
The ghost knifefishes are a family, Apteronotidae, of ray-finned fishes in the order Gymnotiformes. These fish are native to Panama and South America. They inhabit a wide range of freshwater habitats, but more than half the species in the family are found deep in rivers where there is little or no light.

The black ghost knifefish is a tropical fish belonging to the ghost knifefish family (Apteronotidae). They originate in freshwater habitats in South America where they range from Venezuela to the Paraguay–Paraná River, including the Amazon Basin. They are popular in aquaria. The fish is all black except for two white rings on its tail, and a white blaze on its nose, which can occasionally extend into a stripe down its back. It moves mainly by undulating a long fin on its underside. It will grow to a length of 45–50 centimetres (18–20 in).
Knifefish may refer to several knife-shaped fishes:
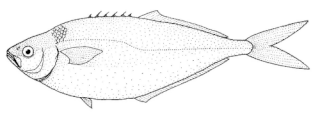
The grey knifefish is a species of ray-finned fish native to the Pacific Ocean from Australia to New Zealand and the Kermadec Islands. This species is a plankton eater which swims constantly within a few meters of the surface of the ocean. This species can reach a length of 30 cm (12 in).

The family Notopteridae contains 10 species of osteoglossiform (bony-tongued) fishes, commonly known as featherbacks and knifefishes. These fishes live in freshwater or brackish environments in Africa and West South East and Southeast Asia.

The Hypopomidae are a family of fishes in the order Gymnotiformes known as the bluntnose knifefish. They may also be called grass or leaf knifefishes. These electric fish are not often eaten, of little commercial importance, rarely kept as aquarium fish, and poorly studied; however, species in this family may constitute a significant fraction of the biomass in the areas they inhabit.

The African brown knifefish is the only species in the genus Xenomystus of the family Notopteridae. This fish is found in the Chad, Nile, Congo, Ogowe and Niger basins, as well as coastal river basins in Sierra Leone, Liberia, Togo, Benin and Cameroon.

The clown featherback, also known as the clown knifefish and spotted knifefish, is a nocturnal species of tropical fish with a long, knife-like body. This knifefish is native to freshwater habitats in Cambodia, China, Hong Kong, Laos, Macau, Thailand, and Vietnam, but it has also been introduced to regions outside its native range. It is one of the world's most invasive species.

Chitala is a genus of fish of the family Notopteridae. This genus contains six species, some of which are important in aquaculture and the aquarium industry. They are commonly known as the Asian knifefishes or featherbacks. They are native to freshwater in South East and Southeast Asia.

The brown ghost knifefish is a species of weakly electric knifefish in the family Apteronotidae. The brown ghost knifefish is the only vertebrate proven to have negligible brain aging thus far. As such, they are extensively researched as a model species for neurological and developmental studies. In the wild, A. leptorhynchus is understudied known only to inhabit deep channels of large, lowland rivers, specifically the Essequibo River drainage in Guyana, where it is active nocturnally and seeks vegetated retreat sites during the day. They are listed as an endangered species by the ICUN.
Eigenmannia vicentespelaea is a species of weakly electric knifefish in the family Sternopygidae. Native to the São Domingos karst area in central Brazil, it is the only known knifefish to exclusively inhabit caves. Measuring up to 21 cm (8.3 in) long, E. vicentespelaea can be distinguished from its relatives by its translucent body and reduced or absent eyes. As some individuals retain well-developed eyes, this fish may have colonized caves only recently in evolutionary time.

Apteronotus is a genus of weakly electric knifefish in the family Apteronotidae, distinguished by the presence of a tiny tail fin. This genus is restricted to tropical and subtropical South America and Panama where found in a wide range of freshwater habitats. They feed on small animals.

Papyrocranus is a genus of freshwater fishes in family Notopteridae found in Middle and West Africa.

The jack-knifefish is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Sciaenidae, the drums and croakers. It is native to the western Atlantic Ocean, where its distribution extends along the eastern coasts of the Americas from the Carolinas in the United States to Brazil, including the Caribbean. Other common names include donkey fish and lance-shaped ribbonfish.
Parapteronotus hasemani, the duckbill knifefish, is a species of ghost knifefish found in main river channels and along the margins in the Amazon basin of Brazil and Peru. It is the only member of the genus Parapteronotus. This dark-colored knifefish reaches up to about 38 cm (15 in) in total length.

Sternarchorhynchus is a genus of ghost knifefishes with a long, decurved snout that are found in river basins in tropical South America.
Microsternarchus is a genus of bluntnose knifefish that is found in creeks and streams, often in areas with submerged vegetation, roots and leaf litter, in the Amazon, Orinoco, Essequibo–Rupununi and Río de la Plata basins in South America. The two recognized species are both small knifefish, with the largest being M. bilineatus at up to 12 cm (4.7 in) in total length. The other is M. brevis, which at up to only 5.3 cm (2.1 in) is the world's smallest knifefish. Microsternarchus are very similar to Brachyhypopomus.

Eigenmannia is a genus of fish in the family Sternopygidae native to tropical and subtropical South America, and Panama. They are typically found in slow-flowing streams, along the edge of large rivers, in deep river channels and in floodplains, and the genus also includes E. vicentespelaea, the only cave-adapted knifefish. Eigenmannia are often found near submerged roots, aquatic plants and floating meadows.
Humboldtichthys is an extinct genus of glass knifefishes from the Miocene Yecua Formation of Bolivia. A single species is currently recognized: Humboldtichthys kirschbaumi.












