Related Research Articles

Rhabditida is an order of free-living, zooparasitic, and phytoparasitic microbivorous nematodes living in soil.

Enoplea (enopleans) is a class, which with the classes Secernentea and Chromadorea make up the phylum Nematoda in current taxonomy. The Enoplea are considered to be a more ancestral group than the Chromadorea, and researchers have referred to its members as the "ancestrally diverged nematodes", compared to the "more recently diverged nematodes" of Chromadorea.

Cristidiscoidea or Nucleariae is a proposed basal holomycota clade in which Fonticula and Nucleariida emerged, as sister of the fungi. Since it is close to the divergence between the main lineages of fungi and animals, the study of Cristidiscoidea can provide crucial information on the divergent lifestyles of these groups and the evolution of opisthokonts and slime mold multicellularity. The holomycota tree is following Tedersoo et al.

Karel Geraerts is a Belgian former footballer and current head coach of Union SG.
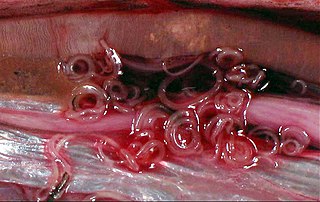
The Chromadorea are a class of the roundworm phylum, Nematoda. They contain a single subclass (Chromadoria) and several orders. With such a redundant arrangement, the Chromadoria are liable to be divided if the orders are found to form several clades, or abandoned if they are found to constitute a single radiation.
Pratylenchus brachyurus is a plant parasitic nematode.

The nematodes or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda, with plant-parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum.

Huffmanela is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Trichosomoididae.

Tylenchidae is a family of nematodes. They are an important group of soil dwelling species that frequently contributes as much as 30% to the nematode species richness of soil samples. They diverged relatively early on and many species pose little risk to economically important plant species. Due to their early divergence, species tend to have relatively basal characteristics. They tend to be small nd slender with small and delicate piercing mouthparts.
Longidorus is a genus of needle nematodes. Some of its species are plant pests.

Diplogastridae, formerly Diplogasteridae, are a family of nematodes (roundworms) known from a wide range of habitats, often in commensal or parasitic associations with insects.
Paratrichodorus is a genus of terrestrial root feeding (stubby-root) nematodes in the Trichodoridae family (trichorids), being one of five genera. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors. The females are didelphic, and are distributed worldwide.
Trichodoridae is a family of terrestrial root feeding nematodes, being one of two that constitute suborder Triplonchida. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors.
Chilenchus is a genus of nematodes in the family Tylenchidae. The name comes from Chile, the country from where it originates.

Cucullanus is a genus of parasitic nematodes. The genus includes more than 100 species.

František Moravec is a Czech parasitologist who specialises on the Nematodes, especially the nematodes parasites of fishes. His research is mainly in the field of taxonomy of the Nematoda.
István Andrássy was a Hungarian nematologist. Starting with his first publication in 1952 on the nematode fauna of Mount Bükk, over his dissertation in 1973 on the evolution of nematodes to his last days he was a very prolific scientist, publishing more than 200 manuscripts, chapters and books on the class of Nematoda. He described 530 taxa of nematodes and at least 60 nematode taxa are named after him, which shows the huge respect he had in the nematologists world.
Lelenchus is a genus of nematodes belonging to the family Tylenchidae.
Boleodorus is a genus of nematodes belonging to the family Tylenchidae.
Ecphyadophora is a genus of nematodes belonging to the family Tylenchidae.
References
- ↑ Karegar, A; E. Geraert (1998). "The Genus Basiria Siddiqi, 1959 (Nematoda: Tylenchidae) Iv. General Discussion, Genus Diagnosis and Key To the Species". Nematologica. Brill. 44 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1163/005225998X00019 . Retrieved October 21, 2013.
- ↑ Geraert, E. 2008: The Tylenchidae of the World. Identification of the family Tylenchidae (Nematoda). Gent, Academia Press. ISBN 978 90 382 1355 2 Google books