
Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life, organisms in the sea. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy.
Oceanography, also known as oceanology, sea science, ocean science, and marine science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamics; plate tectonics and seabed geology; and fluxes of various chemical substances and physical properties within the ocean and across its boundaries. These diverse topics reflect multiple disciplines that oceanographers utilize to glean further knowledge of the world ocean, including astronomy, biology, chemistry, geography, geology, hydrology, meteorology and physics. Paleoceanography studies the history of the oceans in the geologic past. An oceanographer is a person who studies many matters concerned with oceans, including marine geology, physics, chemistry, and biology.

The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution is a private, nonprofit research and higher education facility dedicated to the study of marine science and engineering.
The Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO (IOC/UNESCO) was established by resolution 2.31 adopted by the General Conference of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). It first met in Paris at UNESCO Headquarters from 19 to 27 October 1961. Initially, 40 States became members of the commission. The IOC assists governments to address their individual and collective ocean and coastal management needs, through the sharing of knowledge, information and technology as well as through the co-ordination of programs and building capacity in ocean and coastal research, observations and services.
The Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science is the University of Miami's academic and research institution for the study of oceanography, atmospheric, and earth sciences.

The Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (AOML), a federal research laboratory, is part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research (OAR), located in Miami in the United States. AOML's research spans tropical cyclone and hurricanes, coastal ecosystems, oceans and human health, climate studies, global carbon systems, and ocean observations. It is one of seven NOAA Research Laboratories (RLs).
The Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory (LDEO) is the scientific research center of the Columbia Climate School, and a unit of The Earth Institute at Columbia University. It focuses on climate and earth sciences and is located on a 189-acre campus in Palisades, New York, 18 miles (29 km) north of Manhattan on the Hudson River.

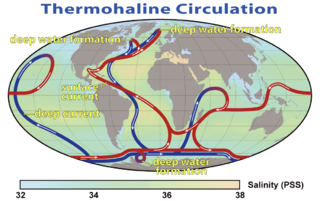
Henry Melson Stommel was a major contributor to the field of physical oceanography. Beginning in the 1940s, he advanced theories about global ocean circulation patterns and the behavior of the Gulf Stream that form the basis of physical oceanography today. Widely recognized as one of the most influential and productive oceanographers of his time, Stommel was both a groundbreaking theoretician and an astute, seagoing observer.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and introduction to Oceanography.
Aquatic science is the study of the various bodies of water that make up our planet including oceanic and freshwater environments. Aquatic scientists study the movement of water, the chemistry of water, aquatic organisms, aquatic ecosystems, the movement of materials in and out of aquatic ecosystems, and the use of water by humans, among other things. Aquatic scientists examine current processes as well as historic processes, and the water bodies that they study can range from tiny areas measured in millimeters to full oceans. Moreover, aquatic scientists work in Interdisciplinary groups. For example, a physical oceanographer might work with a biological oceanographer to understand how physical processes, such as tropical cyclones or rip currents, affect organisms in the Atlantic Ocean. Chemists and biologists, on the other hand, might work together to see how the chemical makeup of a certain body of water affects the plants and animals that reside there. Aquatic scientists can work to tackle global problems such as global oceanic change and local problems, such as trying to understand why a drinking water supply in a certain area is polluted.
William B. Curry is an American oceanographer who is the president and CEO of the Bermuda Institute of Ocean Studies (BIOS). He is known for studying historical climate and ocean circulation. Curry holds a Bachelor of Science in geology from the University of Delaware (1974) and a PhD in geology from Brown University (1980).
The Hawaii Ocean Time-series (HOT) program is a long-term oceanographic study based at the University of Hawaii at Manoa. In 2015, the American Society for Microbiology designated the HOT Program's field site Station ALOHA a "Milestone in Microbiology", for playing "a key role in defining the discipline of microbial oceanography and educating the public about the vital role of marine microbes in global ecosystems."

Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas (HERMIONE) is an international multidisciplinary project, started in April 2009, that studies deep-sea ecosystems. HERMIONE scientists study the distribution of hotspot ecosystems, how they function and how they interconnect, partially in the context of how these ecosystems are being affected by climate change and impacted by humans through overfishing, resource extraction, seabed installations and pollution. Major aims of the project are to understand how humans are affecting the deep-sea environment and to provide policy makers with accurate scientific information, enabling effective management strategies to protect deep sea ecosystems. The HERMIONE project is funded by the European Commission's Seventh Framework Programme, and is the successor to the HERMES project, which concluded in March 2009.

RV Atlantic Explorer is a twin-screw ocean vessel. It is owned and operated by the Bermuda Institute of Ocean Sciences (BIOS) in coordination with and as a part of the University-National Oceanographic Laboratory System (UNOLS) fleet. Atlantic Explorer is in compliance with US Coast Guard, UNOLS and American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) regulations as an uninspected oceanographic research vessel and is supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF). Its homeport is St. George's, Bermuda.

Schmidt Ocean Institute (SOI) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit operating foundation established in March 2009 by Eric Schmidt and Wendy Schmidt. The Institute's goal is to advance innovative oceanographic research and discovery through technological advancement, collaborative research, outreach and education, and open sharing of information. SOI supports oceanographic research by providing collaborators with free ship time aboard their research vessel Falkor (too) and expert technical shipboard support. Collaborating researchers and institutions utilizing Falkor commit to openly share and communicate the outcomes of their research, including raw observations and data. Research proposals are reviewed through a peer-reviewed process and assessed based on their potential for technological innovation, oceanographic research, and overall impact. Since its inception in 2009, SOI has supported over 60 expeditions all around the globe.
Deborah K. Steinberg is an American Antarctic biological oceanographer who works on interdisciplinary oceanographic research programs. Steinberg's research focuses on the role that zooplankton play in marine food webs and the global carbon cycle, and how these small drifting animals are affected by changes in climate.

James Zachos is an American paleoclimatologist, oceanographer, and marine scientist. He is currently a professor in the Department of Earth and Planetary sciences at University of California, Santa Cruz where he was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 2017. His research focuses on the biological, chemical, and climatic evolution of late Cretaceous and Cenozoic oceans, and how past climatic conditions help improve forecasts of the consequences of anthropogenic carbon emissions on future climate change.
Valerie J. Paul is the Director of the Smithsonian Marine Station at Fort Pierce, in Fort Pierce, FL since 2002 and the Head Scientist of the Chemical Ecology Program. She is interested in marine chemical ecology, and specializes in researching the ecology and chemistry of Cyanobacteria, blue-green algae, blooms. She has been a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science since 1996, and was the chairperson of the Marine Natural Products Gordon Research Conference in 2000.
William Li is a Canadian biological oceanographer who did research on marine picoplankton, marine macroecology, ocean surveys of plankton from measurements of flow cytometry, and detection of multi-annual ecological change in marine phytoplankton.











