (bartonellosis).

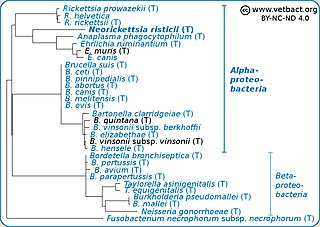
Bartonella is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. It is the only genus in the family Bartonellaceae. Facultative intracellular parasites, Bartonella species can infect healthy people, but are considered especially important as opportunistic pathogens. Bartonella species are transmitted by vectors such as ticks, fleas, sand flies, and mosquitoes. At least eight Bartonella species or subspecies are known to infect humans.

Carrion's disease is an infectious disease produced by Bartonella bacilliformis infection.
Bartonellosis is an infectious disease produced by bacteria of the genus Bartonella. Bartonella species cause diseases such as Carrión's disease, trench fever, cat-scratch disease, bacillary angiomatosis, peliosis hepatis, chronic bacteremia, endocarditis, chronic lymphadenopathy, and neurological disorders.

Bartonella bacilliformis is a bacterium, Gram negative aerobic, pleomorphic, flagellated, motile, coccobacillary, 2–3 μm long, 0.2–0.5 μm wide, and a facultative intracellular bacterium.
Bartonella quintana, originally known as Rochalimaea quintana, and "Rickettsia quintana", is a bacterium transmitted by the human body louse that causes trench fever. This bacterial species caused outbreaks of trench fever affecting 1 million soldiers in Europe during World War I.
Rickettsia typhi is a small, aerobic, obligate intracellular, rod shaped gram negative bacterium. It belongs to the typhus group of the Rickettsia genus, along with R. prowazekii. R. typhi has an uncertain history, as it may have long gone shadowed by epidemic typhus. This bacterium is recognized as a biocontainment level 2/3 organism. R. typhi is a flea-borne disease that is best known to be the causative agent for the disease murine typhus, which is an endemic typhus in humans that is distributed worldwide. As with all rickettsial organisms, R. typhi is a zoonotic agent that causes the disease murine typhus, displaying non-specific mild symptoms of fevers, headaches, pains and rashes. There are two cycles of R. typhi transmission from animal reservoirs containing R. typhi to humans: a classic rat-flea-rat cycle that is most well studied and common, and a secondary periodomestic cycle that could involve cats, dogs, opossums, sheep, and their fleas.

Streptococcus canis is a group G beta-hemolytic species of Streptococcus. It was first isolated in dogs, giving the bacterium its name. These bacteria are characteristically different from Streptococcus dysgalactiae, which is a human-specific group G species that has a different phenotypic chemical composition. S. canis is important to the skin and mucosal health of cats and dogs, but under certain circumstances, these bacteria can cause opportunistic infections. These infections were known to afflict dogs and cats prior to the formal description of the species in Devriese et al., 1986. However, additional studies revealed cases of infection in other mammal species, including cattle and even humans. Instances of mortality from S. canis in humans are very low with only a few reported cases, while actual instances of infection may be underreported due to mischaracterizations of the bacteria as S. dysgalactiae. This species, in general, is highly susceptible to antibiotics, and plans to develop a vaccine to prevent human infections are currently being considered.

Bartonella henselae hypothetical protein 11960 (BH11960) is encoded by the BH11960 gene. This hypothetical protein is conserved in all Bartonella species whose genomes have been sequenced to date, and are highlighted in the picture below.
Neorickettsia risticii, formerly Ehrlichia risticii, is an obligate intracellular gram negative bacteria that typically lives as an endosymbiont to parasitic flatworms, specifically flukes. N. risticii is the known causative agent of equine neorickettsiosis, which gets its name from its discovery near the Potomac River in Maryland and Virginia. N. risticii was first recovered from horses in this region in 1984 but was not recognized as the causative agent of PHF until 1979. Potomac horse fever is currently endemic in the United States but has also been reported with lower frequency in other regions, including Canada, Brazil, Uruguay, and Europe. PHF is a condition that is clinically important for horses since it can cause serious signs such as fever, diarrhea, colic, and laminitis. PHF has a fatality rate of approximately 30%, making this condition one of the concerns for horse owners in endemic regions N. risticii is typically acquired in the middle to late summer near freshwater streams or rivers, as well as on irrigated pastures. This is a seasonal infection because it relies on the ingestion of an arthropod vector, which are more commonly found on pasture in the summer months. Although N. risticii is a well known causative agent for PHF in horses, it may act as a potential pathogen in cats and dogs as well. Not only has N. risticii been successfully cultured from monocytes of dogs and cats, but cats have become clinically ill after experimental infection with the bacteria. In addition, N. risticii has been isolated and cultured from human histiocytic lymphoma cells.
Bartonella alsatica is a bacterium. Like other Bartonella species, it can cause disease in animals. It is small, aerobic, oxidase-negative, and Gram-negative. Its rod-like cells were localized within wild rabbit erythrocytes when first described. The type strain is IBS 382T. It is associated with cases of lymphadenitis and endocarditis.
Bartonella elizabethae, formerly known as Rochalimaea elizabethae, is a bacterium. As with other Bartonella species, it can cause disease in animals.
Staphylococcus schleiferi is a Gram-positive, cocci-shaped bacterium of the family Staphylococcaceae. It is facultatively anaerobic, coagulase-variable, and can be readily cultured on blood agar where the bacterium tends to form opaque, non-pigmented colonies and beta (β) hemolysis. There exists two subspecies under the species S. schleiferi: Staphylococcus schleiferi subsp. schleiferi and Staphylococcus schleiferi subsp. coagulans.
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius is a gram positive coccus bacteria of the genus Staphylococcus found worldwide. It is primarily a pathogen for domestic animals, but has been known to affect humans as well. S. pseudintermedius is an opportunistic pathogen that secretes immune modulating virulence factors, has many adhesion factors, and the potential to create biofilms, all of which help to determine the pathogenicity of the bacterium. Diagnoses of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius have traditionally been made using cytology, plating, and biochemical tests. More recently, molecular technologies like MALDI-TOF, DNA hybridization and PCR have become preferred over biochemical tests for their more rapid and accurate identifications. This includes the identification and diagnosis of antibiotic resistant strains.
Bartonella capreoli is a pathogenic bacteria first isolated from European ruminants. It is small, fastidious, aerobic, oxidase-negative, gram-negative and rod-shaped. Its type strain is IBS 193T.
Bartonella clarridgeiae is a Gram-negative bacteria from the genus Bartonella which was first isolated in the United States. Bartonella clarridgeiae is a zoonotic pathogen which can cause cat scratch disease.
Bartonella vinsonii is a gram-negative bacteria from the genus Bartonella which was isolated from dogs. Rochalimaea vinsonii was reclassified to Bartonella vinsonii. B. vinsonii contains three validly published subspecies B. vinsonii subsp. arupensis, B. vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii, and B. vinsonii subsp. vinsonii, and one effectively published B. vinsonii subsp. yucatanensis. B. vinsonii subsp. vinsonii has been isolated from voles and B. vinsonii subsp. berkhofli was isolated from a dog with endocarditis. B. vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii can cause diseases in humans. Those two subspecies are named after J. William Vinson and Herman A. Berkhoff.
Bartonella tamiae is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria from the genus Bartonella which was isolated from the blood of patients in Thailand. Bartonella tamiae can cause illness in humans.
Bartonella washoensis is a bacterium from the genus Bartonella which was first isolated from a dog with mitral valve endocarditis. Bartonella washoensis can infect squirrels but also can cause meningitis in humans.






