Ophidiiformes is an order of ray-finned fish that includes the cusk-eels, pearlfishes, viviparous brotulas, and others. Members of this order have small heads and long slender bodies. They have either smooth scales or no scales, a long dorsal fin and an anal fin that typically runs into the caudal fin. They mostly come from the tropics and subtropics, and live in both freshwater and marine habitats, including abyssal depths. They have adopted a range of feeding methods and lifestyles, including parasitism. The majority are egg-laying, but some are viviparous.

Saccogaster is a genus of viviparous brotulas. They are found in the western Atlantic and Indo-Pacific.

Bidenichthys is a genus of viviparous brotulas.
Cataetyx is a genus of viviparous brotulas.

Grammonus is a genus of viviparous brotula.

Hephthocara is a small genus of Indo-Pacific viviparous brotula.
Eurypleuron is a genus of pearlfishes, with these currently recognized species:
Onuxodon is an Indo-Pacific genus of pearlfishes from the family Carapidae. The generic name is derived from the Greek onyx meaning "claw" and odon meaning "tooth", referring to the sharp fang like teeth of Onuxodon parvibrachium. Species in this genus are distributed from South Africa to Hawaii. They live commensally with molluscs. The three currently recognized species are:
Pyramodon is a genus of pearlfishes, with these currently recognized species:
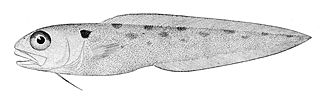
Otophidium is a genus of cusk-eels, part of the subfamily Ophidiinae in the family Ophidiidae. They are found in the western Atlantic and eastern Pacific.
Parophidion is a genus of cusk-eels found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
The faceless cusk is a species of cusk-eel. It is the only species of the monotypic genus Typhlonus. It is found in the Indian and Pacific Oceans at depths from about 3,935 to 5,100 m. This species grows to 46.5 cm (18.3 in) in standard length.
Bidenichthys capensis, the freetail brotula, is an uncommon South African fish of the family Bythitidae. The species is found in intertidal zones and rocky tidepools ranging from East London to the Cape of Good Hope, South Africa. It grows up to 90 mm long TL.

Brosmophycinae is a subfamily of the viviparous brotulas. They are divided from the subfamily Bythitinae by having the dorsal fin, caudal fin and anal fin all separate whereas they are joined in the Bythitinae. It is divided into the tribes Dinematichthyini and Brosmophycini, with the first having hardened genital claspers and the second soft genital claspers. A review in 2016 elevated the Dinematichthyini to the status of a family the Dinematichthyidae.

Brosmophycini is a tribe of viviparous brotula, one of two tribes in the subfamily Brosmophycinae. They are distinguished from the other brosmophycin tribe, the Dinematichthyini, by having a male intromittent organ which has no ossified parts, a scale-covered body and well developed gill rakers.

Bythitinae is a subfamily of viviparous brotulas, one of the two subfamilies in the family Bythitidae. This subfamily is characterised by having the dorsal, caudal and anal fins combined. They are mostly found in temperate to tropical seas, from reefs to the benthopelagic zone, but some species from the North Atlantic Ocean occur in into Arctic waters.
Bythitoidei is a suborder of the order Ophidiiformes, the cusk eels. They are distinguished from the other Ophidiform suborder, the Ophidioidei, by being largely viviparous.

Ophidiinae is a subfamily of the cusk eel family Ophidiidae. The species in the subfamily are characterised by having their pelvic fins situated far forward on the body and supported by a forward orientated extension of the pelvic girdle, they lack barbels on the mouth and chin and they are covered in small cycloid scales arranged in horizontal or diagonal rows. Some species have a modified swim bladder and the anterior vertebrae which enables them to generate sounds. and some of these modifications are sexually dimorphic and make the fish capable of generating sound. They have two rays in each ventral fin and the caudal fin has 9 rays. Most species are benthic and occur on the continental shelf.
Echiodon neotes is a fish species described by Markle and Olney, 1990. Echiodon neotes is part of the genus Echiodon and the subfamily Carapinae.

Onuxodon fowleri is a species of pearlfish first described by Smith, 1955. Onuxodon fowleri is part of the genus Onuxodon and the subfamily Carapinae. No subspecies are listed in the Catalog of Life.






